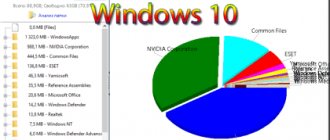
Often, Windows 10 users, after installing the system, are faced with the fact that it does not work fast enough. This can be caused by a number of reasons, but the main one is that the hardware is too weak for the OS. However, the problem can be solved. To do this, you need to configure the system so that it consumes less computer resources.
Setting up Windows 10
A little about performance
Here are the main ways to make Windows 10 run faster:
- remove all graphic “decorations” of the system;
- turn off unnecessary applications in “Autorun”;
- increase the amount of virtual memory;
- disable services for sending user information to Microsoft and displaying advertising.
There is another way. This is installing a solid state drive, or SSD.
In addition, Windows 10 has a number of services that are completely unnecessary for the average user. This is, for example, a Microsoft store that updates programs without the user’s permission. It's better to turn them off too.
Microsoft Store on Windows 10
Restoring GRUB after installing Windows 10
If you had any version of Linux on your computer before installing Windows 10, the GRUB boot loader was installed with it, which can be used as an operating system manager. With its help, you can select which OS will boot at a given time. Unfortunately, any version of Windows removes GRUB upon installation and blocks access to the Linux operating system. With these simple instructions, you can reinstall GRUB and make Windows and Linux work together:
- Download and deploy the Linux LiveCD image to removable media (CD or flash drive).
- Boot from removable media.
- Open a terminal window by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T and perform the following operations in it:
- Use sudo fdisk -l to display the partition structure. You will need it to find out which partitions belong to Windows 10 and which belong to Linux;
The command sudo fdisk -l will display a list of hard disk partitions
- mount partitions belonging to Linux to restore the GRUB bootloader. Enter the command sudo mount /dev/sda5 /mnt;
- write GRUB to the boot area by running sudo grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sda;
Write the GRUB boot loader to the boot sector of the disk
- restart your computer using sudo reboot.
Create a restore point
Now that you've almost finished setting up your new Windows, it's a good idea to save your progress so that if something goes wrong, your hard work won't be lost without a trace. To do this, we will create a Windows restore point and configure the system so that it periodically creates such points itself.
To do this, click the "Start" button and type "Control Panel", and then go to "System and Security" → "System". Open System Protection in the left panel. Click "Recovery Options", enable the creation of restore points and specify how much space you want to allocate for them.
Then select “Create” below. Enter a description of the restore point so you can easily locate it if necessary, and wait until it is created. Ready. Now, if something goes wrong with your system, you can easily restore it.
Action No. 5: Disable unused services
Running services are processes connecting devices in a computer with an operating system. They work in the background. Unfortunately, often some services work even when there is no device to be associated with the system. Of course, all such services create additional load on your Windows 10 computer. Below we provide a list of services that any user can turn off:
- To get to the menu where all services are located, go to “ Start ”. Next, go to the very bottom and click “ Windows Administrative Tools ” from the list that appears, select “ Services ”. Or simply enter the word “ Services ” into the search.
- A window will pop up in which you can select an unnecessary service by double-clicking on it. A window will pop up, click next to the line “ Startup type ” and select “ Disabled ”. Don’t forget to click “ Apply ” at the bottom. In this way, disable all unnecessary services. After completing the procedure, reboot the laptop.
Who is tired of constantly entering a password when turning on the laptop, see: how to remove the password on Windows 10.
Configuring Windows 7 startup (msconfig)
26.11.2009 22:52
System Setup is a diagnostic tool designed to customize Windows 7 startup settings in order to identify the causes of problems with your computer and operating system. Using the System Configuration program, you can identify drivers, programs and components that, due to incorrect operation, cause errors during the startup and operation of Windows 7.
- Launching the System Configuration Program
- Are common
- Download Advanced Options
Launching the System Configuration Program
To launch System Setup, open the Start menu, type msconfig in the search box, and press Enter.
You can also use the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut, type msconfig and click OK.
Top
General tab
On the General tab, you can choose one of three options for starting the operating system:
Normal launch
In this mode, Windows 7 starts in the normal way. “Normal startup” is used when there are no problems loading the OS or after troubleshooting.
Diagnostic run
In diagnostic startup mode, only the basic services and drivers necessary for the functioning of the operating system and computer are launched along with Windows. If the problem does not disappear when diagnostic startup is enabled, then most likely the main Windows files and drivers are damaged. If there are no problems with diagnostic startup enabled, then you need to use the Selective startup mode.
Selective launch
In this mode, Windows 7 starts using basic services and drivers, as well as other services and automatically loaded programs selected by the user. Three additional options are available:
- Load system services – if this option is enabled, the operating system boots with a standard set of services necessary for its operation.
- Load startup items – if this option is enabled, then programs marked with checkboxes on the Startup tab are launched along with the operating system.
- Use original boot configuration – This option is enabled by default and grayed out. This option restores the original Windows 7 startup settings if changes are made on the Boot tab.
Selective startup should be used if the diagnostic startup passed without errors. Turn on additional services and programs one by one, and monitor the system until you identify the cause of the errors.
Top
Loading tab
The Boot tab contains detailed settings for Windows 7 startup options.
Default operating system
If you have multiple operating systems installed on your computer, you can designate any of them as the default boot one. To do this, highlight the desired operating system and click the Set as default button.
You can also set a custom delay time for the multiboot menu by setting the time in seconds in the Timeout field.
To remove an operating system from the list, select it and click the Remove button.
Safe mode
Safe mode is a mode of operation of the operating system with a limited set of services, devices and drivers necessary for the functioning of the computer.
Windows services that start in safe mode:
- Windows Event Log
- Plug and Play device support
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- Cryptography Services
- Windows Defender
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Devices and drivers that run in safe mode:
- Internal hard drives (ATA, SATA, SCSI)
- External hard drives (USB)
- Floppy drives (internal and USB)
- Internal CD and DVD drives (ATA, SCSI)
- External USB drives for CDs and DVDs
- Keyboards and mice (USB, PS/2, serial port)
- VGA video cards (PCI, AGP)
Check the Safe Mode box and select one of the boot options:
Minimum - launch Windows 7 Explorer in safe mode using only basic Windows devices, drivers and services, without network support.
Another shell - loading the command line, basic devices, drivers and services of Windows 7. Explorer and network components are disabled.
Active Directory Recovery - Start Windows 7 Explorer in Safe Mode using only essential services, devices and drivers, and the Active Directory directory service.
Network—Start Windows 7 Explorer in Safe Mode using only the core operating system components, as well as the following network components:
- Network adapters (wired Ethernet and wireless 802.11x)
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP
- DNS
- Network connections
- NetBIOS support module over TCP/IP
- Windows Firewall
You can also enable the following features on the Download tab:
Without GUI - Windows 7 boot animation is disabled.
Boot log - all information about the Windows 7 boot process is saved to the file %SystemRoot%/Ntbtlog.txt.
Basic Video - Loads standard VGA drivers instead of drivers specific to the video card.
OS Information - When Windows 7 boots, the names of the drivers being loaded are displayed.
Make these boot options permanent – If this option is enabled, system settings you change can only be undone manually. You cannot undo changes by selecting Normal Startup on the General tab. You also won't be able to undo changes using the Use original boot configuration option on the General tab.
Top
Additional boot options
To configure advanced boot options for Windows 7, on the Boot tab, click Advanced Options.
Number of processors
This setting allows you to limit the number of both real and virtual processors used in the system. Select the checkbox and use the drop-down list to specify the number of processors that you want to use starting from the next system startup.
Maximum memory capacity
This setting allows you to limit the amount of physical RAM used by the operating system. Select the checkbox and in the text field specify the maximum amount of RAM (in megabytes) that will be used by the system starting from the next startup.
PCI blocking
If this setting is enabled, the operating system does not allocate I/O and interrupt resources on the PCI bus. In this case, the I/O and memory resources specified in the BIOS are preserved.
Debugging
When enabled, you can set global kernel-mode debugging options for device driver developers.
Top
Services Tab
The Services tab contains a list of services that start automatically when Windows 7 boots. All these services are divided into two categories:
- Microsoft services on which the operating system depends;
- Third-party services required for the operation of drivers and some programs.
When identifying the causes of problems that occur during startup or operation of Windows 7, you need to follow these steps:
1. On the General tab:
- Enable Selective startup.
- Select the Load system services checkbox.
- Clear the Load startup items check box.
2. On the Services tab:
- Select the Hide Microsoft services check box.
- Disable all third party services from running.
3. Restart your computer.
If problems do not occur after a reboot, then the Windows 7 system components are working properly, and the cause of the errors is most likely the incorrect operation of one or more third-party services. To identify which service is causing the failure, enable one service at a time, restart the computer, and monitor the system status.
If your system still experiences errors after disabling third-party services, the underlying operating system components may be damaged. To identify the cause of the errors, follow these steps:
1. Clear the Hide Microsoft services check box.
2. Disable all Microsoft services, then enable them one at a time, restart your computer and monitor the changes until you identify all the services causing the failure.
Top
Startup tab
The Startup tab contains a list of programs that automatically start with Windows 7.
- The Startup Item column displays the name of the program.
- In the Manufacturer column – the program developer.
- The Command column indicates the executable file that runs with the OS, as well as the location of this file.
- The Location column displays the registry key responsible for automatically starting the program with Windows 7.
- The Disabled Date column indicates the date on which startup items that do not start automatically with the operating system were disabled.
If problems arise in Windows 7, you can try to determine the cause of the problem by disabling automatic program launch one by one. To identify which program is causing the crash, turn off the startup of all programs, and then turn on one program at a time, restart the computer and monitor the system status.
To prevent the program from starting with Windows 7, you need to uncheck the box next to its name and click the Apply button.
Top
Service tab
The Tools tab allows you to quickly launch Windows configuration, administration, and diagnostic tools. Select the tool you want and click Launch.
About the program – displays information about the version of Windows 7 installed on the computer.
Changing User Account Control settings - setting up UAC, a Windows 7 security component that prompts you to confirm actions that require administrator rights.
Action Center is the primary place to view alerts and take actions that help keep Windows 7 running smoothly. Action Center lists important messages about computer security and maintenance options that require your attention.
Windows Troubleshooter is a set of tools that automatically fixes some common network, hardware, Internet-related device, and program compatibility problems.
Computer Management - a set of tools for managing hardware, software and network components of Windows 7.
System Information is a Windows 7 feature that displays detailed information about your computer's hardware configuration, components, and software, including drivers.
Event Viewer is a tool for viewing detailed information about important events that occur in the system (for example, programs that do not start properly or updates that are downloaded automatically). This information may be helpful in troubleshooting problems and errors in Windows 7 and installed programs.
Programs is a Windows 7 Programs and Features tool designed to enable or disable Windows 7 components, as well as remove programs or change their configuration.
System properties – basic information about the hardware and operating system. Windows 7 version and activation status, performance index, computer name, domain name, and workgroup settings.
Internet Options – Internet Explorer browser settings.
IP protocol configuration – view and configure the computer’s network address (in the command line).
System Monitor is a powerful diagnostic and performance monitoring tool built into Windows 7.
Resource Monitor is a tool for viewing processor, hard drive, network, and memory usage in real time.
Task Manager - Displays applications, processes and services that are currently running on the computer. You can use it to monitor your computer's performance or stop applications that are not responding. Monitoring the network status and viewing its operating parameters.
Command Prompt is a feature of Windows 7 that provides the ability to enter MS-DOS and other commands without a graphical user interface.
Registry Editor is a tool designed to view and change settings in the system registry, which contains information about the operation of the computer.
Top
Msconfig (“Microsoft System Configuration Utility”) is a tool designed to configure and troubleshoot Windows operating systems. It first appeared in Windows 98 and its purpose was to help users manage OS services. It is also designed to provide control over the health of system components.
Action No. 4: Remove unnecessary applications from startup
When you start your computer, in addition to Windows 10, various applications are launched, even those that you very rarely use. The more different programs are running, the greater the load on the system. As a result, your PC runs slowly and freezes. One option to relieve the load is to remove rarely used applications from startup. To do this you need to do the following:
- Enter " Task Manager ". Either by pressing the keyboard shortcut “ Ctrl – Shift and Esc ”, or simply type “ Task Manager ” into the search.
- At the very top, click on the “ Startup ” section. Here you will see all the utilities that automatically launch when you turn on the computer. Your task is to right-click on the application that you want to remove from startup and select the very first line “ Disable ”.
After this manipulation, disabled utilities will never be automatically loaded again. This means the load on the system will decrease, as a result of which you will see an increase in the performance of your device.
How to enter System Configuration
Next, we will look at the ways in which a user can access the System Configuration utility.
Windows Search
The first way to launch MsConfig is quite simple; to call the utility you need to use “Windows Search”:
- in the “Search” line, click the left mouse button;
- after the cursor appears, enter the command “msconfig” and click “Enter”;
- in the search results window, select and launch the desired application.
Run command
This method involves using the Run window:
- Click on the key combination “Win + R” on the keyboard;
- In the window that appears, in the empty field, enter the command “msconfig” and press “Enter”.
Using the Command Line
The launch option will be considered for Windows 7 and older versions. It should be noted that in versions after “seven” the process of launching the command line looks different.
For Win 7:
- open the “Start” menu;
- then select “All programs”;
- then open “Standard”;
- look for the command line and run it;
- In the console, enter the command “msconfig” and press “Enter”.
For Win 8 and 8.1:
- press the key combination “Win+X” on the keyboard;
- in the context menu select “Command Line”;
- In the console window, enter “msconfig” and press “Enter”.
For Win 10:
- open “Start”;
- In the search bar, enter the command “CMD” and click “Enter”;
- Launch the command line and enter “msconfig”.
Opening from a folder
The method involves launching the configuration utility using an executable file located on the system partition of the hard drive:
- open “Explorer”;
- go to the system disk;
- open the “Windows” folder;
- then go to the “System32” directory;
- and look for the executable file “msconfig.exe”;
- You can enter the name of the program in the search bar of Explorer.
Protect your system with antivirus
Windows 10 comes with Windows Defender built-in, always turned on by default. In addition, if you purchased a computer with a pre-installed operating system, a trial version of some antivirus may also be installed on it.
Windows Defender is a good antivirus, which in most cases is quite enough to protect your home PC. However, it may not be enough to deal with possible online threats if you actively install new software and visit untrusted sites. Luckily, you have the option to choose from a list of the best free antivirus software.
Install updates
This is the first step you should take in the new system. Surely, during the time that your computer was on the counter, Microsoft managed to release many patches and fixes. The accumulated updates can take quite a long time to install, so it’s worth dealing with this right away.
First, make sure your computer is connected to the Internet. Then select the Start menu and go to Settings → Windows Update → Check for updates. Wait while the system installs all available updates.
What is MSConfig?
MSConfig or Microsoft System Configuration is a system utility that controls autostart, loading of Windows services and executable files, as well as various operating system settings.
The msconfig.exe program is present in all operating systems starting from Windows 98. The only exception is Windows 2000, where the software was cut for unknown reasons. But later it could be installed as a separate file. You can find the executable file of the msconfig.exe program in the C:\Windows\System32 directory through Explorer.
Find the desired application in Explorer
Minimum required software package
We will not dwell in detail on which applications must be installed, where to get them, etc., we will not go into detail. A separate material is devoted to this. These include:
- browser - Edge, which replaced Internet Explorer, does not satisfy users' needs, so many instead acquire Chrome, FireFox, Opera and Chromium-based programs (Yandex.Browser);
- multimedia player - almost all players are distributed with built-in codecs, unlike the standard one, they allow you to play streaming video, IPTV, and have a huge range of functions for controlling sound, picture, playback;
- audio player - despite the development of online services for listening to music, no music lover can do without a music player;
- a set of office programs - almost everyone needs a text editor, a spreadsheet processor and a tool for creating presentations - for students and office workers, a free suite of office programs would be an excellent choice;
- readers - to view digital copies of documents, books, periodicals, you will need tools for reading pdf and djvu, and sometimes their editors to make changes and even create such documents;
- a program for downloading files - usually a torrent client;
- fans of social networks should pay attention to tools for downloading music and videos from the Internet;
- functional applications for viewing, cataloging and processing pixel graphics - photos and pictures;
- messenger;
- mail clients, a file manager, a program for creating screenshots and other software are installed individually.
How to create a Windows 10 installation disc
How to permanently or temporarily disable updates in Windows 10
What is better to install 32 or 64 bit version on Windows 10