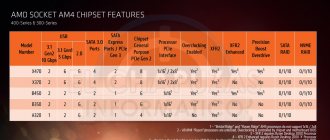
AMD allows us to overclock almost all Ryzen, Ryzen Threadripper and Athlon processors, with the exception of older models - Athlon 2X0GE, which cannot be officially overclocked. It is worth adding that overclocking an AMD processor is possible both on top-end X-series motherboards (stTRX4/X570/X470/X399/X370) and on cheaper B-series motherboards (B350/B450/B550). This feature is not available on budget A320 models.
As an example, I used the Ryzen 5 3600, one of the most popular chipsets of the Matisse generation (Zen 2). It offers us 6 cores and 12 threads as standard, which operate at a clock speed of 3.6 GHz and can be overclocked to 4.2 GHz in Boost mode. For other Ryzen processors the process will look very similar.
How to overclock AMD Ryzen processors from a motherboard
You will be able to find more overclocking options on a UEFI motherboard - this is the method I recommend for more experienced readers who would like to squeeze more megahertz out of their AMD.
As an example, I used the ASUS ROG Crosshair VIII Hero (WI-FI) motherboard. The technique will be similar for boards from other manufacturers. The only thing is that the location of the menu and the names of individual functions may differ slightly, although the process itself. in general it will look the same.
We go into advanced mode - all the necessary options can be found on the Extreme Tweaker tab.
Let's start with changing the processor multiplier - it can be set for all cores (CPU Core Ratio) or separately for individual CCX blocks (CPU Core Ratio (Per CCX)). First, I recommend increasing the value by 1x or 2x - if everything is stable, increase it by another 1x and, thus, until the maximum available value is reached.
The next step is to increase the processor core voltage - a higher value will stabilize the clock frequency, but will lead to increased power consumption and higher temperatures. Manual mode sets a fixed value, while in mixed mode the value by which the voltage should be increased is set by default.
We start with 1.25 V and, if necessary, increase by 0.025 V (at home I do not recommend exceeding 1.4 V).
In some cases, increasing the SOC (processor) voltage may be necessary to stabilize the synchronization process. It's best to start at 1.00V, although I don't recommend going above 1.20V in a home setting.
Load line calibration can also help stabilize timing - helps reduce voltage drop, but leads to increased power consumption, higher processor temperatures and power loads. For overclocking at home, I do not recommend exceeding the average level (for example, on ASUS boards it is marked as level 3). A value that is too high will cause the temperature to rise significantly.
Finally, we save the settings and move on to checking the stability of the processor.
The AMD Ryzen 5 3600 is sold with a small Wraith Stealth cooler, which is not able to maintain acceptable temperatures after overclocking. If you are going to overclock the processor, then you should stock up on more efficient cooling
Overclocking technique
It is recommended to overclock an amd athlon (phenom) processor by gradually increasing its multiplier by one step. After each increase in the multiplier, you need to check the stability of the processor at the new frequency using the Prime95 utility, and if the test fails, make another attempt by increasing the voltage on the CPU by one step. After passing the test without errors at least three times in a row, you can increase the multiplier by one more step and try to pass the tests again. By doing this, you will find the multiplier and voltage value at which the processor will be stable, and the next increase in the multiplier should result in the test failing. Once this value of the multiplier and voltage has been found, it is recommended, for continuous operation, to reduce them by one step. When overclocking, carefully monitor the processor temperature; it should not go beyond the limits set by the manufacturer.
If by changing the value of the multiplier it is not possible to achieve high overclocking, then it is worth trying the second way - increase it by increasing the frequency of the base generator.
In this short article, we talked about the very principle of how to overclock amd athlon and phenom processors, without dwelling on the details. For those who want to learn more about this, there is a lot of literature, both in paper and electronic form.
This might be interesting:
We recommend reading:
- A gaming computer is what any gamer needs Until recently, a gaming computer had to provide only good…
- How to increase computer RAM? Hello, dear blog readers. Today I propose to talk about the problem...
- What can you use to create a bootable USB flash drive for Windows 10? Modern PC models do not include a disk drive, which is a consequence...
- Overheating of the computer and processor Any equipment needs maintenance and the computer is no exception...
- Connecting the motherboard yourself. Methods and Guides Hello, dear blog readers. In this article we will look at connecting...
- Why does the monitor screen flicker? Before looking for ways to solve the problem of image flickering on the monitor...
- What is a tablet and what is it for? “What is a tablet computer?” - this is the question you ask yourself...
How to check the stability of an overclocked processor?
It remains to check whether the given values are stable. For this purpose, it is best to use the Prime95 application (CPU load) and HWiNFO (temperature reading).
We launch the HWiNFO program and go to the menu with sensor readings (Sensors) - here we are interested in the temperature of the processor (CPU (Tctl/Tdie)) and the power section (VRM). In Prime95, select the Small FFT mode, which will begin to heavily load the processor and test its stability.
Leave the test for at least an hour (preferably several hours to be sure). If there are any problems with the stability of the computer (rebooting, blue screen, freezing), you need to reduce the clock frequency or increase the supply voltage.
It is also worth monitoring the temperature of the processor and power unit so that it does not exceed 100 degrees Celsius (the limit value, exceeding which can cause a decrease in clock frequencies and a drop in performance). If the temperature is too high, it is necessary to reduce the time and voltage.
If there are no problems with stability, and the processor and board maintained optimal operating temperatures, we check the performance after overclocking. Later you can try to increase the values even more.
CPU overclocking
This can be done using the AMD OverDrive utility, which allows you to overclock the processor and test its operation. This utility is produced by AMD and is designed to facilitate this process.
But many users prefer to carry out such overclocking through the motherboard BIOS. True, this path requires some theoretical preparation and knowledge. You will also need a utility that will allow you to evaluate the result - this is CPU-Z, it will show the new processor frequency and Prime95 - a utility that allows you to evaluate the stability of the system under overclocking conditions, as well as some others - to monitor temperature and performance.
What performance gains can you get?
Each processor has different overclocking potential. The AMD Ryzen 5 3600 model belonged to a newer batch, so it could run at higher clock speeds. I was able to overclock the chip to 4400 MHz (44x100 MHz) with a supply voltage of 1.375 V. How did this affect performance?
Cinebench R20 – rendering
The gain from overclocking may not be significant, although the difference is noticeable - in the test using all cores, I recorded an increase of 9%, when using a single core - only 5%.
For testing in games, we used a powerful Gigabyte Radeon RX 5700 XT Gaming OC 8G video card. Overclocking the processor did not have a significant impact on the smoothness of the animation - even in the processor sections, I received an increase of only one frame/s.
BIOS settings
Depending on the type of motherboard, the settings in the BIOS may change, but we recommend setting some of them like this:
- For Cool 'n' Quiet, select Disable.
- For C1E select Disable
- For Spread Spectrum select Disable
- For Smart CPU Fan Control select Disable
You should also set the power plan to High Performance mode.
Remember that you perform all actions to overclock the processor solely at your own peril and risk!
Is it worth overclocking an AMD processor?
You decide! For me, overclocking the processor not only led to an increase in performance, but also to a slight increase in power consumption. With a heavy load on the processor, the difference was 23 W, and in games - 14 W. Temperatures also increased - with increased load from 70 to 90 degrees Celsius (I used a cooler - SilentiumPC Fortis 3 HE1425).
System heat dissipation
As the frequency increases, the heat generation of any element always increases and a limit comes when it refuses to work at a given frequency. In order to restore its functionality, the voltage on it is increased. This, in turn, increases the heat it generates. Ohm's law says that increasing the voltage by 2 times increases heat generation by 4 times. Hence the simple conclusion - in order to successfully overclock an amd processor with a hairdryer (athlon), you need to take care of its good cooling. Moreover, if overclocking is carried out through a generator, then the motherboard must also be cooled. For cooling, both high-performance coolers and water cooling are used, and in extreme cases, liquid nitrogen.
Once again about overclocking the AMD Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition
This article was the result of additional testing of the AMD Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition processor, which until recently was the flagship of the merged company. We have previously tested this processor using standard methods [review] and checked its performance under overclocking in modern games [review].
The essence of additional testing comes down to using various CPU cooling systems, testing the new version of the AMD Overdrive 3.0.2 and AMD Fusion For Gaming programs, as well as running a number of tests used as popular performance measures for the world's largest database of results for overclocking components - HwBot.org .
In addition, to obtain higher performance, and simply out of sporting curiosity, we overclocked the test video card - AMD Radeon 4890, within safe limits, which will be discussed in more detail below.
Test bench configuration:
- Motherboard: Gigabyte MA-790GP-DS4H
- AMD Processor: Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition
- Memory: Corsair DDR2 667MHz (5-5-5-15-2T) 2x1024 MB
- Hard drive: Seagate 160 GB SATA2
- Power supply: Corsair HX520 520W
- Operating system: Windows Vista Ultimate SP1 32-bit
The indirect purpose of testing was also to test the power supply in such difficult conditions. Recently, marketers have been quite successful in perpetuating in the minds of buyers the idea that when assembling a powerful system, and even more so when overclocking it, it is impossible to get by with a power supply with a power lower than 750 or even 1000 Watts. Let's try to find out if this is really so.
Let us remind you that an AMD processor with the letters Black Edition (Black Edition) in the name implies the ability to freely change the multiplier, both down and up. This allows you to use almost any motherboard for overclocking, which does not necessarily have to endure increased voltages on the chipset and operation at greatly increased clock generator frequencies.
A nice feature of the test motherboard was the ability to set the processor multiplier not only in the form of integers, but also in increments of 0.5. This further simplifies the overclocking procedure, leaving only fine final adjustments within 100 MHz for painstaking work.
Unfortunately, the memory for the test bench turned out to be definitely the weak link in the entire chain, as a result of which this test does not lay claim to any new records obtained as a result of overclocking. However, you can compare the speed increase relative to the nominal frequency in any case, which is what interests us in the first place.
The video card is a test sample from AMD itself and, of course, has a completely reference design. The original cooling system was not modified or replaced during tests and overclocking.
All tests were carried out on an open bench at room temperature 24 degrees Celsius. The LinX 0.5.9 program was used as a stability test - a simple and convenient GUI for the Linpack benchmark from Intel, popular among overclockers. The achieved frequency was considered stable after successfully passing 25 test passes, the amount of RAM used was 1024 MB.
The following set of tests was carried out at all CPU frequencies considered in this testing:
- WinRAR
- 7zip
- 3DMark Vantage
- PCMark Vantage
- x264 HD Benchmark Ver. 2.0
At the maximum stable frequency achieved as a result of overclocking, the following were additionally launched:
- 3DMark 2006
- Hexus Pifast
- SuperPi
- Wprime
Data on the processor frequency was taken by the CPU-Z 1.51 program; HW Monitor 1.14 was responsible for monitoring voltages and temperatures. All energy-saving technologies were disabled during the tests, the processor fan speed was at the maximum level. Overclocking under a boxed cooler
The processor came to us for testing fully assembled, so it was a sin not to check what this modest-sized cooler, with a copper base, two heat pipes, aluminum fins and a 70mm fan, is capable of.
First of all, we ran the entire set of tests at a nominal frequency of 3000 MHz and a voltage of 1.35 V. The test results are presented in the table:
| AMD Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition, 3000 MHz | |
| WinRAR 3.71, c | 64 |
| 7-Zip 4.57, c | 147 |
| x264 v0.59.819M, fps (1pass/2pass) | 66.00 / 17.46 |
| 3DMark Vantage, 3DMark Score (CPU Score) | P9842 (10011) |
| PCMark Vantage, PCMarks | 5561 |
The test Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition tolerated an increase in frequency to 3400 MHz without increasing the voltage, however, towards the end of the Linpack test, a failure occurred, which was resolved only after increasing the supply voltage to 1.425V.
The next step came with even greater concessions - to reach the 3600 MHz bar, the supply voltage had to be raised by another 0.075V. In such conditions, the boxed cooler coped with its responsibilities only thanks to the open stand. All tests were absolutely stable, but the temperature, according to the thermal sensors built into the core, was very close to 70 degrees Celsius.
| AMD Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition, 3600 MHz | |
| WinRAR 3.71, c | 55 |
| 7-Zip 4.57, c | 142 |
| x264 v0.59.819M, fps (1pass/2pass) | 75.99 / 20.69 |
| 3DMark Vantage, 3DMark Score (CPU Score) | P10276 (11938) |
| PCMark Vantage, PCMarks | 5647 |
This mode can be considered only conditionally suitable for everyday use, and continuing tests using a box cooler was not only pointless, but also dangerous. Nevertheless, it showed a very worthy result, because over the years of the existence of boxed coolers, overclockers have developed a stereotype that such cooling systems are not intended for overclocking at all (which until recently was true). Overclocking under the Zalman CNPS9700 NT
This air cooler model is not the best that exists, but its fairly high efficiency has been proven in practice more than once. Such a cooler is not difficult to find on the market; it is easy to install and does not require additional “file modification”.
During the stability test at 3600 MHz, the temperature of none of the cores exceeded 60 degrees Celsius, which is almost 10 degrees better than the boxed version.
However, further increases in frequency very quickly ran into insurmountable problems. At 3800 MHz, the processor successfully loaded the operating system, but the stability test failed after just a few minutes. An additional increase in voltage did not change the picture - the processor remained unstable even at a voltage of 1.60 V.
After setting the multiplier to 18.5 (3700 MHz), the Phenom regained its stability and added only 1 degree at peak load. By further increasing the clock generator frequency, we were able to identify the maximum stable processor frequency - 3775 MHz (204x18.5). It’s a bit of a shame that we got a sample with such a modest potential, but that’s why it’s overclocked, and no one can give accurate predictions in advance.
| AMD Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition, 3775 MHz | |
| WinRAR 3.71, c | 52 |
| 7-Zip 4.57, c | 137 |
| x264 v0.59.819M, fps (1pass/2pass) | 78.17 / 21.38 |
| 3DMark Vantage, 3DMark Score (CPU Score) | P10378 (12448) |
| PCMark Vantage, PCMarks | 5641 |
There is no error in the table - the processor's result in PCMark Vantage is indeed lower than it was at 3600 MHz. This behavior indicates either that the software is not behaving quite adequately (which is quite possible), or that the processor is operating incorrectly at a given frequency. Although in all other tests a clear increase is visible and the stability test never stopped with an error, no matter how many times we ran it. CPU overclocking NB
As you know, the memory controller of AMD processors has long been built directly into the core, so most of the work of the north bridge on the motherboard is also performed by the processor itself. To speed up the operation of the CPU with RAM and the third level cache (L3), it is possible (and even necessary) to further increase the speed of the CPU NB unit.
To speed it up, you can use both increasing the multiplier and increasing the frequency of the clock generator. By default, CPU NB operates at a speed of 1800 MHz (200x9). At the same time, as practice has shown, the maximum stable CPU NB frequency does not decrease as the processor cores are overclocked.
So, for example, when setting the processor multiplier to x15, raising the setting frequency to 204 MHz and lowering the multiplier that sets the resulting RAM frequency, the CPU NB unit can (in our case) stably operate at a frequency of 2448 MHz (204x12) without raising the voltage. At the maximum overclock achieved during testing, this unit continued to operate stably at a frequency of 2448 MHz, although the voltage had to be increased by 0.05 V in order to achieve full completion of the LinPack test.
| AMD Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition, 3775 MHz, CPU NB 2448 MHz | |
| WinRAR 3.71, c | 49 |
| 7-Zip 4.57, c | 126 |
| x264 v0.59.819M, fps (1pass/2pass) | 80.87 / 21.84 |
| 3DMark Vantage, 3DMark Score (CPU Score) | P10431 (12573) |
| PCMark Vantage, PCMarks | 5641 |
As can be seen from the table, acceleration of the CPU NB block has a good effect on the overall level of performance, and therefore you should not forget about this component of the system in the case of overclocking the processor exclusively using the multiplier. AMD Overdrive 3.0.2
This program gives the user the opportunity to control almost all processor, chipset and RAM options important for overclocking directly from Windows, which, theoretically, makes the overclocking process easier, more convenient and allows you to select the optimal parameters much faster.
The program is absolutely free, you can download the latest version from the AMD website. It works in two modes - simple and advanced. In addition to the “overclocking” options, it also contains a system information module (table, complete list or diagram), a performance and stability test. Overdrive also has the ability to control fans, but it only works if the Smart Fan option is enabled in the BIOS and allows you to slow down the rotation speed to 25% of the nominal value.
When working in simple mode, the entire overclocking is limited to one single slider, the minimum of which corresponds to the default settings, and the maximum in our case raised the processor multiplier from 15 to 16, which provided an overclocking of 6.7%. It’s not at all thick, but it’s safe and within the capabilities of even the youngest gamer. As an alternative to the slider, there is a function to automatically determine the maximum frequency, after launching which AMD Overdrive will begin to slowly, one megahertz at a time, accelerate the clock generator and check the stability of the result. The current version of the program does not consider it necessary to lower the multiplier that sets the RAM frequency during tests, as a result of which the automation very quickly reports about the limit reached, without realizing the possibility of raising the processor multiplier by at least 0.5. Well, that’s why it’s automatic; you shouldn’t expect any miracles from it.
Much more interesting is the advanced mode, with a huge number of manual settings, including a full set of RAM timings. And everything would be fine, if not for one thing - for some unknown reason, the program incorrectly set the PCI Express bus frequency, increasing its value to 142 MHz (standard - 100 MHz). Manual adjustment and reduction did not correct the problem; the frequency itself continued to jump to such a greatly inflated value. In the end, it all ended with a “blue screen of death” and the program being uninstalled through safe mode. We hope that this is atypical behavior of the utility and in most cases it works more accurately and more stable. Overclocking a Radeon 4890 video card
As was said at the very beginning of this material, we received a non-sale sample of this video card for testing, built on the RV790 chip and operating at frequencies of 850/975 MHz for the core and memory, respectively. Since HIS is not shy about releasing these accelerators with a chip frequency of 900 MHz, we had no doubt about their performance under such conditions. It was interesting to find the limit at which the reference cooling system could no longer cope with its direct responsibility.
Overclocking was carried out using the Catalyst 9.5 driver, through the Overdrive utility included in it. There is also an auto-tuning feature here, but she stated that 865/975 is the limit for this video card. Of course, we didn’t believe her :). A gradual increase in core and memory frequencies followed by stability testing made it possible to overclock the Radeon 4890 to the level of 950/1150 MHz for the core and memory, respectively. The fan speed was manually set to 50%; when the speed was increased to maximum, only the frequencies 955/1155 MHz became stable, but the howling was so unbearable that we decided to sacrifice this minor increase.
Note that many manufacturers of video cards based on the chip in question are preparing to release (or are already releasing) accelerators with an alternative cooling system, capable of operating out of the box at a core frequency of 1000 MHz. AMD Fusion For Gaming 1.0
This is a relatively new utility from AMD, the essence of which is to activate processor and video card overclocking profiles made in AMD Overdrive and Catalyst Overdrive; enabling AMD Boost technology; speeding up the hard drive by turning off energy-saving and noise-reducing technologies; as well as stopping services and programs running on the PC in order to free up RAM.
The use of this software can lead to unstable operation of the system and a decrease in the level of security, so it is most logical to limit Internet access before turning on AMD Fusion For Gaming.
Here, as in AMD Overdrive, there are two operating modes - simple (single-button) and advanced, but also not difficult to master. The program has 3 performance profiles built-in, the simplest of which only stops some services that are in low demand, while the extreme one turns off everything that is possible and overclocks everything that it can.
You cannot edit built-in profiles, but you can create your own from a set of available items. For the test, we created our own profile, including all components, with the exception of AMD Overdrive.
The profile takes quite a long time to apply, about one minute. The reverse process takes about three times less time. The most noticeable result of stopping all services available in the list was the freeing of 150MB of RAM. Considering the extremely low cost of 2GB DDR2 sticks, the price for reducing stability and security is, frankly speaking, unjustified. But for sports interest it is quite suitable.
Now that the maximum speed of the system has been achieved (within the framework of the tools and methods discussed in this article, of course), all tests, including an expanded set of HWBot.org recommendations, were repeated.
| AMD Phenom II X4 940 Black Edition, 3775 MHz, CPU NB 2448 MHz, GPU OC, Boost | |
| WinRAR 3.71, c | 49 |
| 7-Zip 4.57, c | 126 |
| x264 v0.59.819M, fps (1pass/2pass) | 81.02 / 21.93 |
| 3DMark Vantage, 3DMark Score (CPU Score) | P11404 (12645) |
| PCMark Vantage, PCMarks | 5683 |
| 3DMark 2006, 3DMark Score (CPU Score) | 18411 |
| Hexus PiFast, c | 24.20 |
| SuperPi 1M, s | 18.486 |
| wPrime, c | 38.267 |
To present the data obtained in a more convenient form for comparison, the following diagram was constructed:
At the same time, we are inclined to attribute the lower performance in the PCMark Vantage test to shortcomings in the algorithms and logic of the program itself, for which many complaints can be found on the Internet. Otherwise, the performance gains are quite decent, taking into account the use of an air cooling system and the fact that the AMD Phenom II X4 940 was recently the company’s top processor.
Note that the test power supply passed all the tests placed on it with honor, providing stable power supply during all even the most difficult tests. During testing, the voltage values along the +12VDC and +5VDC channels were monitored by TRMS multimeters UT-71B; deviations along these lines did not exceed two percent of the nominal value, which can only be assessed positively.
We thank AMD and Corsair for providing the equipment