Samsung has just announced its latest flagship processor in the Exynos 9 series – the Exynos 9820. The chipset will be used in 2020 flagship smartphones including the Samsung Galaxy S10 and Galaxy Note 10.
Main features of Exynos 9820:
- Exynos 9820 SoC is based on 8nm LPP FinFET process;
- Comes with an integrated NPU for enhanced AI capabilities;
- Supports 8K video recording at 30 fps.
The highlight of the Samsung Exynos 9 Series 9820 SoC is the integrated Neural Processing Unit (NPU), which specializes in processing artificial intelligence tasks. According to the manufacturer, the new NPU will allow the chip to perform AI tasks seven times faster than its predecessor.
Performance
The CPU includes three clusters: two proprietary fourth-generation cores, two Cortex A75 and four energy-efficient Cortex A55. Thanks to the transition to the 8-nm process technology, the new product, compared to its predecessor, has become 20% faster in single-core tasks and 15% faster in multi-core ones. Energy efficiency, compared to Exynos 9810, has increased by 40%.
The graphics processor (GPU) is Mali-G76 MP12. Compared to the Mali G72MP18, which is used in the Exynos 9810, the new video chip improves performance by 40% and increases energy efficiency by 35%. The chip supports UFS 2.1 and 3.0 flash memory and LPDDR4x RAM.
Battle of processors: Snapdragon 855, Exynos 9820, Kirin 980 or Apple A12 – which is better?
Miscellaneous 12/06/2018 | 0
The other day, a long-awaited event happened, because the flagship Snapdragon 855 processor was finally presented to the public, thanks to which it can now be compared with all its closest competitors, which are the Exynos 9820, Kirin 980 and Apple A12. All four of these chipsets will remain cutting-edge for at least the next 9-10 months, and based on them, dozens of top-level mobile devices will hit the market, ranging from those based on iOS to models running Android.
The staff of Rozetked decided to compare Qualcomm Snapdragon 855, Samsung Exynos 9820, Huawei Kirin 980 and Apple A12 processors according to several criteria in order to determine the best chipset for mobile devices. The technical process during production, cores and their maximum clock speed, graphics, support for artificial intelligence, memory, modem, graphics accelerator and other features, such as support for Wi-Fi and 5G networks, were taken into account.
Based on the results of the study, it was found that the Snapdragon 855 processor is currently ahead of its closest competitors in all respects, including video processing. This chip is one of the few that can process video in 8K resolution at frame rates above 30 frames per second. In addition, this chip supports Wi-Fi networks of the 802.11ax, 802.11ay and 802.11ad generations, which may soon appear around the world.
| Snapdragon 855 | Exynos 9820 | Kirin 980 | Apple A12 | |
| Technical process | 7nm | 8nm | 7nm | 7nm |
| Cores | 1x Cortex A76, 2.84 GHz 3x Cortex-A76, 2.42 GHz 4x Cortex-A55, 1.8 GHz | 2x custom (4th generation) 2x Cortex-A75 4x Cortex-A55 | 2x Cortex-A76, 2.6 GHz 2x Cortex-A76, 1.92 GHz 4x Cortex-A55, 1.8 GHz | 2x Monsoon, 2.4 GHz 4x Mistral |
| Graphic arts | Adreno 640 | Mali-G76 MP12 | Mali-G76 MP10 | 4x Apple GPU |
| AI | Hexagon 690 | NPU | Dual NPU | Neural Engine |
| Memory | UFS 3.0 | UFS 3.0 | UFS 2.1 | Not known |
| Modem | X24 LTE, 2000 Mbit download, 316 Mbit upload | Cat 20 LTE, 2000 Mbit download, 316 Mbit upload | Cat 21 LTE, 1400 Mbit download, 200 Mbit upload | Intel XMM 7560, 1000 Mbit download, 150 Mbit upload |
| Video | 8K UHD, 360-degree, up to 120 fps, 10-bit, H.265 and VP9 video decoder | 8K 30 fps or 4K 150 fps, 10-bit HEVC (H.265), H.264, VP9 | 4K, 60 fps | Not known |
| Other | Supports 5G and Wi-Fi networks 802.11ax, 802.11ay and 802.11ad. | — | — | — |
Thus, as follows from the study, the Snapdragon 855 processor is significantly better than the Exynos 9820, Kirin 980 and Apple A12, and literally in everything. It is impossible not to notice that the chipset from the Apple corporation is perhaps better in some ways, but Apple hides its detailed technical characteristics, so it is certainly impossible to talk about this. It is the processor from Qualcomm that is the only one in the world that is capable of connecting to 5G networks, albeit at speeds of up to 2 Gbit/s.
Qualcomm previously announced when the first smartphones with true 5G support will appear.
Attention! Until July 26, everyone can receive a Xiaomi Mi Band 5 sports bracelet for free, spending only 2 minutes on it.
Join us on Google News , Twitter, Facebook, VKontakte, YouTube and RSS to stay up to date with the latest news from the world of future technologies.
AKKet.com Telegram channel
Receive notifications about new materials directly in the messenger - on iOS, Windows, Android and Linux.
AppleHuaweiQualcommSamsungProcessorsComparison
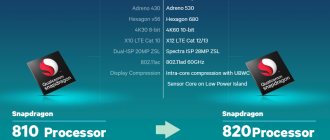
Exynos 9820 vs Exynos 9810: what has changed
Today Samsung introduced its first processor with an 8nm process technology, Exynos 9820. It is the successor to the top-end Exynos 9810, presented at the very beginning of this year, and will probably be installed in the Russian-European version of the Galaxy S10 (February-March 2019) and Galaxy Note 10 (August-September 2019). Comparative characteristics of both processors are presented in the table below:
| Exynos 9820 | Exynos 9810 | |
| Technical process | Samsung 8nm LPP | Samsung 10nm LPP |
| CPU | 2 × M4 2 × Cortex A75 4 × Cortex A55 | 4 × M3 (1 core - up to 2.7 GHz, 2 cores - up to 2.3 Hz, 4 cores - up to 1.8 GHz) 4 × Cortex A55 (1.8 GHz) |
| GPU | Mali G76 MP12 | Mali G72 MP18 |
| NPU | + | — |
| Media | 8K 30 fps 4K 150 fps H.265/HEVC, H.264, VP9 | 4K 120 fps H.265/HEVC, H.264, VP9 |
| Modem | LTE Cat 20/13 download: up to 2 Gbps upload: up to 316 Mbps | LTE Cat 18/13 download: up to 1.2 Gbit/s upload: up to 200 Mbit/s |
| ISP (cameras) | main: 22 MPS front: 22 MPS dual: 16 MPS +16 MPS | main: 24 MPS front: 24 MPS dual: 16 MPS + 16 MPS |
As you can see, the main changes affected:
- technical process - it changed from 10 nm to 8 nm
- structure and composition of the CPU - 2-cluster (4+4) was replaced by 3-cluster (2+2+4), older cores were updated,
- structure and composition of the GPU - the cores were changed to more modern and productive ones (with a double increase in the number of lanes), their number was reduced by 1/3
- NPU - appeared for the first time in a Samsung processor.
Samsung's press release names the following qualitative changes:
- the new custom core (M4) is about 20% faster than its predecessor (M3) in single-core performance (probably at the same level of power consumption)
- Energy efficiency (performance per watt) of M4 compared to M3 improved by 40%
- multi-core performance of Exynos 9820 compared to Exynos 9810 increased by about 15%
- Graphics performance of Exynos 9820 compared to Exynos 9810 increased by 40%
- Energy efficiency of Exynos 9820 compared to Exynos 9810 has improved by 35%
- thanks to the built-in NPU, the speed of machine learning has increased 7 times
- 8K video recording is supported.
Let me remind you that, according to leaks that appeared in the summer, the speed of the Exynos 9820 in the single-core Geeknench test increased by 21% (against Samsung’s stated 20%), and in the multi-core test by 40% (versus 15%).
As Gadgets News already reported, the Exynos 9810 turned out to be a rather controversial processor. On the one hand, in the single-core Geekbench test it was almost twice as good as its predecessor, Exynos 8895, and 37% faster than its main rival, Snapdragon 845. But in the multi-core test, the progress was much less significant - 35% more productive than Exynos 8895 and about the same as Snapdragon 845.
In the GFXBench Manhattan 3.1 graphics benchmark, the performance per watt of power consumption of the Exynos 9810 doubled compared to the Exynos 9810 and was equal to the Snapdragon 845. But thanks to higher power consumption (in this benchmark - approximately 5 W vs 4 W), the peak performance of the top Qualcomm processor was much higher. Both processors show very strong throttling - both had stable (stabilized) performance of 58% (Apple A11 - 54%).
The bottom line is that the Snapdragon 845, its predecessor Snapdragon 835 and A11 Bionic had approximately the same stable performance - about 35 fps in GFXBench Manhattan 3.1 (off-screen). In turn, the Exynos 9810 scored 27 fps in this test - slightly more than its predecessor Exynos 8895 (24 fps).
However, it should be borne in mind that the Qualcomm processors above were tested on the American-Chinese version of the Galaxy S9, and soon after its release - in March 2020. On another smartphone (OnePlus 6), the Snapdragon 845 showed a much better result - 51 fps sustained performance . But for the Galaxy S9 with the Exynos 9810 processor, by October 2020 it even worsened slightly - 25 fps. The favorite in this test among smartphones today is the Apple A12 (iPhone XS) - 61 fps. The following table shows the latest results in GFXBench Manhattan 3.1 (off-screen):
| iPhone XS | OnePlus 6 | Galaxy S9 | ||
| CPU | A12 Bionic | Snapdragon 845 | Exynos 9810 | |
| Crystal area | 83 mm2 | 94 mm2 | 119 mm2 | |
| Initial energy consumption 1 | 6 W | ? | 5 W | 4 W |
| Initial performance | 104 fps | 60 fps | 61 fps | 46 fps |
| Performance is consistent | 61 fps | 51 fps | 35 fps | 27 fps |
1 data on power consumption during stable operation of the processor is available only for the iPhone XS - 3.8 W.
Of course, it is possible that the reason for such significant throttling of both processors in the Galaxy S9 is its high (compared to the same OnePlus 6) display resolution. But judging by the game performance graphs, they run at a lower resolution on the Galaxy S9 (according to NotebookCheck.net):
OnePlus 6
Galaxy S9
As you can see, on both smartphones both games are designed for 60 fps, although of course the Galaxy S9 throttles much more in one of them (Arena of Valor).
This is the approximate situation for today, on the day of the announcement of the Samsung processor for its top smartphones in 2020. Taking into account the 40% increase, the sustained performance of the Exynos 9820 in Manhattan 3.1 (off-screen) can reach 38 fps - but even in this case it will be significantly behind the Snapdragon 845, not to mention the A12 Bionic. In addition, in the coming months the presentation of a new and, of course, more powerful Qualcomm processor is expected, which will be installed in almost all top smartphones next year.
Samsung
Comparison of Snapdragon 865 Plus and Exynos 990
You can find a full video comparing the performance of the two processors below and read all the explanations (in English). If you don’t want to waste time on the video, I’ll tell you in a nutshell what it’s about.
Two smartphones were tested in a test of performance and how quickly they cope with tasks. With the same load, they timed the time it would take them to complete the tasks, and this is what happened.
At the beginning, Exynos was still somehow able to resist Snapdragon, and for a few seconds it was also in the lead, but then it quickly began to lose ground. As a result, when rendering 3D graphics, the Galaxy Note 20 variant based on the Snapdragon 865+ chipset completed the test in 1 minute and 32 seconds , while the Exynos model completed the same tasks in 1 minute and 50 seconds . This is about 20% longer. 20%, Karl!
There were failures on both the central processor and graphics side. There was a slight advantage only in mixed mode, and it was such that we can simply say that the smartphones were equal. Otherwise, the Exynos version was simply crushed to smithereens.
This test also shows a significant difference.
3DMark
Moving on to graphics performance, we ran the 3DMark Sling Shot Extreme test on the iQOO 3 and Galaxy S20 Plus. As you can see in the screenshots, the Adreno 650 GPU on board the Snapdragon 865 outperforms the Mali-G77 GPU in the Exynos 990 - only by a small margin. The Snapdragon 865 seems to handle OpenGL workloads a little better than the Exynos 990. But both chipsets are on par when it comes to Vulkan graphics support.
Why Samsung puts different processors in one smartphone
The passionate desire to install different processors in the same generation of flagship smartphones is easy to explain. The company is a serious chip manufacturer. They may not be on par with their competitors, but using their developments and collecting information to bring them to fruition will make it possible to make chips even better. In an ideal future, this will even help the company become the new leader in the global “chip design”, displacing Qualcomm with its Snapdragon.
Beyond that, there is simply the matter of financial gain. Both companies spend billions of dollars on development , but when you make chips for yourself, you only need to recoup the costs of development and production. When you buy them from competitors, you must also ensure a profit for him, because he will not sell the products at cost. Therefore, your own chips, with plus or minus the same cost of the costs of creating them, will always be more profitable.
Even these three seemingly identical smartphones can differ greatly in operating speed.