Programs for overclocking the processor
Despite the fact that some sources suggest downloading special programs for overclocking different types of processors (Intel or AMD), it is best to increase the CPU clock speed through the BIOS.
There is no proven software that can overclock the processor. This is due to technical limitations and the fact that each “stone” has its own standards for increasing the frequency. These may vary depending on the type of cooling used. We recommend that you find out the load capacity for the installed chip model and gradually change the values using instructions written specifically for your BIOS version. Exceeding the maximum permissible overclocking threshold may result in equipment failure.
How to use
Below we have compiled detailed instructions for installing, activating and using the program. Don't miss this block with useful information!
Download and Install
Since installation of the program on your computer is not required, you can start immediately with activation:
- Download the archive with files from the link at the bottom of the page and unpack it to your hard drive. Open the folder and run setfsb with administrator rights.
- We don’t change anything in the program and launch the setfsb_give_key activator through the same folder. A small window with a combination of numbers will appear on the screen. We rewrite or copy it into the field for entering the key from SetFSB.
Along with this look: Wufuc v1.0.1.201 for Windows 7
- If everything is done correctly, we can start working with the program. After activation, all sliders and functions will become available in the Customize tab. Be sure to check this moment.
The utility can be run both from a hard drive and from an external drive.
Operating instructions
Let's move on to the description of the overclocking procedure:
- First you should find out the generator model - Clock Generator. This can be done through the manufacturer’s website, read from the surface of the processor itself, or found through special software for collecting statistics about a PC. Then, in the Control tab, select the appropriate option.
- Open the Diagnosis tab and click on the Get FSB button to test the generator's ability to determine the current frequencies. After some time, a value will appear in the Current Frequency field.
- Use the slider to increase the processor frequency. The value in the Select Frequency field will change. After selecting the desired position, save the new settings with the Set FSB button.
Remember that you need to increase the frequency in small steps. After each change, conduct stability testing, and only if the outcome is positive, move on!
Programs for overclocking video cards
Programs for overclocking video cards will help you change the main performance indicators on the hardware graphics card of your PC or laptop - voltage, permissible temperature, frequency of the processor and adapter memory, as well as the rotation speed of the cooler. In addition to editing parameters, these utilities allow you to view basic information about the installed equipment.
We emphasize that such programs should be used with external graphics devices that are not integrated into the processor or motherboard. Only in this case will you be able to get a measurable effect from changing the settings.
Among the proposed tools, we highlight MSI Afterburner primarily due to its compatibility with the largest number of devices.
How to overclock an AMD processor
They accelerate much better. The company develops special models designed for such manipulations. A number of the following programs will help with this.
AMD OverDrive
A proprietary utility that provides many settings for adjustment. The main condition for overclocking is the unlocked CPU multiplier, since this is where it increases. Moving the half-signs is the change in the multipliers.
Here you should be careful and attentive, since the processor can easily overheat, and the faster the weaker the heat dissipation system. The program warns if the multiplier is fixed at a critical value. There is also an auto-acceleration mode, and you don’t need to know the type of frequency generator.
Disadvantages include limitations to certain models and lack of Russian localization. After installing the program, the computer must be restarted.
Advanced Clock Calibration
In fact, this is not a full-fledged utility, but a function in AMD OverDrive or BIOS. It supports only Athlon chips of different generations and very accurately overclocks the “stone” (down to every megahertz).
The function is available on all motherboards that support such chips. The easiest way, of course, is to use it in AMD OverDrive, which must be present in the system. When you restart the PC, the settings are saved.
ClockGen
A third-party utility does an excellent job of realtime CPU overclocking. It has a very simple and clear interface, despite the lack of Russian translation.
There are several sliders here. After clicking the “Apply Selection” button, the changes immediately take effect. But before you start overclocking, you need to find out the type of frequency generator in order to indicate it in the “Clock Generator Setup” field and click the “Read CLocks” button.
The program has low requirements for system resources and works quite quickly.
Programs for overclocking random access memory (RAM)
As with the processor, there are no stable utilities that can change the operating frequency of the RAM using the operating system. You need to edit these parameters through the BIOS; moreover, it is important that the new frequency is supported not only by the memory, but also by the motherboard. You can read the instructions for changing frequencies in the user manual for your motherboard.
You may come across the opinion that there are programs for overclocking “old” RAM (DDR) on laptops, but we were unable to find working versions of such utilities.
Preparing for overclocking
Each CPU has a clock speed limit to which it can be overclocked. Exceeding it may have fatal consequences for the device.
Therefore, you need to approach this procedure with at least confidence in yourself and in the capabilities of your processor.
The overclocking standard for Intel “stones” is 10±5% of the initial value. There are also more serious restrictions. The most highly potential of the “blue” models are those whose names include the letter K after the numerical marking.
Increasing processor performance by increasing its clock frequency requires more power from the power supply and a high-quality heat dissipation system, since cycles may be skipped when overheated; This will have a positive effect on temperature reduction, but a negative effect on performance.
Before starting acceleration you should:
- update the motherboard BIOS to the latest version;
- check the reliability and serviceability of the installed cooling system;
- find out the basic CPU clock speed (in the BIOS or a program like CPU-Z).
- Perform processor stability testing at maximum load with an S&M type program.
Important! Operating the most important mechanism of a computer at elevated parameters leads to its accelerated wear compared to normal indicators. Therefore, use this opportunity at your own risk.
Programs to improve disk performance
The main factors influencing the performance of hard drives are its current state and file layout.
You can check the current state through SMART analysis and, if necessary, format the device “correctly” using the HDD Low Level Format Tool; it scored the most points in our thematic review.
In addition, the performance of classic hard drives depends on how evenly the data is distributed over the surface. Many different system utilities contain a file structuring (defragmentation) function. Among specialized solutions, we highlight Defraggler and Auslogics Disk Defrag.
Refrigerator for advanced microdevices CPUCool, WCPUID, WCPREDIT, WCPRSET 1.2, VСool 1.7
14 years ago October 17, 2006 at 03:49 pm 940
Advanced Micro Devices has been very successful with its processors from the Athlon and Duron lines: having simply excellent performance indicators in almost all modern applications at a very reasonable price, they have rightfully earned the title of “people's favorites”, having taken it away from the decrepit “Celerons” in fair competition. In addition, it has long been no big secret that AMD processors, thanks to the ability to unlock the multiplier, give craftsmen great prospects for overclocking, which can significantly increase the already considerable performance for the same money.
AMD processors are good for everyone, but there is always room for a fly in the ointment, and in this case, not just a spoon, but, perhaps, the whole glass, will be a very significant power consumption, and, therefore, the heat dissipation of these processors. The situation is aggravated by the extremely poorly designed thermal protection system of Athlon XP processors, when the built-in thermal diode, which does not have its own protection circuit against core overheating, is not supported by most motherboards.
But it is well known that the operation of electronic devices at high frequencies under conditions of elevated temperature leads to a significant reduction not only in the stability of the system, but also in the lifespan of this very device. In this case, when the average operating temperatures of the processor are already very close to their maximum permissible values, unless special measures are taken, the processor may not reach the time when it becomes obsolete.
And such measures are naturally being taken: the cost of the most sophisticated processor coolers (the filigree radiators of which are made not of cheap aluminum, but of noble copper, and sometimes even gold-plated) is already close to the cost of the processors themselves, and the noise level of powerful high-speed fans competes with the roar of a jet plane taking off. And in the reports about the wonders of overclocking coming from the land of the Rising Sun, it is no longer archaic air coolers of the radiator-fan type that appear, but water cooling systems, and even reinforced with Peltier thermoelements, and in the most clinical cases there is already talk of cryogenic cooling.
But are all these wonders of human imagination always necessary for normal work? What can be done to improve the efficiency of the processor cooling system without resorting to unreasonably high costs? After all, the problem of heat removal from an overheated processor can be solved not only by dispersing hot air through a cramped computer case, but also with the help of software. In cases where the processor’s power is not used to its fullest (and the processor very rarely uses its full power, spending most of its working time idle waiting for one or another system event), you can pause it, which will certainly affect the decrease in its operating temperature.
Programs called “soft coolers” have existed for a long time and are well known, primarily among overclockers. Most of them were developed for computers based on Intel processors running Windows 9x/Me operating systems. A rather unpleasant feature of these operating systems for us is that the entire time the processor is not busy performing the next task, the system forces it to run an empty loop. Apparently, the roots of such a solution must be sought in the distant past, at the time of the birth of MS–DOS.
At that time, the architecture of the first processors was extremely imperfect, and to ensure acceptable performance they had to be artificially maintained in a “hot” state, which now, in an era of completely different speeds, leads to wasted energy consumption and overall overheating of the system. Therefore, the operation of software coolers is based on the use of the HALT command, which pauses the processor when there are no current tasks.
At the same time, the level of processor power consumption is reduced to the minimum necessary to maintain its functionality. But it’s not for nothing that they say that free cheese can only be found in a mousetrap: any program operating in real time will certainly eat up its share of system resources, reducing, to one degree or another, the overall performance of the computer. Now, when the most modern operating systems based on the UNIX ideology (Linux, FreeBSD), as well as OS/2, Windows NT / 2000 / XP can already correctly use the HALT command, soft coolers have largely lost their relevance and are used only as part of multifunctional utilities
An example is the regularly updated CPUCool program (www.podien.onlinehome.de/cpucool9.zip). It performs not only the function of software cooling of the central processor, but also monitoring the main parameters of the motherboard and optimizing the operation of a number of computer subsystems and much more.
As a soft cooler, CPUCool is most effective when working with Windows 95/98. Moreover, unlike most of its analogues, which issue the HALT command as a low-priority task, which causes high processor load when executing this command, CPUCool integrates the HALT operation directly into Windows 95/98 This achieves a reduction in processor load when executing this command.
But you can use software cooling of the processor only in the officially registered version of CPUCool. It can also be used to change FSB frequencies, but unfortunately, this function is not supported for all motherboard models, but only for those that allow you to change the frequency using SMBus.
In addition, you can: turn off the computer using a specific hotkey combination; monitor processor temperature, fan speed, supply voltage, and almost all motherboards based on Intel, ALi, VIA, AMD, SiS chipsets are supported; optimization for AMD K6 and K7, Cyrix and Intel processors (a completely useless feature that has no effect on the overall system performance) and memory optimization (only for Windows 95/98).
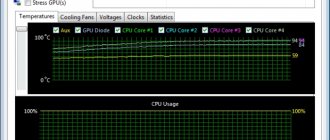
By default, the program runs only in the background. To view information and change some parameters, you need to click on the icon in the system tray. The window that appears will present fairly detailed statistics on computer usage, processor temperature, free RAM, etc. This data is displayed both in text and graphical form.
The program is replete with all kinds of settings, but its interface is too confusing, and, especially at first, it is very difficult to find the right option. The large, main window, convenient for configuring the program but taking up too much screen space, can be replaced with a small one, more suitable for day-to-day control of the most important functions.
CPUCool can work quite easily under any version of the Windows 9x / Me, NT / 2000 / XP operating system, it is distributed as a shareware and works for free for 21 days. The download file size is 2.4 MB, but during operation CPUCool requires much more system resources - the CPUCool.exe process alone takes up 6404 KB of RAM.
Thus, it turns out that in the CPUCool program the softcooler function has faded into the background, replaced by more relevant “features” today, especially since all of the above applies for the most part to processors and chipsets from Intel, while with processors produced by AMD the situation is slightly different. more difficult. The fact is that in order to reduce their energy consumption, when a HALT or similar STPGNT command is received, the northbridge of the chipset must disconnect the processor bus from the system bus. A special bit in the northbridge control registers is responsible for this.
For example, in the most common VIA chipsets, the 7th bit of the 52nd register is used for these purposes. With the default settings, it is reset, that is, the HALT command does not turn off the system bus, and the processor remains in operating mode. Obviously, by somehow gaining access to the internal registers of the chipset, you can organize software cooling of AMD processors without any additional programs.
It is best to use the creation of the famous Japanese programmer H-Oda, the author of the most popular program among overclockers, WCPUID. Using the free program WCPREDIT 1.2a (www.athlonoc.com/tweakvia/wpcre12a.exe), you can view and change system register values for a wide variety of chipsets. In order for the program to be able to identify the chipset used in the system, it needs a register configuration file, for example, for VIA KT133 / KT133A chipsets, you need to place the file 11060391.PCR (www.athlonoc.com/tweakvia/11060391. PCR).
All available registers are located on the left side of the program working window. The register address is specified by a two-digit hexadecimal code in the range 00 - FF. The first column contains the values of the first digit, and the first row contains the values of the second digit. At the intersection of a row and a column, you can see the numerical value of the desired register. After selecting the desired register, its value in binary and hexadecimal codes will appear in the lower panel, available for modification. To facilitate editing, the right window provides a decoding of each bit of the selected register, with bits set to the “logical zero” state highlighted in white, while one is displayed in blue. After making the necessary changes, you must click the Set button and confirm your decision. Everything is quite simple and elegant.
A little higher, I already talked about the 52nd register of the north bridge for VIA chipsets, the 7th (most significant) bit of which controls the Disconnect enable when STPGNT detected mode (disconnecting the processor using the STPGNT command). By default, it has a value of 0, that is, this command is ignored by the chipset, and by setting it to 1, you can reduce the temperature of an idle processor by 10–15 degrees.
To evaluate the effectiveness of using software cooling of the processor, we used a computer that approximately corresponds to the average level of home work and gaming systems.
In my opinion, such a system could be the following:
- processor Duron 650 @ 800 with an unlocked multiplier, overclocking of which was limited to a modest value of 6 × 133 MHz to maintain system stability;
- ADDA B 306 MB processor cooler, quiet and quite decent cooling, with a radiator measuring 55 × 55 × 25 mm and a 4500 rpm fan;
- motherboard - Soltek SL-75KAV on VIA KT133A chipset;
- RAM - 2 × 128 MB PC133 SDRAM NCP module;
- operating system - Russian version of Windows 2000 with Service Pack 2 installed.
To monitor the processor temperature, two sensors were used, one of which was a standard thermal diode installed in the middle of the processor socket. Unfortunately, the current revision of the motherboard (F5) is equipped with a rigid sensor that does not reach the bottom of the installed processor, unlike earlier revisions that used a flexible thermal diode strip, which did not have such problems. The standard thermal diode thus measures not the temperature of the bottom surface of the processor case, but the air temperature in the Socket, which does not contribute to a correct assessment of the dynamics of temperature changes when the thermal regime of the processor changes. Therefore, for more accurate control of the processor temperature, it was necessary to attach an additional thermal sensor, included in the motherboard kit, to the processor case, near the core, fortunately, its flat design allows you to easily secure the thermal diode using adhesive tape so that its “bead” touches processor core crystal.
The readings of both sensors were monitored using the Motherboard Monitor 5.1 program. In normal mode, without changing the value of the 52nd register, after 40 minutes. The idle temperature of the processor core was 38° and 35° inside the processor socket. The dynamics of temperature changes after setting the 7th bit to the single state are given in the table. It is clear that such a decrease in temperature occurs only for an idle processor; when applications are running, the processor temperature is much higher. So, while surfing the Internet, the temperature ranged from 32° to 35°, when working in the Word text editor - from 38° to 40°, and in games it reached 50°.
But I want to immediately note that organizing software cooling of the processor is far from the most important purpose of the WCPREDIT program, because by manually adjusting the values of chipset register parameters, you can significantly increase system performance, especially in cases where some important adjustments are missing in the motherboard BIOS .
Along with its many advantages, the WCPREDIT program also has a small but annoying inconvenience - it cannot remember the set register values, and after each reboot of the computer you have to set them again. Another utility from the restless Japanese will help solve this problem - WCPRSET 1.2 (www.athlonoc.com/tweakvia/wpcrs120.exe), which sets user-specified registers every time the system boots. This is done very simply; after starting the program, you need to set Start in the Startup window and, by clicking the Add button, add register values to the list in the Register Setting List window. Next, you need to make sure that the bus (bus), device (device) and function (function) have values of 0 (default) - this is important. Now in the Register window the number of the register that needs to be changed is entered, and in the Data window its new value (in the form of a hexadecimal number) is entered. After this, every time the system starts, the WCPRSET program will automatically set the specified register values. No hassle!
But I would like to note that not every computer user has sufficient qualifications to manually edit the control registers of the system chipset. In this case, a simple and fairly small-sized free program VСool 1.7 (www.naggelgames.de/vcool) can help, which, in addition to a software cooler optimized for working with VIA chipsets, includes a very decent system monitoring utility, which is a functionally complete solution for software cooling of AMD processors. In addition, there are a number of smaller features that make this program a truly universal tool that eliminates most of the most well-known shortcomings of VIA chipsets.
By default, the softcooler starts simultaneously with the start of the operating system, showing digital values of the temperature of the processor and (or) system sensor in the system tray. When you hover your cursor over this icon, you can see the readings of not only all temperature sensors on the motherboard, but also the fan speed.
All main program settings are concentrated in the Options window, the upper part of which is dedicated to system monitoring, and in the lower part you can configure the operation of the soft cooler and some other additional functions. As a useful property of the monitor, completely or partially absent in other similar programs, we can note the presence of a three-stage display system, performance limitations and, ultimately, shutdown of the CPU when its temperature exceeds predetermined values.
As a cooling utility, VСool allows you to enter the 7th bit of the 52nd register at startup. In most cases, using modern operating systems, the Cool Bit command is quite enough to organize effective cooling of a running processor, but some outdated operating systems, such as Windows 98 (not SE!) and older, do not have the ability to independently organize the HALT cycle. In this case, the Idle Loop command, which emulates the HALT command in modern operating systems, will help ensure the normal functioning of the utility.
Thus, using the WCPREDIT, WCPRSET and VCool utilities can make life much easier for those who would like to use their computer as efficiently as possible. However, sometimes all these programs may not only not make life easier, but also add such a bunch of problems that no one will find it enough. For some unknown reason (probably of a metaphysical nature), AMD processors that have fractional multiplication factors (such as 6.5, 7.5, etc.) really do not like software coolers.
At least for me, the joint use of the above programs with processors that have such coefficients led to constant freezes and system crashes, and in the case of a combination of WCPREDIT and WCPRSET, the negative consequences manifested themselves much more often and on a wider scale. Changing the multiplication factor by an integer, as if by magic, stopped all these outrages. So, when using the programs described above, I strongly recommend that you pay close attention to the problem of fractional multiplication factors of AMD processors.
In addition, when changing the value of the 52nd register, in some cases, sound distortion may occur, and when using both the built-in AC97 encoder and the long-suffering Sound Blaster Live! (it seems that Creative and VIA will never be able to “make friends”), although no such problems were noticed with all other sound cards. To solve problems with sound cards, there is a special PCI Options section in the settings of the VCool utility, in which you can specify several (up to a dozen) necessary settings.
In addition to the above-described options for reducing the temperature of processors by additionally grinding the radiator base and using soft coolers, there is another rather radical way to solve the problem of reducing the heat emission of AMD processors, which for some reason is practically not used. The fact is that the amount of heat generated by a running processor directly depends on its supply voltage. The Athlon processor must fully comply with all technical specifications for it, not only with a nominal core supply voltage of 1.75 V, but also when this voltage varies within the range of 1.65 - 1.85 V, although in real conditions, of course, this range is much wider .
So, for testing we took an Athlon 1000 MHz processor, the supply voltage of which was successively reduced from the nominal 1.75 V to 1.5 V, and all the time the system remained completely stable, and its performance was not affected at all. But the processor core temperature dropped by 10°. Unfortunately, we had to stop there, since the existing motherboard did not allow us to further reduce the processor core voltage, but the high efficiency of this method of cooling the processor can be considered proven. The biggest disadvantage of operating a processor at a reduced supply voltage is the need for individual selection of parameters for each specific processor instance.
| Dynamics of temperature change | ||
| External sensor readings, °C | Sensor readings in the socket, °C | |
| Default Settings | 38 | 35 |
| Register 52 changed; in 2 minutes | 27 | 31 |
| Register 52 changed; in 5 minutes | 24 | 27 |
| Register 52 changed; in 10 minutes. | 23 | 25 |
In closing, let me once again draw your attention to the ambiguity of the benefits of using soft coolers.
Let's remember their advantages:
- high cooling efficiency of an idle or lightly loaded processor, which increases its lifespan;
- when using soft coolers in laptops, not only the battery life of the device is significantly increased, but also the heating of the laptop case during active operation is noticeably reduced;
- the ability to use a less efficient, and therefore much cheaper, cooler;
- greater stability of a “cold” central processor;
- accessibility - all the utilities described above, and most of the other softcoolers are free (to one degree or another).
But at the same time, softcoolers have no less disadvantages:
- a decrease in system performance, even if only slightly;
- software coolers are absolutely ineffective in combination with heavy applications that heat up the processor;
- the stability of both the processor itself and individual expansion cards may be disrupted, and not all such problems can be treated;
- reducing the lifespan of the processor due to thermal expansion of the crystal elements during sudden surges of current that accompany the process of turning the processor on and off, especially when used in applications that periodically load the system.
Thus, it is impossible to give unambiguous recommendations whether or not to use programs of this kind in your daily activities, although, perhaps, when used in laptops, the total positive effect of using soft coolers still outweighs their disadvantages.
For everyone else, I can only recommend paying close attention to the programs described in the article, especially since they are really worth at least watching. In addition, all these utilities can help you solve a number of other problems, since they are all quite multifunctional.
And you, dear readers, will have to make the final decision whether to use soft coolers or not in your daily work, on your own, taking into account the configuration of your computers, the nature of the tasks they perform and other significant subtleties of their use. At least you now know what kind of software animals these are and what they are eaten with.