Recommended Models
For those who do not have time to read the entire article, I immediately give the recommended power supply models with a brief explanation.
The power of the power supply is selected based on the power of the computer, which mainly depends on the power consumption of the processor and video card. It is also necessary that the power supply has at least 80 Plus Standard certification. The optimal price/quality ratio are Chieftec, Zalman and Thermaltake power supplies.
For an office computer (documents, Internet), a 400 W power supply is sufficient; take the most inexpensive Chieftec or Zalman, you won’t go wrong. Power supply Zalman LE II-ZM400 For a multimedia computer (movies, simple games) and an entry-class gaming computer (Core i3 or Ryzen 3 + GTX 1050 Ti), the most inexpensive 500-550 W power supply from the same Chieftec or Zalman is suitable, it will have a reserve in case of installing a more powerful video card. Chieftec GPE-500S power supply For a mid-class gaming PC (Core i5 or Ryzen 5 + GTX 1060/1070 or RTX 2060), a 600-650 W power supply from Chieftec is suitable, if there is an 80 Plus Bronze certificate, then good. Chieftec GPE-600S power supply For a powerful gaming or professional computer (Core i7 or Ryzen 7 + GTX 1080 or RTX 2070/2080), it is better to take a 650-700 W power supply from Chieftec or Thermaltake with an 80 Plus Bronze or Gold certificate. Chieftec CPS-650S power supply If you want to understand why I recommend these particular models, to understand all the parameters of power supplies, then read the article further.
You can download the program for calculating the required power of the power supply in the “Links” section.
Extra options
These parameters affect quality, efficiency, and performance, but you will have to pay extra for them.
Certificate of Performance
80 Plus certification determines the efficiency of the power supply, or, more simply, the energy savings from the outlet. For example, a power supply supplies 400 W to components at 80% efficiency, which means it consumes 480 W from the outlet. It is this extra 80 W that is dissipated as heat, which must be dissipated by the cooling system.
| Test type | 115 V | 230 V | Power factor | |||||||
| Load | 10% | 20% | 50% | 100% | 10% | 20% | 50% | 100% | ||
| 80 PLUS | — | 80% | 80% | 80% | — | 80% | 80% | 80% | 0.8 at 100% load | |
| 80 PLUS Bronze | — | 82% | 85% | 82% | — | 81% | 85% | 81% | 0.9 at 50% load | |
| 80 PLUS Silver | — | 85% | 88% | 85% | — | 85% | 89% | 85% | ||
| 80PLUS Gold | — | 87% | 90% | 87% | — | 88% | 92% | 88% | ||
| 80PLUS Platinum | — | 90% | 92% | 89% | — | 90% | 94% | 91% | 0.94 at 50% load | |
| 80 PLUS Titanium | — | 92% | 94% | 90% | 90% | 94% | 96% | 91% | 0.95 at 50% load | |
Accordingly, this certificate indirectly determines the quality of the power supply itself: the higher its efficiency, the more efficiently the components are used, the circuitry is better thought out, the voltage is more stable, the fan runs at lower speeds, the noise level is lower, and the service life of the entire product increases.
Certification levels: initial - simply 80 Plus, then in increasing order - Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum and Titanium.
- the Enermax Platimax DF 750W power supply
Obtaining a certificate costs money for a manufacturer, and to save money, he may not certify his models or come up with his own analogues of certification. So the lack of an official certificate does not always mean low efficiency. Almost all modern power supplies fit into the parameters of a simple 80 Plus.
Cables
The cables should be long enough for installation in your case, they should not overheat under load, all other parameters are more important for convenience and aesthetics.
Structurally, there are three options for connecting cables to the power supply:
- Fixed cables coming out of the power supply unit in a bundle. They are directly soldered to the board.
- Partially modular design - the main ATX and EPS cables are non-removable, the rest are connected through connectors on a special board inside the power supply. This option is beneficial when all the cables from the kit are not used. This saves space when placing them in the housing.
- Fully modular design - all cables are connected via connectors. This option is most convenient both during assembly and when cleaning the system unit and the power supply itself from dust during operation.
- Review and testing of Thermaltake Smart Pro RGB 650W Bronze Fully Modular power supply
Cables can be assembled with colored wires that are either bundled or have a nylon braid - a completely acceptable option if the aesthetics of the assembly are not important, for example, in a closed enclosure.
Flat cables look neater and are more convenient to install when hidden. They can also be harder or softer.
For modding projects, wires in fabric braids are used, including in various colors - beautiful, expensive, but of no practical use.
- Review of Thermaltake Mod Sleeve Cable Rainbow
Another characteristic of power supply wires is their diameter, or AWG gauge. The lower the number, the larger the diameter. PSU wires most often have gauges AWG 20, 18, 16. This indicator affects the maximum permissible current: 20AWG - 27A; 18AWG - 45A; 16AWG – 70A. Thin wires will get very hot under heavy load, so wires for connecting VGA are used with a larger diameter than wires for connecting drives.
A good case with a bottom-mounted power supply and hidden cable routing is usually demanding on the length of the CPU power cable. Its minimum length in this case is 60-70 cm, otherwise it simply will not reach the connector on the motherboard.
Cooling
PSU circuit components get quite hot during operation, which requires adequate cooling. Active cooling by a fan means possible noise and its failure as a result of the exhaustion of its resource.
Types of cooling:
- Passive – there is no fan, but this option is quite expensive due to the use of efficient components and is rare.
- Semi-passive - at low loads (usually up to 50%), the fan does not rotate; temperature adjustment is also possible. Recently, many manufacturers have equipped power supplies with such a system with a button on the case that turns this mode on/off.
- Active – constant rotation of the fan. Typically, the rotation speed is adjusted automatically depending on the load or temperature.
The purpose of the fan is to cool effectively with less noise and not fail prematurely.
These qualities depend on a number of parameters:
- Bearings used: sliding, rolling and hydrodynamic. The latter are the most reliable and quiet, but are more expensive.
- Standard size – 120 or 140 mm. A larger diameter can theoretically move more air at lower speeds and make less noise. But this is not always true, it all depends on the settings provided by the manufacturer.
In recent years, it has become fashionable to equip power supplies with fans with RGB lighting. Naturally, this does not in any way affect the quality of the power supply itself, but such an attractive design element may be presented by the manufacturer as some kind of advantage, but in fact it may simply be a disguise for other shortcomings.
The noise characteristics given in the form of graphs on the packaging do not always coincide with the actual noise level. More plausible decibels can be seen in power supply tests on independent resources, and you need to focus on them.
Guarantee
Another parameter that is often overlooked, but it can also indicate the quality of the product. The manufacturer, confident in the quality and reliability of its product, provides a guarantee of up to 7 – 10 years. A model with an 80 Plus Bronze certificate, a beautiful design, but with a 1-2 year warranty is questionable.
Power supply or case with power supply?
If you are assembling a professional or powerful gaming computer, then it is recommended to select a power supply separately. If we are talking about an office or regular home computer, then you can save money and purchase a good case complete with a power supply, which will be discussed in the next article.
Primary and secondary power supplies
Primary ones are, in particular, chemical current sources (batteries and batteries) and electrical energy generators located at power plants.
Computers can be used:
- 3V lithium cells to power the CMOS chip that stores the BIOS settings,
- lithium-ion batteries (in laptops).
2032 lithium cells power the CMOS chip that stores the computer's BIOS Setup settings.
The current consumption is small (on the order of a few microamps), so the battery energy lasts for several years .
Once the energy is exhausted, such energy sources cannot be restored.
Unlike cells, lithium-ion batteries are renewable sources. They periodically either store energy or release it. Let us immediately note that any batteries have a limited number of charge-discharge cycles.
But most desktop computers are powered not by batteries, but by an alternating voltage network.
Currently, every home has sockets with an alternating voltage of 220 V (in some countries 110 - 115 V) with a frequency of 50 Hertz (in some countries - 60 Hertz), which can be considered primary sources .
But the main components of the computer cannot directly use this voltage.
It needs to be transformed. This work is performed by the secondary power supply (popularly called “ power supply ”) of the computer. Currently, almost all power supplies (PSUs) are switching. Let's take a closer look at how a switching power supply works.
What is the difference between a good power supply and a bad one?
The cheapest power supplies ($20-30) by definition cannot be good, since in this case manufacturers save on everything possible. Such power supplies have bad heatsinks and a lot of unsoldered elements and jumpers on the board.
At these places there should be capacitors and chokes designed to smooth out voltage ripples. It is because of these ripples that the motherboard, video card, hard drive and other computer components fail prematurely. In addition, such power supplies often have small radiators, which cause overheating and failure of the power supply itself.
A high-quality power supply has a minimum of unsoldered elements and larger radiators, which can be seen from the installation density.
How the power supply cooling system works
There are three hot air exhaust zones in total. The cooling process is carried out by three fans, which are located near the central processor, video card and on the power supply itself. One of the common ways to cool a PC power supply is to introduce a cooler with a diameter of 80 mm. Once the unit starts up, the fan begins its work and is distributed inside the computer, delivering cool air flow to demanding areas. This is exactly how the ATX12V and CFX12V devices work.
If we take, for example, the STX12V model, then everything here is arranged somewhat differently: fans are installed here that do not exceed 60 mm in diameter. As a rule, these are some of the expensive models that have the ability to adjust the speed of the fan rotor.
Units that are not equipped with a fan have a different type of cooling.
Some power supply models regulate the speed automatically only from the moment an increased load is placed on the processor. Due to the presence of a thermostat, the cooler rotation speed begins to vary from 1000 to 3000 rpm.
The type of fan grille plays a big role in cooling. The most relevant is considered to be made of wire steel with a small cross-section. This design transfers air flow inside the system unit faster.
Power supply manufacturers
Some of the best power supplies are made by SeaSonic, but they are also the most expensive.
Power supplies from popular brands Thermaltake, Cooler Master, and Chieftec have proven to be of good quality. Marriage is rare among them.
Well-known enthusiast brands Corsair and Zalman recently expanded their range of power supplies. But their most budget models have rather weak filling.
AeroCool power supplies are among the best in terms of price/quality ratio. The well-established cooler manufacturer DeepCool is closely joining them. If you don't want to overpay for an expensive brand, but still get a high-quality power supply, pay attention to these brands.
FSP produces power supplies under different brands. But I would not recommend cheap power supplies under their own brand; they often have short wires and few connectors. Top-end FSP power supplies are not bad, but they are no longer cheaper than famous brands.
Of those brands that are known in narrower circles, we can note the very high-quality and expensive be quiet!, the powerful and reliable Enermax, Fractal Design, the slightly cheaper but high-quality Cougar and the good but inexpensive HIPER as a budget option.
Top 9 computer power supplies
Now I will present to your attention my independent rating of the best power supplies up to 750 W, up to 1000 W and monsters up to 2000 W.
The Best Power Supplies for a Gaming PC
AeroCool KCAS PLUS 700W
The ATX power supply is more powerful - 700 W. It costs only a little more - around 4,000 rubles. 80 PLUS Bronze certified, plus on-site short circuit, overload and surge protection. The wires of this power supply are long, the cooling is quiet, and the power is quite decent. Suitable for building a good gaming PC with one powerful video card. Although the presence of as many as four 6+2-pin connectors clearly hints that the manufacturer sees this power supply as the basis for a gaming system with two video cards.
Price: RUB 5,135
Thermaltake Smart RGB 600W
Definitely the most beautiful power supply in its category: all thanks to the RGB backlight, which can be adjusted using a button on the back wall. Perfect for building a gaming PC with a transparent case. In addition to its spectacular appearance, this power supply can boast of having a simple 80 PLUS certificate, all the necessary protections (short circuit, overvoltage, overload) and a 10-year warranty. True, not all buyers are satisfied with the quality of the components, so be prepared for the fact that the warranty card will be useful to you. The device costs about 3,500 rubles.
Thermaltake Smart: ₽ 3,470 Check on CITYLINK
The best power supplies up to 750 W
Be quiet System Power 9 500W
A 500 W ATX power supply costs about 4,000 rubles. Certified to 80 PLUS Bronze standard. Cooled by an almost silent fan with a diameter of 120 mm: the maximum noise level does not exceed 28 dB. There is protection against overload, overvoltage and short circuit. The motherboard is powered through a 20+4-pin contact, the video card is powered through two 6+2-pins. A quiet and cool power supply from a reliable manufacturer is ideal for a home or office PC without claims of super-performance.
Price: RUB 3,880
The best power supplies up to 1000 W
Thermaltake Toughpower Grand RGB Gold (Fully Modular) 850W
A good power supply from the same manufacturer as the previous one, but for completely different money. This beast with a power of 850 W costs more than 9,000 rubles. For this money you will get a modular power supply with detachable cables (unnecessary wires can simply be disconnected and removed from the power supply so that they do not spoil the view or get in the way), customizable RGB lighting, a quiet 140 mm fan and certification to the “gold” standard 80 PLUS Gold. A great option for serious gaming machines.
Thermaltake Toughpower: ₽ 9,130 Check on CITYLINK
Chieftec BDF-1000C 1000W
A modular power supply of the ATX standard with detachable cables similar to the previous one. True, its power is higher - a whole kilowatt, there is no RGB backlight, and the 80 PLUS certificate is simpler - only the Bronze standard. But this power supply is not that expensive for its characteristics, only about 6,000 rubles. It works quietly, does not heat up, produces very decent power - just what is needed for a serious user for whom performance for affordable money is more important than a flashy appearance.
Price: ₽ 6,200
AeroCool Higgs 850W
The most budget power supply in its category costs less than 4,000 rubles. But even for that kind of money, it can boast a power of 850 W, a fully modular design and a fairly quiet fan with a diameter of 140 mm. The manufacturer claims that the efficiency of this device is as much as 90%, which corresponds to certification according to the 80 PLUS Gold standard. However, the power supply does not have an official 80 PLUS certificate, and this is its main drawback.
Price: ₽ 4,290
The best power supplies up to 2000 W
ASUS ROG-THOR-1200P 1200W
Power supply from the Republic of Gamers gaming line from ASUS. Like everything else in this series - beautiful, powerful, reliable and very expensive. For just over 25,000 rubles you will get a monster capable of delivering 1200 W of power and certified to the 80 PLUS Platinum standard. The design is, of course, modular: there are many cables and they are long. You can switch between passive and active cooling modes using a button. Power consumption is displayed on a special display. Enthusiast's choice.
Price: RUB 23,041
COUGAR CMX1200 1200W
This power supply is a champion in terms of price-power ratio. For just 6,000 rubles you will get a device that produces 1,200 W and is certified to the 80 PLUS Bronze standard. An excellent option for a budget-conscious gamer who plans to build a system with two powerful video cards and does not want to overpay for multi-colored lights, displays and other unnecessary functionality. Keep in mind, however, that the manufacturer has saved some money on the cooling system. The fan may make noise and will require replacement after some time.
Price: RUB 5,993
AeroCool Strike-X 1100W
A beautiful power supply in a bright red case worth a little over 7,000 rubles. Power 1100 W, energy efficiency certificate 80 PLUS Gold, detachable wires. The included cables are long and quite soft, so they can be pulled inside the case along any route. It does not heat up, does not make noise (the maximum volume produced by a 139 mm fan is 35 dB), and produces a stable and honest voltage. There is enough power for at least 3 video cards. A good option for a gaming PC.
AeroCool Strike-X: ₽ 6,990 Check on CITYLINK
Power supply power
Power is the main characteristic of a power supply. The power of the power supply is calculated as the sum of the power of all computer components + 30% (for peak loads).
For an office computer, a minimum power supply of 400 watts is sufficient. For a multimedia computer (movies, simple games), it is better to take a 500-550 Watt power supply, in case you later want to install a video card. For a gaming computer with one video card, it is advisable to install a power supply with a power of 600-650 Watts. A powerful gaming PC with multiple graphics cards may require a power supply of 750 watts or more.
5.1. Power supply power calculation
You can independently calculate the power of the power supply you need based on how much each element of your computer consumes.
- Processor 25-220 Watt (check on the seller’s or manufacturer’s website)
- Video card 50-300 Watt (check on the seller’s or manufacturer’s website)
- Entry class motherboard 50 Watt, mid class 75 Watt, high class 100 Watt
- Hard drive 12 Watt
- SSD 5 Watt
- DVD drive 35 Watt
- Memory module 3 Watt
- Fan 6 Watt
Don’t forget to add 30% to the sum of the powers of all components, this will protect you from unpleasant situations.
5.2. Program for calculating power supply power
To more conveniently calculate the power of a power supply, there is an excellent program “Power Supply Calculator”. It also allows you to calculate the required power of an uninterruptible power supply (UPS or UPS).
The program works on all versions of Windows with Microsoft .NET Framework version 3.5 or higher installed, which is usually already installed for most users. You can download the “Power Supply Calculator” program and, if you need it, “Microsoft .NET Framework” at the end of the article in the “Links” section.
Choosing the optimal power supply for your PC
This work was submitted to our “unlimited” article competition and the author receives an incentive prize - a set of notes and paper from ASRock.
1. Background.
The story began when a couple of years ago I heard about the need for a powerful power supply for Athlon/P4-based computers and decided to replace my old Linkworld 200W, which was then on my Athlon 1333. I suspect that then I was very lucky and this unit was all- I finally retired without taking half of the components with me, despite the fact that under load I increased the voltage by +12V up to +13.2V, causing all the system fans to howl when running something resource-intensive, such as Photoshop or BurnK7. In my naivety, I thought that I had a “smart” cooler that changed the speed depending on the load on the thermal sensor, but when I found out that this was not so, my hair stood on end. A week later, having saved the necessary amount for a new power supply, I came to the company and bought an LCT unit, stated as 300W. While driving home, I read the stickers and rejoiced at the huge declared currents, but after installing this unit in my computer, I realized that they had cheated me. The voltages became even worse and, in addition, the computer began to shut down when the load increased. The block was returned after a lengthy argument with the managers in exchange for money, which I immediately took to another LPK (Linkworld). The situation repeated itself - abnormally high voltages, strong heating of the unit. After talking with the manager, we managed to find a new unit in the company’s reserves, which turned out to be the PowerMaster FA5-1 (300W peak) and although it pulled out its 250W (It would seem, what else is needed?), subsequently new problems arose... more on that later.
2. ATX/ATX12V power supplies
To begin with, a few words about the requirements for power supplies according to generally accepted standards.
There is a certain standard for PC power supplies, which is recommended for unit manufacturers to adhere to. The document describing the requirements can be read at www.formfactors.org. It should be noted that for ATX power supplies, the requirements are slightly lower than for ATX12V, so older power supplies of similar power may have lower maximum output currents. Load distribution for ATX12V standard units.
announcements and advertising
2080 Super Gigabyte Gaming OC for 60 rubles.
Compeo.ru - the right comp store without any tricks
RTX 2060 becomes cheaper before the arrival of 3xxx
Ryzen 4000
series included in computers already in Citylink
The price of MSI RTX 2070 has collapsed after the announcement of RTX 3xxx
Core i9 10 series is half the price of the same 9 series
The price of memory has been halved in Regard - it’s more expensive everywhere
| +3.3 VDC | +5 VDC | +12 VDC | -5 VDC | -12 VDC | +5 VSB | |
| 200W | 14A | 21A | 10A | 0.3A | 0.8A | 1.5A |
| 250W | 20A | 25A | 13A | 0.3A | 0.8A | 1.5A |
| 300W | 28A | 30A | 15A | 0.3A | 0.8A | 2.0A |
This table shows the maximum possible loads on single outputs for power supplies certified to comply with the standard. The total load for all outputs of the block should not exceed 200/250/300W, respectively. I will also give a diagram of the output loads for a 300W unit.
In this diagram, the Y scale shows the maximum load on the +12V output, and the horizontal scale shows the total load at +3.3V and +5V. The circled area is the permissible currents for the outputs in various combinations, for example, with a load of 180W at +3.3V & +5V, the power supply is required to output +12V up to approximately 100W, the remaining 20W is distributed between additional outputs.
Within this area, the voltage on the power supply must be within the range allowed by the standard:
| Exit | Range | Minimum | Maximum |
| +12V | +-5% | +11.40V | +12.60V |
| +5V | +-5% | +4.75V | +5.25V |
| +3.3V | +-5% | +3.14V | +3.47V |
If you go beyond the permissible standards, all sorts of troubles are possible, such as overheating and spontaneous shutdown of hard drives or system reboots. This means that in the future we will focus on mandatory compliance of voltages with the standard.
3. Power supply
Oddly enough, most serious reviewers of power supplies agree on the same opinion - the consumption of the most sophisticated computer does not exceed 150-200W and a more powerful unit does not make sense. And yet, users complain about the lack of power of even three-hundred-watt units from renowned manufacturers, and equipment manufacturers, such as video cards or motherboards, are increasingly declaring the need to use power supplies with a power of 300-350W and higher... What's the matter? There is an opinion that manufacturers are trying in this way to protect themselves from low-quality power supplies that hold a given load only for a few seconds, having a real power much lower (the peak power is usually 30% higher than the long-term power, if the manufacturer did not cheat by simply re-labeling). Therefore, a unit with a peak power of 200W has a long-term, God forbid, 180W, or even lower.
This assumption is partly true, but users on forums are increasingly reporting a lack of power in high-quality power supplies that can easily withstand a long-term load of 300-350W, up to the point where the overload protection triggers and voltages go beyond the tolerances stated in the ATX/ATX12V standard, which high-quality blocks are usually fully compliant. What's the matter? Why does a powerful computer, which according to all calculations consumes no more than 250 W, require a high-quality power supply that honestly delivers its power, 400-500 watts?
In order to understand this issue, a program was written in which data on the consumption of various devices, collected bit by bit from a large number of sites, was entered. The first version, which calculated power according to recommendations for assemblers from AMD, showed mixed results. The AMD manual suggests finding out the processor's power consumption by multiplying the core current by the voltage, dividing by 12, and multiplying by 1.25 (taking into account the approximate efficiency of the processor power regulator on the motherboard). Then, the total consumption of computer components is calculated, multiplied by 0.8 (80% of the power of all devices) and added to the processor consumption. But as you can see, for some reason this algorithm implies powering the processor from +12V, which is not available on all systems (especially old ones) based on AMD processors. In addition, in such systems, the main load often falls on the +5V output, leaving virtually no load on the +12V output. Here it is! It turns out that if the system, by all calculations, consumes no more than two hundred watts, it is necessary to take into account the distribution of loads across the outputs, and if the load on +5V & +3.3V reaches 180-200W, you need to think about a power supply with an honest 300W or higher, otherwise troubles with protection is triggered or voltages exceed permissible limits when the power supply is only two-thirds loaded. It also seemed a little strange to me that the recommendations for ATX12V power supplies do not include units more powerful than 300W, although there are already many such power supplies on the market. Perhaps a system with standard components does not really need a more powerful unit, and more powerful ones are required by overclocking and modding enthusiasts.
4. Program for calculating the power of the power supply
This program was written to calculate the power supply power required by a user's system with a selected configuration. It is the power of the unit, not the components. Data were entered on a large number of processors, their base power, with coefficients that allowed us to estimate changes in power consumption during overclocking and increasing core voltage. You can also select the power supply for the processor, which is useful for owners of motherboards that do not support additional ATX12V (P4) power supply; for example, on the popular Epox 8RDA+ in overclocking circles, the processor is powered from +5V. In general, the algorithm is simple, the approximate consumption for various outputs is calculated, the most loaded one is selected and scaled based on the requirements for ATX12V power supplies. The program tries to automatically determine some parameters, but most others require manual correction (such as for coolers, etc.). Also, there is a voltage test function at idle and under load, with the display of percentage deviations from standard values. Unfortunately, this function was debugged only on three motherboards with Winbond monitoring chips and incorrect readings are possible on motherboards with other monitoring systems.
As you can see from this screenshot, my FSP300-60BTV(PF) power supply is already loaded quite close to its limit, which indirectly confirms the +5V voltage drop by 4% during the processor load test, which is already close to the maximum permissible voltage of +4.75V .
You can download and try the program here - Power.exe
Be careful, the program requires administrator mode in Windows XP and may cause the system to hang due to the use of low-level access to the hardware. Before testing, it is recommended to close all applications to reduce the load on the processor and obtain more correct test results.
5. Criteria for choosing a power supply
First, make sure that the power supply is from a reputable manufacturer and that its wattage matches what is stated on the label. But the power of the power supply is not everything; in addition, it must provide “quality watts.” That is, it should not interfere with the equipment located in the computer and have a low ripple level. You may be asking - why? But this is a power supply, it feeds your computer. Why feed it all sorts of crap?
But the power of the power supply is not everything; in addition, it must provide “quality watts.” That is, it should not interfere with the equipment located in the computer and have a low ripple level. You may be asking - why? But this is a power supply, it feeds your computer. Why feed it all sorts of crap? It might even cause an upset stomach.
It might even cause an upset stomach.
One day, after reading reviews on the Internet, I decided to change my dubious PowerMaster FA5-1 to something more noble and my choice fell on the FSP300-60BTV(PF). Despite the fact that the voltages became only slightly better, one interesting thing was noticed - the integrated audio in the Epox 8RDA+ sharply increased the quality according to the Audio RightMark test. But I was already desperate to get high-quality sound on the nForce2 APU... and as it turned out, it was too early. Below are the results of testing with different power supplies, a cord from TV-Tuner was used as LoopBack, recording was made to the linear input of the motherboard (when recording to a higher-quality board, some parameters are many times better, so pay attention only to the difference):
| Audio RightMark, 8RDA+ | PowerMaster FA5-1 | FSP300-60BTV(PF) |
| Frequency response unevenness (from 40 Hz to 15 kHz), dB: | +0.35, -0.85 | +0.37, -1.03 |
| Noise level, dB (A): | -68.4 | -80.5 |
| Dynamic range, dB (A): | 66.7 | 80.3 |
| Nelin. distortion,%: | 0.010 | 0.0074 |
| Intermod. distortion,%: | 0.281 | 0.348 |
| Interpenetration of channels, dB: | -57.8 | -76.7 |
As you can see, the difference is simply huge. So lovers of high-quality sound should also pay attention to what you feed your pets 
And that's not all... Some time ago I wrote an article about “frequency dances” on motherboards with the nForce2 chipset, which turned out to be APIC timer dances. So, after changing the power supply the situation changed for the better. The timer began to behave much more stable, and I noticed the beating only when setting the “Bus Throttle” parameter in the motherboard BIOS. Perhaps this is a coincidence, but who knows... There were also reports from other owners of nForce2-based motherboards that this problem disappeared when changing the power supply.
Also, an important criterion when choosing a power supply is its noise level. Cheap units, like PowerMaster or Linkworld, often do not have an automatic fan speed control system, or simply overheat, and for this reason the fans in them always operate at maximum speed, drowning out all the coolers in the system. Changing to less revving ones is, in my opinion, a bad idea, especially if the block gets very hot. For weak units, the fan may be the only thing keeping them from burning out.
Also, an indirect criterion for the quality of a power supply is its weight. It must be at least 2 kg, and even more on units with passive PFC. Large weight means no savings on components, and large transformers with radiators.
Of the power supplies available on the Russian market, the following manufacturers have proven themselves well:
1. FSP. Power supplies are manufactured by the Fortron/Source division (FSP Group) - - SPI Electronic, and are OEM suppliers of power supplies for InWin, AOpen, Zalman. Be careful when purchasing, there are suspiciously cheap FSP300 power supplies on the market, priced just above $20, which may be a lightweight option for entry-level systems, or secretly rebranded from 250W. By the way, my power supply has 470 MF capacitors at the input, and the cross-section of all wires corresponds to the minimum allowable, although older versions of this unit had 680 MF capacitors, and all the wires were equally thick. In addition, instead of six connectors, this unit has only five. The simplification is insignificant, but the trend is alarming... but perhaps it did not affect blocks for third-party FSP customers.
2.InWin. One of the most well-known manufacturers of housings previously used blocks from FSP Group, but has now established its own production of no less quality. These power supplies usually have the PowerMan logo, which is not a registered trademark, and therefore can be freely used (the Russian company Nienschanz sells Sirtec power supplies under this brand).
3. Sirtec. The units of this company are sold under the brands High Power, Powerman, PowermanPro, Thermaltake. Models 360W and higher are recommended for purchase.
4. Delta/LiteON. Currently found in HP cases, sometimes they require modification with a soldering iron.
Power supplies like Antec and Enermax are very popular on the foreign market, but, unfortunately, they are practically not supplied to Russia.
6. Conclusion
No matter how trivial, it only makes sense to repeat the phrase that has been said many times - you should not save on a power supply, because by saving 30-50 dollars on a unit, you can lose a thousand dollars worth of components. In addition, using a good power supply improves the parameters of other components of the computer, such as the sound card, and increases the stability of the system as a whole. And most importantly, the need for a powerful power supply is not a myth, but a harsh reality. Especially for those owners of AMD-based systems whose motherboards do not support powering the processor from the ATX12V (P4) tail.
Certificate 80 PLUS
A high-quality power supply must have an 80 PLUS certificate. These certificates come in different levels.
- Certified, Standard – entry-level power supplies
- Bronze, Silver – mid-class power supplies
- Gold – high-end power supplies
- Platinum, Titanium – top power supplies
The higher the certificate level, the higher the quality of voltage stabilization and other parameters of the power supply. For a mid-range office, multimedia or gaming computer, a regular certificate is sufficient. For a powerful gaming or professional computer, it is advisable to take a power supply with a bronze or silver certificate. For a computer with several powerful video cards - gold or platinum.
Fan size
Some power supplies still come with an 80mm fan.
A modern power supply should have a 120 or 140 mm fan.
I recommend purchasing a power supply with a 120 mm fan, as it makes less noise, cools better, and is easy to find a replacement in case of failure.
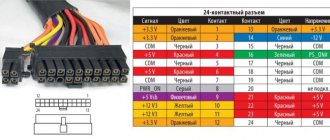
Power supply connectors
| ATX (24-pin) - motherboard power connector. All power supplies have 1 such connector. |
| CPU (4-pin) - processor power connector. All power supplies have 1 or 2 of these connectors. Some motherboards have 2 processor power connectors, but can also operate from one. |
| SATA (15-pin) - power connector for hard drives and optical drives. It is advisable that the power supply have several separate cables with such connectors, since connecting a hard drive and an optical drive with one cable will be problematic. Since one cable can have 2-3 connectors, the power supply must have 4-6 such connectors. |
| PCI-E (6+2-pin) - video card power connector. Powerful video cards require 2 of these connectors. To install two video cards, you need 4 of these connectors. |
| Molex (4-pin) - power connector for older hard drives, optical drives and some other devices. In principle, it is not required if you do not have such devices, but it is still present in many power supplies. Sometimes this connector can supply voltage to the case backlight, fans, and expansion cards. |
| Floppy (4-pin) - drive power connector. Very outdated, but can still be found in power supplies. Sometimes some controllers (adapters) are powered by it. |
Check the configuration of power supply connectors on the seller's or manufacturer's website.
Parameters that are important to consider when choosing
Form factor
This is the first characteristic you need to pay attention to. The choice depends on the enclosure planned for assembly. The main form factor is ATX. This standard has a height of 86 and a width of 150 mm. The length can vary significantly, and the case specifications indicate how long the power supply will fit there.
For compact cases, as a rule, power supplies of the SFX standard are required - height 60 and width 100 mm. There are also a number of less common formats: TFX, FlexATX, EPS, CFX, LFX.
Power
The next characteristic that you need to pay attention to when purchasing is the total power across all lines and the load characteristics of all lines.
In a modern system, the main consumption is on the +12 V channel. It is the power through this channel that you need to look at. In more expensive models, it may be equal to or slightly less than the value indicated in the model name.
In budget models, manufacturers often indicate the total power as the sum of the maximum output watts across all lines. For example, along the +12 V line - 530 W, along the +3.3 and +5 V lines - 120 W, and the model is labeled as 650 W, although in fact it is a 550 W model.
You should also pay attention to such an indicator as the permissible load in Amperes for each channel. A higher indicator for identical models is better. You can find on sale power supplies with several virtual +12 V lines, which share this permissible load among themselves. Such models do not provide any advantage, and recently the fashion for using virtual lines has faded away.
How to choose a power supply for your PC? The easiest way is to use online calculators. They give adequate values, but they may overestimate them a little for reliability, so to speak, “with a margin.”
- be quiet! power supply Dark Power Pro P11 550W
The second option is more difficult - calculate the power consumption yourself based on the characteristics of the components. The main consumption is on the processor and video card, and it’s worth focusing on them. The main thing is not to confuse such characteristics as TDP (heat dissipation requirements) of the processor and its power consumption; they may differ, although both characteristics are indicated in Watts. You can use the TDP value as an approximate indicator; actual power consumption may be slightly lower.
All other components consume quite little in total - from 50 to 100 W maximum.
So that your power supply does not work all the time under full load, you need a small power reserve - 20-30%, but excess power is not required - this is an extra expense.
On average, a gaming PC with one video card requires models from 500 to 700 W, with two video cards - from 650 to 850 W. For office PCs without a video card, a power supply of 300–400 W is sufficient.
- Review and testing of the GIGABYTE P650B power supply
Connectors
There should be enough connectors to connect all consumers; all kinds of adapters are a bad option, especially for connecting video cards.
The main connectors that you cannot do without are ATX 24-pin and 4-pin for powering the CPU. The EPS12V standard requires the use of a detachable 8-pin connector to power the CPU, so it is almost impossible to find a modern power supply model with a 4-pin connector, only very budget options.
Also, recently, more and more often, power supplies are equipped with two cables with 8-pin connectors, and not only in top-end, but also in mid-budget options. This is due to the increased power requirements of modern overclockable processors, and motherboards that support overclocking are equipped with exactly two such connectors.
To connect video cards, if they do not have enough power via the PCI-E x16 line (which is 75 W), 8-pin and 6-pin connectors are used (150 and 75 W, respectively). Typically, power supplies are equipped with a cable with two collapsible 6+2-pin connectors - this is the required minimum.
For connecting other peripherals, storage devices, etc. SATA and Molex connectors are used. The latter is outdated and increasingly rare. Not only HDD or SSD drives are connected via SATA, but also lighting, LSS pumps, and various controllers, so you need quite a lot of these connectors.
Setting up filters in an online store
- Go to the “Power Supplies” section on the seller’s website.
- Select recommended manufacturers.
- Select the required power.
- Set other parameters that are important to you: standards, certificates, connectors.
- Look through the items sequentially, starting with the cheapest ones.
- If necessary, check the connector configuration and other missing parameters on the manufacturer’s website or another online store.
- Buy the first model that meets all parameters.
Thus, you will receive the best price/quality ratio power supply that meets your requirements at the lowest possible cost.