If you right-click on the “This PC” icon and select Properties , you will find that the computer sees all the installed RAM, but less is available. I’ll explain what “RAM memory available” means, why this happens and how to deal with it.
“RAM available” - this means the system uses exactly the amount of memory that is available. The reasons why the available RAM is less than the installed memory and methods for solving them are described below by category.
BIOS settings
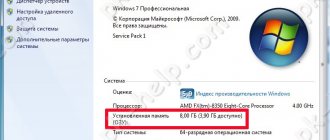
Perhaps the most common problem is when 8 GB (or 6 GB) of RAM is installed, but 4 GB is available, maybe less.
Without hesitation, we reboot the computer, and when we turn it on, we enter the BIOS. Go to the Advanced , select Chipset Configuration ,
find the line Memory Remap Feature , change Disabled to Enabled .
Save the settings and exit by pressing the F10 key. The location of “Memory Remap Feature” may differ from the one indicated above, since the BIOSes are different. After loading Windows, we check the available memory again, it should be like this.
Windows shows less memory than installed. Nothing canbe done?
There are still options when Windows starts using memory to its fullest. As you understand, this results primarily in the requirements for the installed computer configuration.
a) The motherboard chipset must support at least 8 GB of address space. A chipset with this capability, in turn, must meet the following requirements (specific brands):
- Intel 975X, P965
- Intel 955X on socket 775
- for AMD processors these are sockets F, 940, 939, AM2 (these chipsets include any combination of AMD sockets and processors in which the memory controller is physically located in the processor)
b) The processor must support processing the x-64 instruction set.
c) The BIOS must support memory address space remapping. This setting allows a segment of system memory that has just been overwritten by PCI configuration space to be redirected to a level above the 4 GB address line (each such line on the address bus specifies one address bit, so the more physical memory the processor addresses, the more address lines it needs to have (for example, the Pentium processor had 32 address lines, which allowed it to address 4 GB of memory). This setting can be observed directly in the BIOS or in the specifications in your motherboard. But, unfortunately, there are very few materials describing this setting, so I personally have to dig into it manually. You can find it in the BIOS settings under the name Memory Remapping (Feature) and activate it by setting it to Enabled.
Memory limit in Windows boot options
Another common reason is when the operating system limits the use of all RAM in the boot options. The fix is simple, you just need to do the following:
Open the Run window using the Win+R key combination, enter the msconfig command and press Enter.
Go to the “Download” tab, click on the Advanced options button.
Uncheck the box next to “Maximum memory” and click OK.
Close the remaining “Downloads” page by clicking OK, reboot the system, and check the amount of available memory.
How to increase RAM on your computer: step-by-step guide
Every year programs and games consume more and more RAM. More recently, 4 GB was enough for absolutely every user for any need. Today, the figure easily exceeds 8. In order to keep your PC in good shape, you need to add a few gigs to the slots on the motherboard from time to time. In today's article we will answer the following questions:
Find out the type of memory
The first thing you need to do is find out what type of RAM your motherboard supports. At the moment, the most current type is DDR4. Legacy formats (DDR1, DDR2, DDR3) are not compatible with each other and cannot be used together. You can check the type of RAM supported by your motherboard specifications. Traditionally, it is best to check this on the official website of the developers.
Please note that laptop brackets are different from desktop computer brackets. The so-called DIMM memory is a full-size option. SO-DIMM is a stripped-down version for portable devices. It differs in size, location of contacts and location of chip installation. Of course, both types are incompatible with each other.
Determining the availability of slots
The second step is to find out the number of RAM slots on the motherboard. Modern boards are usually equipped with 2-4 connectors. To achieve maximum memory performance, it is recommended to use a minimum of two slots. In this case, the RAM will operate in dual-channel mode.
Multi-channel mode
- operating mode of RAM, in which the data transfer speed can be increased by using several channels at once to access a combined memory bank.
Thus, when using, for example, two memory modules in dual-channel mode, the system can operate faster than when using one module equal to their total capacity. The performance gain from 2 strips is about 10% in games.
In heavy applications that consume a lot of RAM, the increase can reach up to 80%. Designers, editors and sound engineers will be the most likely to see the difference.
There is also a three-channel and even four-channel memory mode. However, this technology is supported by very few processor models (yes, RAM, memory and the motherboard are interconnected in many tasks).
In order for the processor to be able to use two memory channels, it is necessary to use modules of the same type. If the modules have different frequencies, then this setup will work at the speed of the slowest bracket. The RAM must be installed in symmetrical slots, that is, either the first and third slots, or the second and fourth (if we are talking about a motherboard with 4 slots). If there are only two slots, then the first and second ones, respectively, there are no other options. Modules of different sizes can also operate in dual-channel mode.
Clock speed and timings
RAM performance directly depends on these indicators. The higher the frequency and the lower the timings, the better. However, this is a double-edged sword. To achieve high RAM frequencies, developers have to increase timings. At first glance, it seems like completely meaningless manipulations. However, frequency is the main criterion when it comes to performance. This is especially noticeable with modern AMD processors. Timings in this case fade into the background.
Bit capacity of the operating system and capabilities of other components
Legacy 32-bit OSes only support a maximum of 3.2 GB of RAM. And although these are echoes of the past, such systems are still found in office solutions. Therefore, before purchasing new modules, it is recommended to upgrade to the 64-bit version.
The maximum possible amount of RAM is also limited by the capabilities of the motherboard. In the technical specifications, the developers indicate the maximum amount of RAM that can be installed. Values vary greatly and depend on the specific model. The same goes for processors. Each model has its own limit. Therefore, be sure to check out the characteristics of the above components to determine whether they can handle the latest 32 gigabyte kit.
Memory installation process
Adding a new module is very simple. Each slot is equipped with special clips on each edge. These clips should be moved to the side, after which you will need to insert the purchased module until it stops. The clamps snap into place and the memory is then ready for use. You can configure the frequency, voltage and other parameters of the RAM in the BIOS.
Source: https://ichip.ru/sovety/ekspluataciya/kak-uvelichit-operativnuyu-pamyat-na-kompyutere-poshagovyy-gid-625032
Windows version does not support installed memory capacity
If not all RAM is available to Windows, then first of all you should pay attention to the bit depth of the operating system, for example x86 (also called 32-bit) supports no more than 4 GB of RAM, and even if you install 8 GB, it can use the maximum 4GB.
Many users are unaware that each version of the Windows operating system supports a certain maximum amount of RAM. As noted above, x86 uses a maximum of 4 GB of RAM in all versions of Windows. Now let's take a look at RAM support in x64 bit operating systems:
Windows 7
- Starter x86 2 GB
- Home x64 8 GB
- Home extended x64 16 GB
- Professional x64 192 GB
- Corporate x64 192 GB
- Maximum x64 192 GB
Windows 8/8.1
- Home x64 128 GB
- Professional x64 512 GB
- Corporate x64 512 GB
Windows 10
- Home x64 128 GB
- Professional x64 512 GB
By checking your version of Windows with the information in the table, you can make a conclusion, and if this is not a solution to your problem, then read the article further.
Checking RAM Installation
Once you're done installing the RAM, you need to make sure it's working properly. Depending on your PC, the BIOS may display the amount of memory on the boot screen. If you don't see it, you can boot into your PC's BIOS or simply start the operating system and then check the amount of recognized RAM there. In Windows 10, you can simply go to Settings (Win+i) → System → About System or open Task Manager.
If your PC has less RAM than it should, there are several possible explanations.
First, you made a mistake during installation and one or more modules are not fully installed. To resolve this issue, simply go back and double check that all modules are fully seated in their slots.
The next possibility is that the RAM is not compatible with your motherboard (perhaps of the wrong generation), or you installed a module whose capacity exceeds the capacity of the socket. You need to go back to the compatibility checks and make sure you are using the correct RAM.
Finally, if all else fails, you may have a faulty memory module that needs to be replaced.
Related article: What to do if the computer does not see memory
Memory is used by the integrated video card
And perhaps another option why not all RAM is available is the use of the built-in graphics core for video memory.
As a rule, an integrated video card takes up 128-750 MB of video memory. That is, if you have 4 GB of RAM installed, and 3.87 GB is available, then draw the conclusion that the built-in video card is eating up. All this is not critical and you can simply close your eyes to it.
In cases where your computer or laptop has an additional discrete video card, you can try disabling the integrated one via the BIOS. Unfortunately, not all models support disabling the graphics core. But if you succeed, then the memory should become available in full. In some BIOS versions, it is possible to change the size of video memory used.
Well, that’s probably all, now you know the reasons why the available RAM is less than the installed one.
Share your situation and I will try to help. The best “Thank you” is your repost
Memory allocation for Shadow RAM
Shadow RAM or “shadow” memory is an area of RAM into which the contents of the motherboard ROM BIOS chip, as well as additional BIOS of peripheral adapters, are copied or unpacked. This was originally intended as an option purely to improve performance, since RAM is significantly faster than ROM. Modern BIOS implementations use packaged storage of the main unit; at startup it is unpacked into Shadow RAM. Thus, the Shadow operation has turned from optional to mandatory. The packaging allows the use of a smaller ROM chip, therefore cheaper. For correct ROM emulation, the mapping logic included in the “north bridge” of the chipset blocks writing to this RAM area. The unpacked BIOS block placed in Shadow RAM is sometimes called the Runtime block.
On most platforms, the range 000C0000h-000EFFFFFh is allocated for BIOS Runtime blocks of peripheral adapters. For the Runtime block of the system BIOS, the range is 000F0000h-000FFFFFh. Note that even if the specified ranges are partially used or not used, the entire 256-KB block 000C0000h-000FFFFFh is “cut off” from RAM. Almost all modern chipsets allow it to be used only as Shadow RAM.
Note
The statement that RAM (RAM) is significantly faster than ROM (ROM) is true for a particular case - in relation to the element base and circuitry of personal computers, since slow ROM chips and fast RAM chips are used, in addition, the width of the RAM data bus much more on the motherboard. This statement does not apply to the physical principles of operation of RAM and ROM cells.