What is the difference between Intel i3, i5, i7 and i9 processors
Let's now look at the main differences between i3, i5, i7 and i9 processors. These are the processors we typically deal with today.
- i3 processors are entry-level dual-core processors. So this assumes having two processors on one chip. i3 processors have Hyper-Threading for efficient processing.
- i5 processors come with two (Dual Core) as well as four cores (Quad Core). These processors feature Intel Turbo-Boost Technology, which allows the cores to run faster than their operating frequency when needed. This process is also known as overclocking.
- i7 processors have two (Dual Core) or four cores (Quad Core) and are equipped with Hyper-Threading and Turbo-Boost technologies.
- Core i9 processors support Intel Thermal Velocity Boost for +100 MHz Turbo . High class i9 processors are suitable for high-performance gaming games. These laptops feature Musclebook, a new name for similar DTR devices.
So, an initial look at the three levels shows that the i9 processor is better than the i7 processor, and the i5 processor is more efficient than the i3 processor.
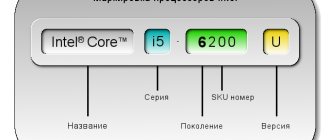
Now let's look at the numbering and letters that are found on each processor.
How to find out what generation an Intel processor belongs to
For example, you have a Core i7-8650U processor and a Core i5-6200U processor. The first number represents the generation. So the i7 processor is 8th generation and the i5 processor is 6th generation in this example.
Naturally, the higher the number, the later the generation.
6th generation processors appeared in 2020. But today there are already 10th generation .
The next part in the notation is a three-digit number, 650 and 200 respectively.
SKU (stock keeping unit) number Or more clearly: model number.
The model number is followed by a letter. In our example, this is U. Letter designations distinguish one processor from others in the same generation.
Intel uses different letters for each processor. They represent a category of computer systems for which the processor is ideally suited. What do these letters stand for?
| 10th generation i5 processors | ||
| Suffix | Indicates | Examples |
| U | Ultra-low power consumption | 10210U |
| Y | Ultra low power consumption | 10310Y, 10210Y |
| G | Processor with discrete graphics chip | 1035G4, 1035G7, 1035G1, |
The G suffix is followed by numbers from 1 to 7, indicating the level of graphics. The higher the number, the better the graphics.
| 9th generation i5 processors | ||
| Suffix | Indicates | Examples |
| T | Processor with reduced power consumption and heat dissipation | 9400T, 9600T, 9500T, 9900T |
| N | High-Performance Graphics | 9300N, 9400N, |
| TO | Possibility of overclocking the processor (increasing the processor clock frequency) | 9600K, 9900K |
| F | Processor without integrated graphics, discrete graphics card required | 9900F |
| S | Performance optimized processors | 9900S |
| 8th generation i5 processors | ||
| Suffix | Indicates | Examples |
| U | Ultra-low power consumption | 8265U, 8295U, 8296U |
| Y | Ultra low power consumption | 8200Y, |
| T | Processor with reduced power consumption and heat dissipation | 8400T, |
| H | High-Performance Graphics | 8300H, |
| IN | No description | 8400B, 8500B |
| G | Discrete graphics on packaging | 8305G |
We focused on the 8th, 9th and 10th generation i5 processors, so we'll compare these three generations. This will help you buy the right model as per your requirements.
Fifth generation (2015, Broadwell)
As part of the fifth generation Intel Core i5, mass-produced Intel desktop processors were not released. The line was actually a transitional stage, and the chips were the same Haswell, but transferred to a new 14 nm process technology. There were only 3 quad-core models in the series: i5-5575R, 5675C and 5675R .
© AnandTech
All desktop i5-5xxx had an improved Iris Pro graphics processor, 128 MB of eDRAM memory. Models with the R index were also soldered onto a board and sold only as part of finished computers. The i5-5675C, in contrast, was installed in a regular 1150 socket and was compatible with older boards.
Difference between 8th, 9th and 10th generation Intel i5 processors
While you may not see much difference in quality between the 8th generation i5 and 9th generation i5 processors, the 10th generation processors are in a class of their own.
The 10th Gen Processor is an Ice Lake 10Nm Processor, Whereas the 8th and 9th Gen Processors are 14Nm Sky Lake Processors.
The Sky Lake chip was introduced in 2020 as a 6th generation processor. So the 7th, 8th and 9th (all of which are 14nm Sky Lake processors) are upgraded versions of the 6th generation with some incremental improvements.
Read: Intel Core i3 vs i5 processors: Compare and choose the best
The 8th generation processors offer the full range of processors, while the 9th generation offers only high-end processors.
Although 10th Generation Processors Do Not Provide High-Performance Graphics, They Are Significantly Faster Than Previous Generations.
Let's now compare the 8th, 9th and 10th generation i5 processors and understand the difference.
Parameters for comparison:
When comparing 8th, 9th and 10th generation processors, we will only look at the main features without going into technical details.
Lithography
Lithography is a semiconductor technology used to make a processor. Denoted in nanometer (nm). The lower the number, the more compact and energy efficient your processor is.
Processor cores
Core, a hardware term, refers to the number of independent central processing units on a chip.
Threads
The software term Threads refers to a sequence of functions that can be processed by a single CPU core.
Base frequency
This is the operating frequency of the CPU processing time. Measured in GHz.
Maximum turbo frequency
This is the maximum single-core frequency at which the processor can operate using Turbo Boost and Thermal Velocity technologies (if available).
CPU Cache
CPU Cache is an area of fast memory located on the processor.
Using these critical parameters, we will now compare four processors, each of the 8th, 9th and 10th generation processors.
Read: Which processor is better Intel or AMD? Compare and choose
| 8th generation i5 processors | |||||||||||
| Model | 8265U | 8400T | 8300H | 8269U | |||||||
| Lithography | 14 nm | 14 nm | 14 nm | 14 nm | |||||||
| Number of cores | 4 | 6 | 4 | 4 | |||||||
| Threads | 8 | 6 | 8 | 8 | |||||||
| Base frequency | 1.60 GHz | 1.70 GHz | 2.30 GHz | 2.60 GHz | |||||||
| Maximum turbo frequency | 3.90 GHz | 3.30 GHz | 4.00 GHz | 4.20 GHz | |||||||
| Cache | 6 MB | 9 MB | 8 MB | 6 MB | |||||||
| Memory | 64 GB | 128 GB | 64 GB | 32 GB | |||||||
| Integrated video chip | Intel UHD Graphics 620 | Intel UHD Graphics 630 | Intel UHD Graphics 630 | Intel Iris Plus Graphics 655 | |||||||
| 9th generation i5 processors | |||||||||||
| model | 9600 | 9400T | 9500T | 9300H | |||||||
| Lithography | 14 nm | 14 nm | 14 nm | 14 nm | |||||||
| Number of cores | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | |||||||
| Threads | 6 | 6 | 6 | 8 | |||||||
| Base frequency | 3.10 GHz | 1.80 GHz | 2.20 GHz | 2.40 GHz | |||||||
| Maximum turbo frequency | 4.60 GHz | 3.40 GHz | 3.70 GHz | 4.10 GHz | |||||||
| Cache | 9 MB | 9 MB | 9 MB | 8 MB | |||||||
| Memory | 128 GB | 128 GB | 128 GB | 128 GB | |||||||
| Integrated video chip | Intel UHD Graphics 630 | Intel UHD Graphics 630 | Intel UHD Graphics 630 | Intel UHD Graphics 630 | |||||||
| 10th generation i5 processors | |||||||||||
| model | 10210U | 10310Y | 1035G7 | 1035G1 | |||||||
| Lithography | 14 nm | 14 nm | 10 nm | 10 nm | |||||||
| Number of cores | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |||||||
| Threads | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |||||||
| Base frequency | 1.60 GHz | 1.10 GHz | 1.20 GHz | 1.00 GHz | |||||||
| Maximum turbo frequency | 4.20 GHz | 4.10 GHz | 3.70 GHz | 3.60 GHz | |||||||
| Cache | 6 MB | 6 MB | 6 MB | 6 MB | |||||||
| Memory | 64 GB | 16 GB | 64 GB | 64 GB | |||||||
| Integrated video chip | Intel UHD Graphics | Intel UHD Graphics | Intel Iris Plus Graphics | Intel UHD Graphics | |||||||
Sixth Generation (2015, Skylake)
The sixth generation has become a full update to the Intel Core i5 processor line. Chips with Skylake architecture were produced using a 14 nm process technology and had 4 cores. Processor model numbers range from i5-6400 to 6600K , all CPUs are quad-core.
© Phoronix
The new architecture did not provide a big performance increase, but the chips had a number of changes. Firstly, they were installed in the new socket 1151, and secondly, they received a combined DDR3/DDR4 memory controller.
In the sixth generation, chips with Iris Pro graphics were also released - i5-6585R and 6685R . They still allow you to run modern games (even at low graphics settings) and remain relevant. Due to the BGA connector, CPUs with the R index were not sold separately, only as part of finished PCs.
Comparison of 8th generation and 9th generation Intel i5 processors
If you compare the 8th and 9th generation i5 processors, there are few differences, with the exception of clock speeds, especially in the i5 9600 with a base processor frequency of 3.10 GHz.
Thus, 9th generation processors are comparatively faster than their 8th generation counterparts.
However, if you include 9th generation processors, the difference in clock speed will be barely noticeable. As for prices, 8th generation processors may be cheaper.
10th generation Intel i5 processors
When it comes to comparing 10th generation processors, they are in a class by themselves. If you compare the main characteristics of 9th and 10th generation processors, there will be little difference between them.
However, when it comes to advanced features, the 10th generation processors are ahead.
- 10th Gen processors feature Intel Iris Plus
- These processors feature 2.5x faster AI, 3x wireless speeds, and 2x graphics performance.
- 10th Gen processors deliver faster wireless speeds as they feature WiFi 6 (Gig+) technology and the most versatile and fastest port possible thanks to Thunderbolt 3 technology.
Why is the 10th generation Intel i5 processor better?
Here are a few reasons why 10th generation i5 processors are preferable to previous generations.
New process
Lithography is seeing a huge shift with Intel's 10th generation processors moving to 10nm from the previous 14nm process.
Intel's chip architecture has been based on the 14nm process since the introduction of sixth-generation Sky Lake processors in 2015.
The highlight of the 10th generation processors are the 10nm Ice Lake chips.
Read: How to choose a good laptop and which one to buy? Buying Guide
Faster processes
Intel's 10th generation processors feature Sunny Cove cores, which are significantly faster than the previous generation cores.
Intel estimates that these cores increase IPC (instructions per clock) by about 18%.
Additionally, these cores come with Dynamic Tuning 2.0 to control the Turbo Boost capability. So you get better performance even though these chips run at slightly lower clock speeds compared to the 9th generation chips.
Highly advanced features
Integrated graphics have been in CPUs since the 2nd generation Sandy Bridge processors.
If that was a landmark introduction, then Thunderbolt 3 in 10th generation chips is the next big integration.
Certain high-end laptops offered Thunderbolt 3 support using a Thunderbolt 3 controller.
However, 10th generation Intel chips get Thunderbolt 3 as a built-in feature. This could lead to lower costs for PC manufacturers, as well as more space inside laptops.
Another positive aspect of the 10th generation processors is that all laptops will have WiFi 6 compatibility.
It was previously known as 802.11ax. The advantage is that it offers much faster speeds at 2.4GHz and can also handle multiple devices simultaneously.
It is also compatible with 5 GHz operating frequency. Thus, people who have a WiFi 6 router at home will benefit greatly.
Large memory and high speeds
10th generation Intel processors support LPDDR4X RAM. The immediate benefit is that it provides almost 50% more memory bandwidth.
This way the games will become more improved. Professionals in the video editing industry welcome this valuable addition of memory to their systems.
Today, 8th and 9th generation processors support LPDDR3 RAM. The maximum memory capacity is 16 GB. Now this amount of memory should be more than enough for the average user.
However, LPDDR4X opens up new possibilities for video editors and avid gamers.
Gamers will love the 10th Gen Intel processor
Gamers are still unhappy with the capabilities of Intel Integrated Graphics. With the arrival of new Gen11 graphics in 10th generation processors, they have a reason to rejoice.
1080p gaming experiences . VESA Adaptive-Sync support makes it doubly enjoyable for the avid gamer.
Read: Lenovo laptop: How to choose and which one to buy?
Now gamers won't need onboard DRAM to get better graphics performance. Intel claims that its Gen11 graphics can perform better than Iris Plus graphics even without the use of e-DRAM.
Eighth generation (2017, Coffee Lake)
After numerous “+5% again” (the magnitude of the increase is eloquently evidenced by the fact that the overclocked Core i5-2500K of 2011 is almost as good as any i5-7500 of 2011) in the eighth generation of Intel, progress has moved forward. This was facilitated by competition from AMD.
Intel Core i5 processors based on Coffee Lake architecture are manufactured using the already familiar 14 nm process technology, are minimally architecturally different from Skylake and Kaby Lake, and have approximately the same performance per core. However, increasing the number of cores from 4 to 6 increased their performance up to 1.5 times compared to their predecessors. The series released chips with names in the format i5-8xxx, and numbers from 8400 to 8600K .
© Overclockers
Despite the fact that the chip socket remains the same (1151), this is a new version of the socket and is not compatible with boards of previous generations Intel Core i5 8xxx series. This fact does not allow you to upgrade a computer on a conventional i3-6100 or i5-6400 by replacing the CPU with a new six-core one.
At the time of writing, the most modern are the eighth generation Intel Core i5, although the sixth and seventh are also relevant. However, the ninth generation is approaching, codenamed Cannon Lake architecture. By the beginning of 2020, at least 3 models will go on sale: i5-9400 , 9500 and 9600K .
You shouldn't expect anything revolutionary from them. As with Skylake and Kaby Lake, the new generation is just a cosmetic improvement of the previous one (Coffee Lake), which, in turn, was also not new. Thus, all Intel Core i5 from the 6th to the 9th generation differ from each other only in the number of cores, frequencies and socket.