The question of how to find out the chipset model of a motherboard does not arise for ordinary users. Such information may be required by all those specialists who repair computer equipment or replace components on the motherboard so that the new installed components work correctly and do not cause conflicts with the installed hardware. However, sometimes information about the chipset is extremely necessary for ordinary users. But not everyone knows how to find out the chipset version of the motherboard installed on a stationary terminal or laptop. Even greater confusion arises only because ignorant users very often believe that the name of the chipset and the name of the motherboard itself are one and the same.
Brief introduction
So, first, let's take a quick look at some important aspects that will help you understand the difference between the main device (motherboard) and the installed chipset. A chipset is a set of chips and connectors that ensures the interaction of the main components installed on the motherboard with each other. The name of the motherboard model may differ from the nomenclature designation of the chipset. Often in descriptive documentation or information obtained through operating system tools or additional software, you can find special designations regarding the north and south bridges.
Today, the binding is mainly applied specifically to the north bridge, but its modification exactly corresponds to the name of the chipset. Thus, you can find out which chipset is on the motherboard using this information, since the full name of the motherboard can only be used when searching for relevant information on the Internet, for example, on the manufacturer’s official resource.
Now it’s time to move on to the practical part. To obtain the information we are interested in, we can use either the operating system tools (we take Windows as a basis) or third-party information utilities, the use of which looks more attractive because they provide much more information on any “hardware” component.
How does the chipset work?
Chipset block diagram
Conventionally, the chipset is divided into two components:
- north bridge;
- south bridge.
The first is responsible for the proper and coordinated operation of the processor, video card, RAM (conventionally this set is called “logic”), the second is responsible for all other connected devices and peripherals.
The chipset is divided into northbridge and southbridge
On a note! More modern motherboards, and especially laptops, use combined bridges called multicontrollers (or “hubs”).
Knowing the chipset model, you can find out which processors the motherboard supports, the maximum amount of RAM, as well as the allowed number of USB ports and drives. Today, the most famous chipset manufacturers are Intel and AMD (a few years ago Nvidia was also in this field, but later the company focused on video adapters).
If you want to learn in more detail how to find out the chipset of a motherboard, you can read an article about it on our portal.
How to find out the motherboard chipset: the simplest method
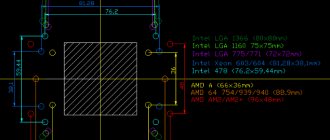
To determine the name of the chipset, we use the simplest method as the simplest method. Apparently, many users have noticed that immediately after turning on their computer or laptop, some brief information appears on the screen, which sometimes you don’t even have time to read.
This is where the information you need is found. To delay the start screen for a longer period of time, immediately at start you need to press the pause button, usually marked on the keyboard with the double name Pause/Break. The chipset name will be shown either in one of the top lines or at the bottom right after the system date is displayed next to the key or keyboard shortcut to access the BIOS.
Note: If we are talking about how to find out the motherboard chipset on a laptop, the start screen delay keys may be different. On full-size keyboards, the pause most often coincides with the Insert key, but it can only be used in conjunction with the Fn button.
Basic methods
In order to correctly install drivers for peripheral devices - for example, a sound or network card, you need to know exactly the manufacturer and model of the motherboard. If the user bought a ready-made system unit in a specialized office equipment store, the sellers had to provide the corresponding boxes complete with warranty sheets and receipts.
This is precisely the first method of defining a model. You need to find the motherboard box and enter the manufacturer's name with a unique combination of letters and numbers in a search engine. It is very easy to recognize them, so the brand will most likely be one of the first in the search results.
There are quite a few manufacturers on the market today. Unless it's a so-called branded PC, most likely the average user will have a board from one of these manufacturers:
- Asus.
- MSI.
- AsRock.
- Gigabyte.
As you can see, it is not so difficult to find out the specific company from whose production facilities the board came off. But that is not all. There are two major players in the processor market - Intel and AMD. Processors from these manufacturers use different connectors for installation, called sockets (socket in English) and different chipsets that contain the necessary sets of PCI-Express lines that allow you to control peripherals and built-in multimedia devices.
The name of a particular model will depend on the chipset and, to a lesser extent, on the socket . There are several accurate methods to find out which motherboard is on the computer:
- Visual inspection.
- Using the operating system.
- Third-party programs - CPU-Z, AIDA64 and Speccy.
- Via BIOS.
Visual inspection of the board
If the system unit case is not sealed, the easiest way to recognize your motherboard is visual. To do this, you need to remove the side cover and find the manufacturer's logo. As a rule, the model marking is located nearby.
If it is impossible to find the logo on the first try, it is worth looking to see if it is obscured by other components, for example, a video card. Modern video accelerators can have quite massive cooling systems, the radiators of which cover one or two slots below them. The exact brands of motherboards are located there on some models.
In addition, improper cable management or cable routing may interfere. Some assemblers do not lay cables from drives, cables from power supplies and fans neatly using zip ties, and therefore they can interfere with the view.
In short, there are several places where the manufacturer places the model number:
- Near the processor socket.
- Not far from the RAM slots.
- Above or below the video card connector.
- Some Chinese brands have processor power management chips on their heatsinks.
Information in primary BIOS/UEFI systems
Along the way, it’s worth considering how to find out the motherboard chipset directly in the primary system.
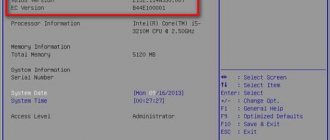
When the startup screen above appears, you need to use a key or key combination to enter the BIOS, and then find the chipset section (something like Chipset Configuration), which may be presented in the main panel or located in the Advanced settings ). When you expand the options, the bridge configuration is displayed there. The North Bridge is marked in the North Bridge section. There you need to look for the necessary information.
The best chipsets for Intel and AMD motherboards
As mentioned above, the concept of “best chipset” is very relative. The best choice will always be the most suitable option for a particular assembly. Nevertheless, Intel has assigned chipsets at the top of the “food chain” for motherboards with the Z index, usually (though not always) equipped with more functionality, so they will top the rating.
Intel chipsets
In addition to letter markings, chipsets are divided into series (the 300th, 200th, 100th series are relevant today). The 300th is adapted for the eighth generation of processors, the 200th is suitable for the seventh and sixth, the 100th is suitable for Intel Core, Pentium and Celeron. The indices Z, H, B, Q indicate the categories of chipsets (Z – gaming with overclocking capabilities, H – functional mainstream chipsets, B – for office or home, Q – for business).
300
Let's start the list of Intel chipsets from the top. Motherboards equipped with these particular chipsets are shining in the ratings today.
- Z370/390. The difference between the chipsets is not that big. The Z370 chipset is the pioneer of the series, one of the best, but, despite the possibility of overclocking, some of the functionality inherent in subsequent copies of the 300 is missing (compare the same H370 with the new USB1 Gen 2 and support for wireless networks). The new Z390 is a slightly more modernized analogue of the Z370 with the same configurations of PCI-Express channels and USB drives, but with the addition of USB 3.1 Gen 2 and Intel Wireless-AC MAC;
- Q Like Z-chipsets, the use of multiple video cards is supported, but there is no overclocking option. It is adapted to business needs, so you can’t count on an assortment of motherboards with its participation;
- The H370, located one step below, is very similar to its brother Z370, and although it does not have overclocking capabilities, and there are slightly fewer PCI-Express and USB channels, the H370 is superior in having USB1 Gen 2 and supports Wi-fi and Bluetooth 5.0. If the mainland is not purchased for the purpose of overclocking, then this chipset is worth paying attention to when assembling a productive computer;
- B360 is not as sophisticated a chipset as the one discussed above, but it is also not as limited in functionality as the H310, it has a dual-channel memory controller, USB1 Gen 2, supports version 3.0 buses, and also allows the use of a graphics core integrated into modern Intel processors;
- H310 is a budget version of the series with a minimum set of functions for undemanding users. The chipset does not support the PCI-Express bus version 3.0, like other representatives of the series; there is a second one, which has lower bandwidth. The situation is exactly the same with the DMI version, the memory controller is single-channel, and in general many features have been reduced.
100 and 200
There is no significant difference between the series, although the 200th and more have been modernized.
- X299 is worth special attention, it is designed for the line of high-performance Kaby Lake-X and Skylake-X CPUs without integrated graphics and supports overclocking;
- Z170/270. Like other Z-index carriers, chipsets are ideal for overclocking processors and are equipped with good functionality;
- H170/270. With boards equipped with H chips, the user has much more options than when using B, but there is no overclocking on such motherboards;
- B150/250 is the golden mean between a budget option and a gaming one. Boards based on these chipsets are installed with average power, sufficient to perform various everyday tasks on a PC;
- The H110 has limited functionality, but is great for budget builds, because purchasing an expensive motherboard with many capabilities can be unreasonable, for example, in the case of office work, etc.
Chipsets with the Q index are not too different from H, but have a certain set of corporate goodies. In all Intel series, a certain structure can be traced, ranking models taking into account their inherent bells and whistles. The announced X399 chipset (the name echoes the AMD model for the Ryzen Theadripper CPU) may soon become the icing on Intel’s cake.
AMD chipsets
The company offers two options for chipset configurations - chipsets, where the south and north bridges coexist in one set and exist separately from each other. The combined variations are aimed at processors with the new AM4 and TR4 sockets; a separate configuration is used for earlier sockets.
TR4 processors
The company released the X399 chipset for powerful AMD Ryzen Theadripper CPUs. A significant proportion of controllers have now migrated to the processor, which has increased performance and reliability (it’s no secret that the processor is cooled better). The equipment includes 4-channel RAM, connecting devices via NVMe and other useful features. Overclocking supported.
AM4 processors
Chipsets for AM4 also have a combined version, and the lion's share of the controllers moved into the processor, leaving only the peripherals for the chipset.
- X470 is a new top-end chipset that is a more upgraded version of X370. The chipset is perfect for gamers and overclockers. Features include overclocking, support for multiple video cards, loading from NVMe RAID, etc. In addition, the X470 supports AMD StoreMI technology, which allows you to combine hard drives into one volume and automatically move frequently used files to the SSD.;
- B350 is a more modest representative of chipsets for motherboards of gaming computers, while also providing the ability to overclock and work with multiple video cards;
- A320 is an option for “workhorses” operating with one video adapter. Overclocking is not supported in this case, but the capabilities of the chipset are quite sufficient to solve pressing problems.
For small form factor motherboards, the X300 (analogous to the gaming X370) and A300 (analogous to the A320) chipsets are produced. The difference lies in the reduced support for connection interfaces.
AM3+ processors
Chipsets for AM3+ sockets are available in a north and south bridge configuration.
- The 990FX and 990X chips are designed for gaming platforms, support overclocking and OverDrive control, and do not have integrated graphics. 990FX supports 4 video cards, 990X – two;
- There is also an AMD 970 chipset with similar characteristics, but it supports one video adapter;
- 980G with integrated graphics is ideal for office and low-power home PCs without a connected video card. It will be possible to play not too demanding games, if the processor power allows, one connector for a video card is available.
FM2+ processors
FM2+ chipsets and similar sockets are suitable for use in conjunction with A-series and Athlon hybrid processors.
- A88X provide overclocking capabilities, support the connection of two video cards, RAID functionality (it is advisable to use with AMD A8 - A6);
- A78 also has an arsenal for overclocking, supports one video adapter (it is better to use it on CPUs of the A6 - A4 line);
- A58 and more advanced brother A68N. Both chipsets support dual graphics (increased graphics performance is achieved through the use of hybrid processors in conjunction with some AMD graphics adapters).
Results
Considering the modern market, you should take into account that Intel's Coffee Lake generation processors are compatible only with the new 300 chips and the LGA1151v2 socket, while new AMD processors, including the second generation Ryzen, are compatible with AM4. Chipsets from Intel, marked Z or X, allow you to overclock the machine, while others do not, even if the processor has a free multiplier, suggesting similar manipulations with its frequency. With AMD, overclocking can be done on a motherboard with an X or B chipset.
When the underlying goals are completely different and the extra expenditure of money is not justified or a very limited budget for assembly plays a decisive role, you can get by with not particularly outstanding motherboards. By the way, among them you can find interesting specimens with a good set of interfaces and connectors.
How can I find out what chipset is on my motherboard in Device Manager?
All Windows operating systems have a special manager, which presents all the data on the installed equipment. Just as in the case of primary systems, here you need to find a component whose name contains the designation Chipset.
Only it can be seen directly in the system devices section. Please note that your motherboard model may not be listed here. If you need to find out its exact name, you can use either the name of the chipset or view the hardware identifiers presented in the details tab.
How to determine the motherboard chipset on a work computer
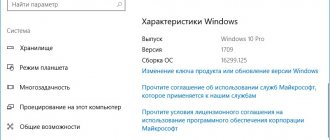
If your computer is working and has the Windows operating system installed, then you can find out the name of the motherboard using built-in tools. For example, you can press the Win-R key combination and execute the command “msinfo32” in the window that opens.
This will open the System Information window. Here, on the main screen of the program, all the basic information about your computer will be collected. Among other things, the name of the motherboard will be here.
You can also get information about the name of the motherboard using the commands “wmic baseboard get Manufacturer” and “wmic baseboard get product”. The first command displays the name of the board manufacturer, and the second the exact name of the model. You need to enter these commands into the command line (cmd).
Once you have the motherboard information, you can find the name of the chipset using an internet search, as described above.
Additional information on the chipset driver
By the way, if we are talking about how to find out the motherboard chipset driver, information about it can be viewed in the hardware properties, and if necessary, using the identifiers defined in the information, find the most appropriate control software for installing, for example, an updated driver.
Usually this is not required, since it is very doubtful that the computer will function normally if there is an incorrectly installed or missing driver.
Why do you need a chipset?
The main chip on the motherboard is the processor (CPU), it issues commands to other devices, but cannot do it directly. The chipset connects the CPU with other systems: random access memory (RAM), input/output system, adapters and peripheral controllers. Communication is carried out via a bus system.
General diagram of the motherboard chipset
Different buses are used to connect to different components:
- with processor – system bus;
- with memory – memory bus;
- with graphics adapter – PCI, PCI-Express or AGP;
- with LPT, PS/2 devices – Low Pin Count bus.
The chipset only controls the interaction of systems, but does not interfere with their operation.
Chipset defines:
- number of components in subsystems: possible number of processors, memory slots, graphics adapters, expansion slots and ports on the motherboard.
- bus frequency and bit depth through which it communicates with the subsystem;
- Is it possible to increase the characteristics of individual subsystems: clock frequency of the processor(s), memory voltage;
- technology support by subsystems: dual operation mode of video cards – CrossFire and SLI; dual memory mode – DUAL RAM, caching on SSD – Smart Response Technology.
- support for interaction with special or legacy controllers: RAID, PCI, AGP.
The chipset provides: performance, expandability and stability in different computer modes.
Searching for information via the command line
Another solution to the problem of how to find out the motherboard chipset is to use information that can be obtained from the command line or the PowerShell console, which is a kind of extended analogue of the first tool.
To do this, just run the command shown in the image above, and then view information related to the chipset itself.
Using system information
Sometimes it makes sense to use system information. This informative tool is called up through the Run menu with the abbreviation msinfo32. The necessary information will be displayed in the hardware section, and in several places at once (for example, in the subsections of conflicts and shared access or IRQ interrupts). The only inconvenience of this technique is that only the general name of the chipset of a certain family is indicated without an exact nomenclature designation.
For example, the image above shows the Intel® Series 6/C200 Series Chipset Family, which is the name used to refer to both PCI slots, USB ports, etc.
Main functions
As already mentioned, the functions of the chipset include the integration of various devices located on the motherboard - memory, processor, I/O buses, ports, etc. and coordination of their interaction. The chipset also often contains a built-in video and audio output system and a network controller.
The south and north bridges are responsible for different functions. The north bridge controls high-speed devices such as processor, memory, . Also in the northbridge there is a built-in video system. The South Bridge is responsible for all other peripherals, usually low-speed ones. These are PCI, SATA, USB and many others. By the way, if you remember that the north bridge is called a memory controller, then this rule is often not followed, since in many chipset models memory management is not part of the north bridge’s functions, but is carried out using the capabilities of the central processor.
Many motherboards also have a small Super I/O chip responsible for low-speed ports such as LPT and PS/2. The south bridge and the Super I/O controller are connected by a special bus.
Northbridge, Intel 815 chipset
South Bridge
CPU-Z utility
Finally, let's move on to more advanced software applets that allow, as they say, to “squeeze” the maximum information about any component of the computer hardware. The presented utility is one of the most popular and revered programs among users all over the world (and is also completely free).
In the application itself, you need to go to the information tab about the motherboard (Mainboard), where just below you will see not only its markings, but also information directly about the installed chipset.
AIDA64 program
It is believed that the former Everest program, at one time renamed AIDA64, is more informative. To get maximum information about all computer components, and not just the chipset, it is better to use the Extreme version.
You can view the necessary information in the Northbridge information item. True, the only and most important drawback of this utility is that it is paid, and the trial version can only be used during the 30-day trial period, although in our case this does not really matter.
PC Wizard app
The free PC Wizard app is also a good option for getting chipset information.
However, you will have to make several additional transitions through sections, and all the necessary information on the chipset will be presented in the microprocessor information item (information on the north and south bridge will be displayed in the lower window).
Device
So, in general terms, we figured out what a motherboard is and why it needs a chipset. But how it works is still unclear. Let's correct this oversight. When starting a conversation about the design of the chipset, first of all decide which model we are talking about - old or new. This is of fundamental importance.
Old models are built on the interaction of two separate blocks of microcircuits. They were called the North and South Bridges. The name reflects their location on the MP, relative to other elements. The North Bridge performs the following functions:
- Ensuring interaction between the processor and the graphics device;
- Ensuring interaction between RAM and processor elements;
In turn, the South Bridge allows you to:
- Transmit signals from the central processor to the storage disks of a personal computer;
- Coordinate the operation of the sound card;
- Manage optical drives;
- Work with other peripheral devices via controllers: USB, PCI, SATA and IDE;
Note! Work with various elements of each bridge is implemented through system buses with different bandwidths.
The new models are built on a different architecture, in which the North Bridge is integrated into the processor and only the South Bridge remains as an independent element. This technology allows you to increase the speed of processing and transferring information, increasing performance. In addition, the use of integrated bridge technology makes it possible to:
- Reduce the cost of MP production;
- Free up space occupied by the Northbridge for other components;
- CPU cooling elements help maintain the operating temperature of the chipset in a comfortable range, which affects performance and durability;
- By integrating the bridge into the processor, overall energy consumption is reduced;
Speecy information applet
Now let's see how to find out the motherboard chipset model using the Speecy program. By its nature, it is quite reminiscent of the utilities described above and is no less informative.
It is also necessary to use the subsection related to the motherboard, however, the name of the chipset will be shown in the model and revision items of the northbridge.
Intel chipsets for LGA 1150 motherboards
In May 2014, the premiere of the 9th generation of Intel chipsets took place. This family includes the following models: Z97 and H97, intended mainly for use in computers intended for games, graphic work, as well as for more demanding users that support an LGA 1150 motherboard. Chipset models for home computer equipment, for example, B85 and H81 are still in the game, and the 1150 models are also suitable. Unlike the 8th generation chipsets, which consist of 6 bridges, the 9th has only two, but allows you to overclock the processor through a multiplier.
Which chipset for i3, i5 or i7 processors?
The main question is which chipset to choose for which processor? In the case of i7-core, the answer is simple - the most powerful 9th generation media communication processors, i.e. H97 and Z97. In the case of an i5-core processor, the best choice would be a motherboard based on the B85 chipset, possibly with earlier versions of the Z87 and H87 models. For i3-core, a motherboard based on the H81 chipset is suitable - perfect for simple work.
| Model | H81 | H97 | B85 | Z97 |
| Generation | 8 | 9 | 8 | 9 |
| USB version | 3.0, 2.0 | 3.0, 2.0 | 3.0, 2.0 | 3.0, 2.0 |
| USB quantity | 8x 2.0, 2 x 3.0 | 8x2.0, 6x3.0 | 8 x 2.0, 4 x 3.0 | 8x2.0, 6x3.0 |
| Number of SATA ports | 4 (including 2 x6.0 Gb/s) | 6 SATA 6.0 Gb/s | 6 (including 4 x6.0 Gb/s) | |
| Hi-tech | Intel® Smart Connect Technology | Intel® Rapid Storage Technology, Intel® Smart Connect Technology Intel® Smart Response Technology Intel® Rapid Start Technology | Intel® Smart Connect Technology, Intel® Small Business Advantage Intel® Rapid Start Technology, Anti-Theft Technology | Intel® Rapid Storage Technology, Intel® Smart Connect Technology Intel® Smart Response Technology Intel® Rapid Start Technology, Intel® Small Business Advantage |
| Overclocking | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Proposed processor | i3 | i5/i7 | i3/i5 | i5/i7 (for K version) |
| Application | Equipment for home and office use | Ideal for home use, gaming, graphic work | Ideal for office use and for protecting small personal data databases | Ideal for office work, games |
Which chipset should I choose for home use?
If we are talking about budget solutions for home use, then a motherboard based on the B85 chipset would be an excellent solution. It allows you to overclock the processor on a weaker logic system, thanks to which you can achieve quite attractive results.
B85, thanks to the use of additional technologies like Small Business Advantage, is also perfect for a small office. The H81 chipset is also suitable for browsing the Internet, less graphically complex games and office work. The advantage of the H81 and B85 over later models is cost.
Which chipset should you choose for gaming?
If we are talking about budget solutions, then for games we recommend motherboards with the B85 chipset, mainly due to the possibility of overclocking. Most B85 motherboards allow you to play the latest games. However, the equipment for “maniacs” of computer games will be the sets that are equipped with motherboards with Z97, which gives very great possibilities when paired with an i7 processor.
SSU utility
Finally, you can get information about the chipset from a special portable SSU program developed by Intel. After launching the application, which, as is already clear, does not need to be installed on your hard drive, you need to select the computer components for which you want to find information (to be sure, you should check the motherboard and processor), and then select the display of extended information in a special drop-down list.
General information will be provided at the end of the motherboard specifications, and more detailed information can be found in the processor description section.