The processor is the heart of the computer, and its good “well-being” should be constantly monitored. Sometimes you need to find out the clock frequency of the processor - not the one that the developers write on the boxes, but the real one. It is worth taking this issue seriously and familiarizing yourself with the necessary information so as not to be deceived.
Articles on the topic “How to find out the processor frequency?”
- How to change the mac address of a computer's network card in Windows XP and 7?
- How to find out if the system is 32 or 64 bit?
- How to find out your/someone else's computer IP address?
- How to find out the MAC address of a computer's network card in Windows 7 and XP?
Using the CMOS Setup utility
Required OS and software
This method does not even require an installed operating system (convenient when you bought a brand new “clean” computer).
Instructions
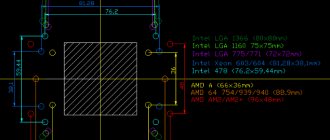
1)When turning on the device, press the Delete or F2 button, depending on the motherboard model (usually at startup you will be prompted about which button to press).
2) In the menu that appears, enter the “Frequency/Voltage Control” section. The open window will list the characteristics of all the main elements of the system unit. There you will also find the processor frequency.
Adviсe
Some of the values can be changed, but this should not be done unless you are an experienced hardware specialist or are familiar with the necessary technical information.
How to overclock a processor and check its stability
Our site is becoming more and more famous and popular, more and more often people who have no idea about overclocking look at it. Therefore, more and more often I receive letters with approximately the following content: “I have a XXX mother, a YYY processor, a ZZZ video card. How can I disperse all this? I get confused every time I receive letters like this. We all once drove for the first time and there is nothing shameful in ignorance, but how to respond to such a letter? If you answer in a nutshell, then a person will not understand anything. If you answer in detail, then a whole day will not be enough. To rid myself of doubts and emails that are almost impossible to answer, I decided to recall the basic principles of successful overclocking.
The most important thing is information. Changing something at random is as pointless as randomly tapping on the keyboard in the hope of getting coherent text. To begin, collect all possible information about what you will have to work with. Get out the dusty manual for the motherboard and find out its capabilities. It’s a good idea to update the BIOS before overclocking and make sure that the mother is still working reliably. Take a look at our Overclocking Statistics and find out the theoretical capabilities of your processor. Our FAQ on overclocking is a little outdated, but still relevant. They continue to overclock by changing the multiplication factor and increasing the bus frequency, and the latter is increasingly being chosen. Before you start overclocking, switch the system to the most gentle operating mode. You can load Fail Safe Options into the BIOS. Remove overclocking from the video card and memory, if any. Set the memory timings to the slowest possible so that nothing interferes with overclocking the processor. Take care of cooling: fresh thermal paste or an additional fan will not be superfluous.
There are two opposing approaches to overclocking a processor: overclocking from maximum and from minimum, the second being safer, but the first being faster. In the first case, having learned the theoretical overclocking limit of your processor, you immediately set the maximum reasonable voltage and bus frequency. You check the performance and if everything works stably (which is unlikely), then increase the frequency, and if not, then reduce it until the system starts working normally. This overclocking option is relatively fast and allows you to achieve the highest possible frequency for your system. The downside is that without proper planning, you can easily destroy the operating system, even burn the mother, the processor, or both. Although not only for me personally, but also for my friends, nothing like this has ever happened, but it’s better to warn, in case it works out for you :o).
For beginners, the second option is easier and safer: gradually increase the frequency, testing for stability after each change. In this case, it is almost impossible to burn something, because at the first failure you roll back several positions and as a result get a reliably working overclocked system. There is no need to get too carried away with raising the voltage, since excessive voltage leads to overheating. But a slight increase in voltage will not cause damage, but will increase reliability.
After you have figured out the processor, you can increase the overall performance of the system. Adjusting BIOS settings, reducing timings and increasing memory frequency can give a serious improvement in performance. The only request is not to change several parameters at the same time. Changed - check the speed and reliability, only then continue. This way you won't have to guess why problems occur.
We have not considered another very important issue: how to test an overclocked system. There are many programs specifically designed for this. The operating principle of not all, but many: the processor calculates some complex mathematical expression and the resulting result is compared with a previously known one. If they match, then everything is in order and the cycle repeats again. If they differ, an error message is displayed. I have posted several similar programs in the Files
, but not so that you use them, but to make sure that they are almost useless :o). Not once, on any processor, not a single program gave me an error message, although the processor was clearly overclocked. No, they fell out on their own, the computer went to reboot, but in order to give me a message: “Bro, you got excited, turn down the frequency!” - not even once. Maybe I just didn’t have the patience to wait for this message - most programs promise to detect overclocking only after several hours, or even days of testing :o(.
Some recommend creating an archive file of two gigabytes, when the processor has not yet been overclocked, and then testing this archive and if errors appear, then reduce the frequency. Try it, but it didn't work for me.
Many people suggest testing in games. Indeed, the game loads the entire system, the processor, video, and memory. Then testing in games is much more interesting than looking at changing numbers in some program specially designed for testing processors. If you’re tired, you can choose some game where the demo or screensaver automatically scrolls, Unreal, for example, and leave it overnight, let it spin. For the same purpose, you can make a set of tests or a demo run in a loop in 3DMark - it also helps.
Programs from the Burn series have also helped me out several times: BurnP6 or BurnK7. They also force the processor to constantly count something in a loop. It works continuously, gets very hot, and if the program crashes, then either the processor is overclocked or it is not cooled well, which is the same thing :o).
announcements and advertising
2080 Super Gigabyte Gaming OC for 60 rubles.
Compeo.ru - the right comp store without any tricks
RTX 2060 becomes cheaper before the arrival of 3xxx
Ryzen 4000
series included in computers already in Citylink
The price of MSI RTX 2070 has collapsed after the announcement of RTX 3xxx
Core i9 10 series is half the price of the same 9 series
The price of memory has been halved in Regard - it’s more expensive everywhere
In a word, you understand what I’m getting at – there is no universal remedy. Hence the corollary: you need to test in those programs and games that you constantly use. What is the benefit to you from the fact that the test program says that the processor is overclocked if everything works great for you? No! And vice versa, if the program says that everything is fine, but your games are crashing, then maybe try reducing the overclocking?
My overclocked Celeron worked wonderfully until Diablo II came along. The game kept crashing and I blamed the damned pirates, but it turned out that my friend’s game from the same discs was absolutely stable. I reduced the overclock and the problems disappeared. Please note that all other programs and games worked perfectly. Another example is closer to today. The speed of the game Sid Meier's Civilization III is very dependent on the power of the computer. I found a point in the game where it would 100% throw an error if my Athlon was overclocked. Delighted that I had found such a trouble-free test, I brought a recording of the saved game to another system, but it turned out that the overclocked P4 didn’t even falter in this place, but crashed on another. I don’t know what this depends on, the processor, the motherboard, or both, but so far I have not found a universal test.
Thus, if all your favorite programs or games work without failures with an overclocked processor, then the overclocking is within normal limits. If errors constantly occur, then it’s easier to reduce the frequency a little in order to work calmly. Naturally, you first need to make sure that no failures occur with the processor operating in nominal mode, otherwise it may turn out that the failures are caused by errors in the game or program itself. I wrote all the time about processors, but you can also check overclocked memory or video card. Good luck with overclocking!
Required OS and software
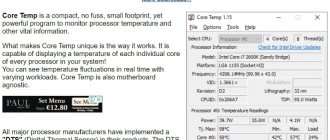
Owners of the Windows XP and Windows 7 operating systems can download and install the CPU-Z program completely free of charge. It is especially convenient to use the application on laptops, where the clock frequency can change dynamically.
Instructions
Launch the program window along with other applications and monitor all changes in real time.
How the speed of a computer and laptop depends on the clock frequency
The processor frequency is responsible for the number of clock cycles a computer can execute in one second, which in turn reflects performance. However, do not forget that different architectures use different numbers of clock cycles to solve one problem. That is, “measuring by indicators” is relevant within at least one class of processors.
What is affected by the clock speed of a single-core processor in a computer and laptop?
Single-core CPUs are rarely found in nature anymore. But you can use them as an example. One processor core contains at least an arithmetic-logical unit, a set of registers, a couple of cache levels and a coprocessor.
Lithography layout for placement on the CPU. The frequency with which all these components perform their tasks directly affects the overall performance of the CPU. But, again, with a relatively similar architecture and command execution mechanism.
What is affected by the number of cores in a laptop?
The CPU cores do not add up. That is, if 4 cores operate at 2 GHz, this does not mean that their total value is 8 GHz. Because tasks in multi-core architectures are executed in parallel. That is, a certain set of commands is distributed to the cores in parts, and after each execution a common response is generated.
Each core is a separate CPU. Thus, a certain task can be completed faster. The whole problem is that not all software can work with multiple threads at the same time. That is, until now, most applications, in fact, use only one core. There are, of course, mechanisms at the operating system level that can parallelize tasks across different cores, for example, one application loads one core, another loads a second, etc. But this also requires system resources. But in general, optimized programs and games perform much better on multi-core systems.
Using Windows XP (Windows 7) elements
Required OS and software
As the name suggests, this method will work on Windows XP and Windows 7.
Instructions
1) In the “Start” menu, right-click on the “My Computer” icon.
2) In the open window there is a “Properties” button, after which you need to go to the “Hardware” tab, and then to the “Device Manager”. You will see a list of all the hardware of the system unit. Select the “Processors” item, where there is all the information about your model.
Adviсe
In Windows 7, it is not necessary to complete all steps. The Properties menu reveals a lot of information about your computer.