Hi all! Today we will talk about processor sockets. I will also reveal all the secrets of their types and differences. Let's start with a definition. Processor socket (CPU Socket) is a connector on the motherboard designed for installing CPU cards and central processors.
Before the advent of sockets, manufacturers often offered to solder the processor into the motherboard socket, which caused the cost of the equipment to increase greatly, repairs were many times more expensive, and no one thought about manually upgrading the computer. But with the advent of the “CPU Socket,” the life of PC owners has become easier - from now on, processors (along with cooling) are removed and replaced with socket-compatible equipment. But first things first. Let's start with the features.
Physical differences
The connectors intended for installing central processors, although they have the same purpose, differ in both design and third-party parameters, such as performance. If we take into account the physical difference, then it is worth highlighting the number and type of contacts placed on the socket, and the method of attaching processor coolers.
In simple words, sockets resemble a socket (the number of socket contacts and recesses depends on the “manufacturer” and the country: in Europe - 2 pieces, in the USA and Japan - 3 each), and processors resemble a plug, which must be compatible with the contacts.
For convenience, manufacturers even describe differences in the names of motherboard sockets: as an option, LGA 775 displays the number of contacts (775 pieces) and the type of mounting - without contact pins on the installed processor.
There are no easy solutions
Both products from Intel and AMD do not have a middle ground. You can't just walk into a store and buy cheap components that will be easily upgraded in the coming decades. Here you need to explore the market, study the offers of all manufacturers and find at least some guarantees of timely BIOS updates and support for modern technologies that the motherboard should have. Socket 775 and socket AM3 demonstrate by their example that financial savings are quite possible over the course of a decade. However, not all brands allow you to enjoy this.
The best recommendation for all buyers before buying a computer is to purchase a basic motherboard from a well-known manufacturer that specializes in the production of other components: video cards, tablets, network equipment, phones, etc. And only after choosing the main device can you select a processor, memory and other components, as did the owners of devices on socket 775, processors for which are still in great abundance on the market.
Technological nuances
The connectors suggest the presence of additional controllers, support for integrated graphics, and even describe the possible level of performance. The compatibility of chipsets and the method of equipping the motherboard also depend on the socket. For mid-price segment processors, manufacturers diligently equip motherboards with dual-channel RAM, SATA 3.0 ports with maximum bandwidth, and PCI Express ports. But the “simpler” the socket, the less technology and innovation there is.
LGA775. Platform Features
The Intel Socket 775 processor socket debuted on the computer technology market in 2004. It replaced socket 478. Its key difference from its predecessor is its support for 64-bit computing technology. All previously existing platforms could only process code in 32-bit format. Initially, chips from the Pentium or Celeron lines were installed in this socket in single- or dual-core versions based on an architecture code-named NetBurst. Then this list was supplemented by the first representatives of the Core line based on the new microarchitecture of the same name - these are dual-core 2 Duo and 4-core 2 Quad.
Today, this hardware platform is completely outdated. The latest semiconductor chips within its framework were released in 2010. Now Intel has completely abandoned support for these computing solutions, since they have an extremely low level of performance, which does not allow such CPUs to process complex program code.
Why do you need a socket?
The key purpose of the connectors on the motherboard is to simplify the process of upgrading and installing various parts at home and without special equipment. And we’re not just talking about central processors—video cards, RAM, hard drives, and even case fans work in a similar way. In a global sense, connectors make life easier and allow you to less often turn to specialists for help and more often adjust your computer to changing (professional or entertainment) needs.
LGA 2011
The LGA 2011 socket was released in 2011 after LGA 1155 as a socket for high-end Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge E/EP processors. The socket is designed for six-core processors and all Xenon processors. For home users, the X79 motherboard will be relevant. All other boards are designed for enterprise users and Xenon processors.
In tests, Sandy Bridge-E and Ivy Bridge-E processors show pretty good results: performance is 10-15% higher.
- Haswell-E Core i7 - 5820K, 5930K, 5960X;
- Ivy Bridge-E Core i7 – 4820K, 4930K, 4960X;
- Sandy Bridge-E Core i7 - 3820, 3930K, 3960X, 3970X.
These were all modern intel processor sockets.
Types of AMD sockets
AMD specialists are conservative and rarely resort to frequent socket updates, which is why the sockets are often compatible and eliminate the need to purchase new equipment for a full computer upgrade.
List of released sockets:
- Super Socket 7 . Designed based on a universal socket. Appeared modified and specially adapted for processors with increased computing power.
- Slot A. _ Produced since 1999 specifically for the Athlon, a processor that acted as a catching-up competitor to the Pentium III.
- Socket A (462 ). A new modification aimed at supporting expensive Athlon, budget Duron and Sempron.
- 754. A technological update released for 64-bit Athlons; at the same time, support for working with DDR RAM appeared.
- 939. Socket used since 2004 for server processors;
- AM2 . Produced since 2006. Based on 940 pins, supports DDR memory
- AM2+ . Modification that appeared in 2007. Fully compatible with AM2, supports HyperTransport bus.
- AM3 . Technological replacement of previous generation sockets, supports DDR RAM
- AM3+ . Modification for AMD FX processors based on the Bulldozer architecture - 32 nm technology, intended for servers or expensive and high-performance computers.
- FM1 . 905-pin socket for installing CPUs with AMD Fusion microarchitecture - 64-bit hybrid microprocessors.
- FM2 . Available since 2012 for Piledriver architectures.
- FM2+. A new modification that supports, in addition to Piledriver, also Steamroller.
- AM Since 2014, a socket for the Jaguar architecture has been produced.
- AM Available since 2020, designed for processors based on the ZEN, ZEN+ and ZEN2 architecture. Support for DDR4 standard RAM is declared.
- TR4 and TRX The most current sockets for processors running on the Zen, Zen+ and Zen2 architecture, which appeared in 2017 and 2020. (14, 12 and 7 nm CPUs).
And, although it is difficult to understand the listed items right away, the task is noticeably simplified by the equipment specifications described by the manufacturer. The description of each processor necessarily includes details about compatible (or even partially compatible) sockets.
Mobile processor sockets [ edit | edit code ]
For mobile processors, low-profile versions of connectors are used.
Intel
- Socket 495[en] - since 2000; for Intel Celeron mobile (FC-PGA2) Connector type: PGA-ZIF
- Socket 479 (mPGA479M) - since 2001; 479 contacts (478 used); for Pentium III-M, most common for Pentium M and Celeron M 3xx, also the version is compatible with Socket M (Intel Core Solo, Core Duo, Core 2 Duo and Celeron M 4xx/5xx)
- Socket M (mPGA478MT) - in 2006 to replace Socket 479 for processors of the Core/Core 2 family;
- Socket P (mPGA478MN) - from May 9, 2007 to replace Socket M; for processors of the Core 2 family;
- Socket G1 (rPGA988A) - since 2009 to replace Socket P, for first generation Core family processors
- Socket G2 (rPGA988B) - since 2011 to replace Socket G1, for second generation Core family processors
- Socket G3 (rPGA946) - since 2013 to replace Socket G2, for the third generation Core processor family
AMD
- Socket A (Socket 462)
- Socket 563 - Mobile Athlon XP-M with low power consumption
- Socket 754
- Socket S1 - mobile Athlon 64, Turion 64 and Mobile Sempron
- Socket FS1
- Socket FP2, Socket FP3, Socket FP4
- Socket FT1, Socket FT3
As part of this review, we will consider the most common modifications of Socket Intel processor sockets at the moment. This eminent manufacturer of computer equipment updates its product range with enviable regularity. Therefore, almost every two years he gets a new socket that is incompatible with the previously existing one.
Types of Intel sockets
While AMD specialists are piling up modifications and diligently refusing to release new platforms, Intel is calm about the frequent dynamics of updates. And although this approach causes buyers to often change motherboards for new and improved processors due to physical incompatibility, serious changes and discoveries are taking place in the technology market.
All sockets from Intel:
- Socket 8. Appeared specifically before the release of the powerful sixth generation Pentium Pro processor.
- 370. Released in 1999, designed for Pentium III, Celeron and Cyrix II.
- 423. The legendary connector that gave the world a classic – Pentium
- Designed for Northwood, Prescott, Willamette architecture.
- PAC481 and PAC Developed for Itanium CPU - a joint project between Intel and Hewlett-Packard (more recently - HP);
- J ( LGA771). Designed for server and desktop XEON and Core
- T ( LGA775). A socket that supports an impressive collection of processors, from Pentium to Core 2 Duo. In some educational institutions and office buildings, computers with LGA are still found
- LS ( LGA1567). Introduced in 2010, by 2011 replaced by a more successful modification LGA
- B ( LGA1366). Supports Gulftown microarchitecture, Bloomfield, replaced LGA
- H ( LGA1156). A budget alternative to LGA1366 with dual-channel RAM, but without the usual QuickPath connection (hence the savings).
- H2 ( LGA1155). A technological replacement for Socket H, adapted for processors with Sandy Bridge architecture.
- R( LGA2011). Supports Core i7 and Xeon CPUs, tailored for Broadwell and Haswell cores. Equipped with a bunch of technologies, including QuickPath.
- Socket R3 ( LGA2011-3). Technological replacement for R, introduced in 2014.
- R4 ( LGA2066). Replacement for Socket R3, introduced in 2020 and supporting the latest developments from Intel.
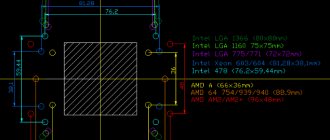
Processor sockets: generations in photographs
A CPU socket is a connector located on the computer motherboard to which the central processor is connected. The processor, before it is installed on the motherboard, must fit the socket. It is very easy to understand what a processor socket is, if you remember that the latter is a microcircuit, only of relatively large size. The socket is located on the motherboard and looks like a low rectangular structure with many holes, the number of which corresponds to the processor legs. To securely fix the inserted microcircuit in the socket, a specially designed mechanical latch is used. Note that Intel, unlike AMD, has recently been using a different principle of connecting the processor and board.Sometimes on forums the question is asked about which socket to choose. In fact, you should first select a processor, and then a board with the appropriate socket for it. However, one important point must be taken into account. because often each new generation of processors involves the use of a new socket. This may lead to the fact that a recently purchased computer based on a processor from this company will be difficult to upgrade in a few years due to the incompatibility of the installed microprocessor and new ones offered on the market. AMD has a more loyal attitude towards customers: changing sockets occurs more slowly, and backward compatibility is usually maintained. Although, times are changing.
| Number of contacts | Year of issue | ||
| PIN DIP | 8086/8088, 65С02 | 40 | 1970 |
| CLCC | Intel 80186, 80286, 80386 | 68 | 1980 |
| PLCC | Intel 80186, 80286, 80386 | 68 | 1980 |
| Socket 80386 | Intel 386 | 132 | 1980 |
| Socket 486/Socket 0 | Intel 486 | 168 | 1980 |
| Motorola 68030 | Motorola 68030, 68LC030 | 128 | 1987 |
| Socket 1 | Intel 486 | 169 | 1989 |
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket 2 | Intel 486 | 238 | 1989 |
| Motorola 68040 | 68040 | 179 | 1990 |
| Socket 3 | Intel 486, 5x86 | 237 | 1991 |
| Socket 4 | Pentium | 273 | 1993 |
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket 5 | Intel 486 | 238 | 1994 |
| Socket 463 NexGen | Nx586 | 463 | 1994 |
| Motorola 68060 | 68060, 68l0C60 | 206 | 1994 |
| Socket 7 | Pentium, AMD K5, K6 | 321 | 1995(Intel), 1998(AMD) |
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket 499 | DEC EV5 21164 | 499 | 1995 |
| Socket 8 | Pentium / Pentium 2 | 387 | 1955 |
| Socket 587 | DEC EV5 21164A | 587 | 1996 |
| Mini-Cartridge | Pentium 2 | 240 | 1997 |
| MMC-1 Mobile Module Connector | Pentium 2, Celeron | 280 | 1997 |
| Apple G3/G4/G5 | G3/G4/G5 | 300 | 1997 |
| MMC-2 Mobile Module Connector | Pentium 2.3, Celeron | 400 | 1998 |
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| G3/G4 ZIF | Power PC G3 G4 | 288 | 1996 |
| Socket 370 | Pentium 3, Celeron, Cyrix, Via C3 | 370 | 1999 |
| Socket A/Socket 462 | AMD Athlon, Duron, MP, Sempron | 462 | 2000 |
| Socket 423 | Pentium 4 | 423 | 2000 |
- Socket 370 is the most common socket for Intel processors. It is with this that the era of dividing Intel processors into inexpensive Celeron solutions with a trimmed cache and Pentium – more expensive full versions of the company’s product – begins. The connector was installed on motherboards with a system bus from 60 to 133 MHz. The socket is made in the form of a square plastic movable box; when installing a processor with 370 contacts, a special plastic lever presses the processor legs to the connector contacts. Supported processors Intel Celeron Coppermine, Intel Celeron Tualatin, Intel Celeron Mendocino, Intel Pentium Tualatin, Intel Pentium Coppermine. Speed characteristics of installed processors from 300 to 1400 MHz. Supported third party processors. Produced since 1999.
- Socket 423 is the first socket for Pentium 4 processors. It had a 423-pin grid of legs and was used on personal computer motherboards. It existed for less than a year, due to the inability of the processor to further increase in frequency, the processor could not pass the frequency of 2 GHz. Replaced by Socket 478 connector. Production began in 2000.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket 478 / Socket N / Socket P | Intel 486 | 238 | 1994 |
| Socket 495/MicroPGA 2 | Mobile Celeron/Pentium 3 | 495 | 2000 |
| PAC 418 | Intel Itanium | 418 | 2001 |
| Socket 603 | Intel Xeon | 603 | 2001 |
| PAC 611 / Socket 700 / mPGA 700 | Intel Itanium 2, HP8800, 8900 | 611 | 2002 |
- Socket 478 - released to follow the competitor (AMD company) Socket A, since previous processors were unable to raise the bar of 2 Gigahertz, and AMD took the lead in the processor production market. The connector supports Intel solutions - Intel Pentium 4, Intel Celeron, Celeron D, Intel Pentium 4 Extreme Edition. Speed characteristics from 1400 MHz to 3.4 GHz. Produced since 2000.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket 604/S1 | Intel 486 | 238 | 2002 |
| Socket 754 | Athlon 64, Sempron, Turion 64 | 754 | 2003 |
| Socket 940 | Opteron 2, Athon 64FX | 940 | 2003 |
| Socket 479/mPGA479M | Pentium M, Celeron M, Via C7-M | 479 | 2003 |
| Socket 478v2/mPGA478C | Pentium4, Pentium Mobile, Celeron, Core | 478 | 2003 |
- Socket 754 was developed specifically for the Athlon 64 processor model. The release of new processor sockets was associated with the need to replace the Athlon XP processor line, which was based on Socket A. The first processors of AMD K8 platforms were installed in Socket 754 processor sockets measuring 4 by 4 centimeters . This need was dictated by the fact that the Athlon 64 processors had a new bus and integrated memory controllers. The voltage output from this socket was 1.5 volts. Of course, the 754 became an intermediate stage in the development of the Athlon 64. The high cost and initial shortage of these processors did not make this platform very popular. And by the time the availability and cost of components had just returned to normal, AMD presented the release of a new socket - Socket 939. By the way, it was he who helped make the Athlon 64 a popular and truly affordable processor.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket 939 | Intel 486 | 939 | 2004 |
| LGA 775/Socket T | Pentium4, Celeron D, Core 2, Xeon | 775 | 2004 |
| Socket 563 / Socket A / Compact | Mobile Athon XP-M | 563 | 2004 |
| Socket M/mPGA478MT | Celeron, Core, Core 2 | 478 | 2006 |
| LGA771/Socket J | Xeon | 771 | 2006 |
- Socket 775 or Socket T is the first socket for Intel processors without sockets, made in a square form factor with protruding contacts. The processor was installed on the protruding contacts, the pressure plate was lowered, and using a lever it was pressed against the contacts. Still used in many personal computers. Designed to work with almost all fourth generation Intel processors - Pentium 4, Pentium 4 Extreme Edition, Celeron D, Pentium Dual-Core, Pentium D, Core 2 Quad, Core 2 Duo and Xeon series processors. Produced since 2004. Speed characteristics of installed processors range from 1400 MHz to 3800 MHz.
- Socket A. This connector is known as Socket 462 and is a socket for processors from Athlon Thunderbird to Athlon XP/MP 3200+, as well as for AMD processors such as Sempron and Duron. The design is made in the form of a ZIF socket with 453 working contacts (9 contacts are blocked, but despite this, the number 462 is used in the name). The system bus for Sempron, XP Athlon has a frequency of 133 MHz, 166 MHz and 200 MHz. The weight of coolers for Socket A, recommended by AMD, should not exceed 300 grams. The use of heavier coolers can lead to mechanical damage and even lead to failure of the processor power system. Processors with a frequency of 600 MHz (for example, Duron) and up to 2300 MHz (meaning the Athlon XP 3400+, which never went on sale) are supported.
- Socket 939, containing 939 contacts with an extremely small diameter, making them quite soft. This is a "simplified" version of the previous Socket 940, usually used in high-performance computers and servers. The absence of one hole in the socket did not make it possible to install more expensive processors into it. This connector was considered very successful for its time, as it combined good capabilities, dual-channel memory access and low cost of both the socket itself and the controller on computer motherboards. These connectors were used for computers with conventional DDR memory. Immediately after the transition to DDR2 memory, they became obsolete and gave way to AM2 connectors. The next step is the invention of new DDR3 memory and new AM2+ and AM3 sockets designed for the next models of AMD quad-core processors.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket S1 | Athon Mobile, Sempron, Turion 64/X2 | 638 | 2006 |
| Socket AM2/AM2+ | Athon 64/FX/FX2, Sempron, Phenom | 940 | 2007 |
| Socket F / Socket L / Socket 1207FX | Athon 64FX, Opteron | 1207 | 2006 |
| Socket/LGA 1366 | Core i7, Xeon | 1366 | 2008 |
| rPGA988A/Socket Q1 | Core i3/i5/i7, Pentium, Celeron | 988 | 2009 |
- Socket LGA 1366 – Made in 1366 contact form, produced since 2008. Supports Intel processors – Core i7 series 9xx, Xeon series 35xx to 56xx, Celeron P1053. Speed characteristics from 1600 MHz to 3500 MHz. Core i7 and Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series) with integrated three-channel memory controller and QuickPath connection. Replacement of Socket T and Socket J (2008)
- Socket AM2 (Socket M2), developed by AMD for certain types of desktop processors (Athlon-LE, Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron-LE and Sempron, Phenom X4 and Phenom X3, Opteron). It replaced Socket 939 and 754. Despite the fact that Socket M2 has 940 pins, this socket is not compatible with Socket 940, since the older version of Socket 940 cannot support dual-channel DDR2 RAM. The first processors to support Socket AM2 were single-core models Orleans (or the 64th Athlon) and Manila (Sempron), some dual-core Windsor (for example, Athlon 64, X2 FX) and Brisbane (AthlonX2 and Athlon 64X2). In addition, Socket AM2 includes Socket F, designed for servers, and a Socket S1 variant for various mobile computers. Socket AM2+ is absolutely identical in appearance to the previous one, the only difference is the support for processors with Agena and Toliman cores.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket AM3 | AMD Phenom, athlon, Sempron | 941 | 2009 |
| Socket G/989/rPGA | G1/G2 | 989 | 2009 |
| Socket H1/LGA1156/a/b/n | Core i3/i5/i7, Pentium, Celeron, Xeon | 1156 | 2009 |
| Socket G34/LGA 1944 | Opteron 6000 series | 1944 | 2010 |
| Socket C32 | Opteron 4000 series | 1207 | 2010 |
- LGA 1156 socket – Made using 1156 protruding pins. Produced since 2009. Designed for modern Intel processors for personal computers. Speed characteristics from 2.1 GHz and higher.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| LGA 1248 | Intel Itanium 9300/9600 | 1248 | 2010 |
| Socket LS/LGA 1567 | Intel Xeon 6500/7500 | 1567 | 2010 |
| Socket H2/LGA 1155 | Intel Sandy Bridge, Ivy Bridge | 1155 | 2011 |
| LGA 2011/Socket R | Intel Core i7, Xeon | 2011 | 2011 |
| Socket G2/rPGA988B | Intel Core i3/i5/i7 | 988 | 2011 |
- Socket LGA 1155 or Socket H2 - designed to replace the LGA 1156 socket. Supports the latest Sandy Bridge processor and the future Ivy Bridge. The connector is made in 1155-pin design. Produced since 2011. Speed characteristics up to 20 GB/s.
- Socket R (LGA2011) - Core i7 and Xeon with integrated quad-channel memory controller and two QuickPath connections. Replacement Socket B (LGA1366)
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| Socket FM1 | AMD Liano/Athlon3 | 905 | 2011 |
| Socket AM3 | AMD Phenom/Athlon/Semron | 941 | 2011 |
| Socket AM3+ | Amd Phenom 2 Athlon 2 / Opteron 3000 | 942 | 2011 |
| Socket G2/rPGA989B | Intel Core i3/i5/i7, Celeron | 989 | 2011 |
| Socket FS1 | AMD Liano/Trinity/Richard | 722 | 2011 |
- Socket FM1 is AMD's platform for Llano processors and looks like a tempting proposition for those who love integrated systems.
- Socket AM3 is a processor socket for a desktop processor, which is a further development of the Socket AM2+ model. This connector has support for DDR3 memory, as well as higher speeds for HyperTransport buses. The first processors to use this socket were the Phenom II X3 710-20 and Phenom II X4 models 805, 910 and 810.
- Socket AM3 + (Socket 942) is a modification of Socket AM3, developed for processors codenamed “Zambezi” (microarchitecture - Bulldozer). Some socket AM3 motherboards will allow you to update the BIOS to use socket AM3+ processors. But when using AM3+ processors on AM3 motherboards, it may not be possible to obtain data from the temperature sensor on the processor. Also, the power saving mode may not work due to the lack of support for fast core voltage switching in the Socket AM3 version. The AM3+ socket on motherboards is black, while AM3 is white. The diameter of the holes for the pins of processors with Socket AM3 + exceeds the diameter of the holes for the pins of processors with Socket AM3 - 0.51 mm versus the previous 0.45 mm.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| LGA 1356/Socket B2 | Intel Sandy Bridge | 1356 | 2012 |
| Socket FM2 | AMD Trinity/athlon X2/X4 | 904 | 2012 |
| Socket H3/LGA 1150 | Intel Haswell/Broadwell | 1150 | 2013 |
| Socket G3/rPGA 946B/947 | Intel Haswell/Broadwell | 947 | 2013 |
| Socket FM2/FM2b | AMD Kaveri/Godvari | 906 | 2014 |
- Socket H3 or LGA 1150 is a processor socket for Intel processors of the Haswell (and its successor Broadwell) microarchitecture, released in 2013. LGA 1150 is designed as a replacement for LGA 1155 (Socket H2). Made using LGA (Land Grid Array) technology. It is a connector with spring-loaded or soft contacts, to which the processor is pressed using a special holder with a grip and a lever. It is officially confirmed that the LGA 1150 socket will be used with Intel Q85, Q87, H87, Z87, B85 chipsets. The mounting holes for cooling systems on sockets 1150/1155/1156 are completely identical, which means full comprehensive compatibility and identical installation procedures for cooling systems for these sockets.
- Socket B2 (LGA1356) - Core i7 and Xeon with integrated three-channel memory controller and QuickPath connections. Replacement Socket B (LGA1366)
- Socket FM2 - Processor socket for hybrid processors (APU) from AMD with the Piledriver core architecture: Trinity and Komodo, as well as the canceled Sepang and Terramar (MCM - multi-chip module). Structurally, it is a ZIF - a socket with 904 pins, which is designed for installing processors in PGA-type cases. The FM2 connector was introduced in 2012, just a year after the FM1 connector. Although socket FM2 is an evolution of socket FM1, it is not backward compatible with it. Trinity processors have up to 4 cores, Komodo and Sepang server chips have up to 10, and Terramar have up to 20 cores.
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| LGA 2011-3 / LGA 2011 v3 | Intel Haswell, haswell-EP | 2011 | 2014 |
| Socket AM1/FS1b | AMD Athlon/Semron | 721 | 2014 |
| LGA 2011-3 | Intel Haswell / Xeon / haswell-EP / ivy Bridge EX | 2083 | 2014 |
| LGA 1151/Socket H4 | Intel Skylake | 1151 | 2015 |
- The LGA 1151 socket is a socket for Intel processors that supports Skylake architecture processors. LGA 1151 is designed as a replacement for LGA 1150 (also known as Socket H3). LGA 1151 has 1151 spring-loaded contacts to contact the processor pads. According to rumors and leaked Intel advertising documentation, motherboards with this socket will feature DDR4 memory support. All Skylake architecture chipsets support Intel Rapid Storage Technology, Intel Clear Video Technology and Intel Wireless Display Technology (when supported by the processor). Most motherboards support various video outputs (VGA, DVI or HDMI - depending on the model).
| Type | Purpose | Number of contacts | Year of issue |
| LGA 2066 Socket R4 | Intel Skylake-X/Kabylake-X i3/i5/i7 | 2066 | 2017 |
| Socket TR4 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper | 4094 | 2017 |
| Socket AM4 | AMD Ryzen 3/5/7 | 1331 | 2017 |
- LGA 2066 (Socket R4) is a socket for Intel processors that supports Skylake-X and Kaby Lake-X processors without an integrated graphics core. Designed to replace the LGA 2011/2011-3 (Socket R/R3) socket for high-end Basin Falls desktops (X299 chipset), while the LGA 3647 (Socket P) will replace the LGA 2011-1/2011- 3 (Socket R2/R3) in server platforms based on Skylake-EX (Xeon “Purley”).
- AM4 (PGA or µOPGA1331) is a socket produced by AMD for microprocessors with Zen microarchitecture (Ryzen brand) and subsequent ones. The connector is a PGA (pin grid array) type and has 1331 contacts. It will be the company's first socket with support for the DDR4 memory standard and will be a single socket for both high-performance processors without an integrated video core (currently using Socket AM3+), and for low-cost processors and APUs (previously using various sockets of the AM / FM series).
- Socket TR4 (Socket Ryzen Threadripper 4, also Socket SP3r2) is a type of connector from AMD for the Ryzen Threadripper family of microprocessors, introduced on August 10, 2020. Physically very close to the AMD Socket SP3 server connector, however, it is incompatible with it. Socket TR4 became the first LGA-type socket for consumer products (previously LGA was used in the server segment, and processors for home computers were produced in FC-PGA packages). It uses a complex multi-stage process of mounting the processor into the socket using special holding frames: an internal one, secured with latches to the cover of the chip case, and an external one, secured with screws to the socket. Journalists note the very large physical size of the connector and socket, calling it the largest format for consumer processors. Due to its size, it requires specialized cooling systems that can handle up to 180W. The socket supports HEDT (High-End Desktop) segment processors with 8-16 cores and provides the ability to connect RAM via 4 DDR4 SDRAM channels. The socket has 64 PCIexpress 3rd generation lanes (4 are used for the chipset), several USB 3.1 and SATA channels
Share:
Leave your comment!
- Comment on VKontakte
- Facebook comment
Comments
+6 roman 11.11.2018 13:38 Colossal work. Very helpful. I remembered my youth. Thank you.
Answer
0 213 09.19.2019 12:15 I finally found a photo of the connectors and understood the differences!!
Answer
0 RomanSRS 05/04/2020 03:05 where are the mobile processors?
Answer
0 Artemy 06/05/2020 14:26 Please update the article already lga 00 is there.
Answer
0 petcom 06/07/2020 02:47 Thanks for the post
Answer
Update list of comments
Add a comment
| < Previous | Next > |
Similar articles:
- Processor sockets: generations in photographs
LGA 1151
LGA 1151 is Intel's latest socket. It was released in 2020 for the Intel Skylake generation of processors. These processors used the 14 nanometer process technology. Since the new Kaby Lake processors haven't changed much, this socket is still relevant. The socket is supported by the following motherboards: H110, B150, Q150, Q170, H170 and Z170. The release of Kaby Lake brought the following boards: B250, Q250, H270, Q270, Z270.
Compared to the previous version of LGA 1150, USB 3.0 support has appeared here, the operation of DDR4 and DIMM memory modules has been optimized, and SATA 3.0 support has been added. DDR3 compatibility was still maintained. From video, DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort are supported by default, while VGA support can be added by manufacturers.
LGA 1151 chips only support GPU overclocking. If you want to overclock the processor or memory, you will have to choose a higher-end chipset. In addition, support for Intel Active Management, Trusted Execution, VT-D and Vpro has been added.
In tests, Skylake processors show better results than Sandy Bridge, and the new Kaby Lake ones are even a few percent faster.
Here are the processors that are currently running on this socket:
SkyLake:
- Pentium - G4400, G4500, G4520;
- Core i3 - 6100, 6100T, 6300, 6300T, 6320;
- Core i5 - 6400, 6500, 6600, 6600K;
- Core i7 - 6700, 6700K.
Kaby Lake:
- Core i7 7700K, 7700, 7700T
- Core i5 7600K, 7600, 7600T, 7500, 7500T, 7400, 7400T;
- Core i3 7350K, 7320, 7300, 7300T, 7100, 7100T, 7101E, 7101TE;
- Pentium: G4620, G4600, G4600T, G4560, G4560T;
- Celeron G3950, G3930, G3930T.
conclusions
In this article, we looked at generations of intel sockets that were used before and are actively used in modern processors. Some of them are compatible with new models, while others have already been completely forgotten, but are still found in user computers.
Latest intel socket 1151, supported by Skylake and KabyLake processors. We can assume that the CoffeLake processors that will be released this summer will also use this socket. There used to be other types of intel sockets, but they are already very rare.
LGA 1150
The LGA 1150 socket was developed for the previous, fourth generation of Intel Haswell processors in 2013. It is also supported by some fifth-generation chips. This socket is supported by the following motherboards: H81, B85, Q85, Q87, H87 and Z87. The first three processors can be considered entry-level devices; they do not support any advanced Intel capabilities.
The last two boards added support for SATA Express, as well as Thunderbolt technology. Supported processors:
Broadwell:
- Core i5 - 5675C;
- Core i7 - 5775C;
Haswell Refresh
- Celeron - G1840, G1840T, G1850;
- Pentium - G3240, G3240T, G3250, G3250T, G3258, G3260, G3260T, G3440, G3440T, G3450, G3450T, G3460, G3460T, G3470;
- Core i3 - 4150, 4150T, 4160, 4160T, 4170, 4170T, 4350, 4350T, 4360, 4360T, 4370, 4370T;
- Core i5 - 4460, 4460S, 4460T, 4590, 4590S, 4590T, 4690, 4690K, 4690S, 4690T;
- Core i7 - 4785T, 4790, 4790K, 4790S, 4790T;
Haswell
- Celeron - G1820, G1820T, G1830;
- Pentium - G3220, G3220T, G3420, G3420T, G3430;
- Core i3 - 4130, 4130T, 4330, 4330T, 4340;
- Core i5 - 4430, 4430S, 4440, 4440S, 4570, 4570, 4570R, 4570S, 4570T, 4670, 4670K, 4670R, 4670S, 4670T;
- Core i7 - 4765T, 4770, 4770K, 4770S, 4770R, 4770T, 4771;
LGA 1156
The LGA 1156 socket was released for the new line of processors in 2008. It was supported by H55, P55, H57 and Q57 motherboards. New processor models for this socket have not been released for a long time.
Supported processors:
Westmere (Clarkdale)
- Celeron - G1101;
- Pentium - G6950, G6951, G6960;
- Core i3 - 530, 540, 550, 560;
- Core i5 - 650, 655K, 660, 661, 670, 680.
Nehalem (Lynnfield)
- Core i5 - 750, 750S, 760;
- Core i7 - 860, 860S, 870, 870K, 870S, 875K, 880.