The installation flash drive does not boot through bios. Laptop won't boot from flash drive
Instructions
To open the BIOS, press Del after you turn on the computer and before the operating system starts loading. You may need to press a different key to enter the BIOS on your computer. In the lower left corner when checking RAM there is the inscription Press Del to enter setup. If another key is written instead of Del, press it.
The BIOS window opens. You need to control the BIOS using arrow keys and the Enter and Esc keys. Basic parameters for equipment: Disabled – disable, Enabled – use. Depending on the manufacturer and model, the versions and directory names in the BIOS may differ. The following are the most common names.
In the Advanced menu (Advanced BIOS features) you can prohibit or use the USB controller under the USB Functions command (USB Controller/USB Ports/USB Device/Integrated (OnChip) USB Controller). The Enabled/Disabled command turns all USB ports on/off, Both makes all ports available, Primary makes ports on the rear panel only available. 2/4/6/8 USB Ports – number of ports available for operation.
USB 2.0 Controller (High Speed USB/USB 2.0 Supports/USB 2.0 Device). Option to disable or allow the use of USB 2.0. USB 1.1/2.0 Controller item for using all USB controllers, commands: All Disabled - disable everything, All Enabled - enable everything.
USB Speed. An option that changes the operating frequency of the USB bus. Its parameters: 24 MHz and 48 MHz.
Legacy USB Support (USB Device/USB Driver Select/USB Function to DOS/USB Keyboard(Mouse) Support). Section for USB keyboard/mouse support at the BIOS level. The Enabled/Disabled command – enables/disables support, Auto – disables standard keyboard/mouse when USB devices are connected and vice versa, OS – provides support for the operating system, BIOS – provides support for the motherboard BIOS.
Port 64/60 Emulation (USB 1.1 64/60 Emulation) – an option for optimizing devices connected to the USB port in legacy OS. Enabled/Disabled command – turns it on/off. Emulation Type (UFDDA USB Floppy/ UFDDB USB Floppy/ USB Mass Storage Emulation Type/ USB Mass Storage Device Boot Setting) – with different values of the option, the USB drive is emulated in Auto mode – detected automatically, Floppy (FDD Mode or USB Floppy) – as removable media, Forced FDD - like a floppy disk, Hard Disk (HDD Mode or USB HDD) - like a hard drive, CDROM - like an optical disc drive.
To boot the OS from a USB drive, go to the Boot menu (or find First Boot Device in Advanced BIOS features). In the Boot Device Priority section, select 1st Boot Device, then check the box next to the name of your device, or opposite the USB-HDD item.
BIOS is a set of microprograms located on a memory chip located on the computer motherboard. When you turn on the computer, even before loading the operating system, the BIOS recognizes the installed devices, checks their functionality and starts them with the specified settings. USB support in the BIOS should be enabled in most cases, because... many devices use this interface to connect to a computer.
Instructions
Enter the BIOS setup program. To do this, you need to press a specific key or key combination after turning on the computer when checking devices, before loading the operating system. The most common option is to press the Delete, or Del, key. To find out which key to press in a particular case, carefully observe the text on the screen when you turn on the computer. One of the lines will have a hint that reads something like this: Press F2 to enter Setup.
Find the menu item that will contain the setting responsible for enabling USB support in the BIOS. Depending on the BIOS manufacturer, this item may be called differently. Common options are Integrated Peripherals, Peripherals, Advanced. If there is no such item, try going to other sections - in one of them you will find the required item from the next step.
Select the option that directly affects the USB controller. It may also have different names in different BIOS versions. But its name will definitely include the word USB, for example, USB Controller, USB Device, USB Function, OnChip USB, Onboard USB Device. It can be located either directly in the previous paragraph or in the sub-item Onboard Device, USB Configuration, OnChip Device.
How to reinstall Windows or attempt to revive the operating system using Live disks if the laptop does not boot from a flash drive? This does not mean rare devices, which in principle do not support booting from USB drives, but modern laptops, which allow booting from a flash drive, but do not offer a clear mechanism for setting boot priority from the start. Using one of the tested Asus models as an example, below we will understand the specifics of booting modern laptops from a flash drive and consider common reasons why problems may arise with this matter.
Why Windows 10 cannot be installed from a flash drive: the main and most common reasons
So, let's start by describing an approximate list of all the reasons that may affect the occurrence of such unforeseen situations. Among the countless number of them, the following are particularly noteworthy:
- the hardware does not meet the requirements of Windows 10;
- some computer devices do not work correctly or do not work at all;
- the upgrade is impossible due to the lack of installed updates for the existing OS;
- there is not enough free space in the system partition;
- incorrect parameters of the primary system are set;
- The bootable USB flash drive was created incorrectly;
- installation is performed on an MBR partition, not a GPT partition;
- The device is protected at the hardware level.
Please note that the list shows only the most common causes and not all possible causes. It is also possible that installing Windows 10 from a flash drive can be completed successfully, but after a reboot or during the installation of updates, if an Internet connection was made at one of the stages, the computer stops responding to user actions, and a blue color appears during the restart process. or a black screen, the update process freezes, etc. Most often this is due to either hardware, or a lack of free disk space, or an Internet connection.
Setting boot priority in the hard drive selection menu
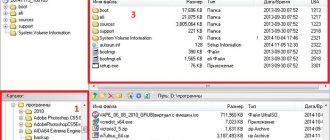
The inability to prioritize booting a BIOS flash drive is a problem not only for laptops, but also for PCs, and it is usually due to the fact that many programs for writing bootable media create a bootable flash drive based on the principle of a hard drive. In such cases, the flash drive is not included in the general list of boot device priorities; you need to look for it in a separate menu, where the priority hard drive is determined. In this menu, connected USB media are listed as hard drives along with the laptop’s internal storage devices – HDD or SSD. But even users who have previously encountered this nuance may not remember it, since they may be misled by the fact that in the BIOS UEFI the flash drive is listed as a UEFI boot device (with the addition “UEFI” in front). It appears, but in fact the laptop does not boot from such a flash drive. If the bootable flash drive is not UEFI or we are dealing with a laptop based on a regular BIOS, the flash drive needs to be set in the hard drive priority menu. For example, in the Asus laptop we are testing, you need to go to the “Boot” section and install the hard drive in the “Boot Option #1” column.
Then go down to the “Hard Drive BBS Priorities” column.
2
And choose a flash drive.
3
In the general list of boot devices, the flash drive will not be listed as a UEFI device, and boot will take place from it.
4
But it will be implemented subject to the active compatibility mode with Legacy.
Errors in upgrading to Windows 10
Now let's see how to install Windows 10 from a flash drive if we are talking about upgrading an existing OS. The main problem here is that in order to carry out such operations, it is necessary to integrate all updates specifically for it into the source system (this, by the way, is recommended even by the developers themselves). In this case, you should not rely on automatic updates.
When calling the “Update Center”, and only for the seventh and eighth modifications of Windows (Vista and XP are not supported), the search for all available updates must be done manually, and the new system must be installed only after they are fully integrated into the existing OS.
If a so-called clean installation is envisaged, in which the hard drive or system partition will be formatted, which will accordingly lead to the loss of user data, including installed programs, there should usually be no problems.
Switching a flash drive to a USB 2.0 port
Many modern laptops have a USB 3.0 port (with a blue tab). This is a great advantage when it comes to working with USB devices inside Windows, but problems may arise when booting computers from flash drives that do not have drivers supporting USB 3.0 in the distribution. These distributions include official ISO installation images of Windows 7 (and versions below), as well as builds of some, usually older, Live disks. A difficult way to solve this problem is to integrate USB 3.0 drivers into the distribution and repackage the ISO image. Simple and recommended - connect a flash drive to a USB 2.0 port on a laptop. Only the USB port on the laptop matters; the fact that the flash drive itself supports USB 3.0 does not play any role. You can learn more about the differences between USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports.
Have a great day!
It so happened that recently, several times in a row, I was faced with the fact that when I tried to install ISO images from a flash drive
I couldn’t do this with various programs in Windows 10. After startup, either a cursor on a black screen or various inscriptions appeared on the monitor. Everything stopped there; attempts to wait for a while led to nothing. Nothing was loading. Installing an image from a USB drive simply froze without starting. I tried for a long time to find all sorts of solutions to this problem: I formatted the disk, downloaded the images again, re-uploaded them to other flash drives - but it was all in vain. From this I concluded that the problem, apparently, is not at all in the files or in my USB storage.
I began to guess that the problem lay in the structure of the flash drive itself. As usual, I began to google solutions to such problems. And I found a solution that has helped me out several times already. The big advantage of this method is that the Windows 10 ISO image already recorded on a flash drive does not need to be deleted, nor does it need to be formatted on the USB drive itself.
The point, apparently, is that when creating a bootable flash drive, we use a variety of programs to write ISO images. We often abuse the same drive with these experiments more than once. As a result, the internal layout changes, additional sectors invisible to us may appear, and existing ones may be modified. How exactly and why this happens is not important to us, as amateurs in general. It is important that neither deleting files from a flash drive, nor even completely formatting a USB drive often helps resolve this issue.
Of course, my solution to the problem with the inability to load an ISO image from a flash drive
far from the only one. Perhaps your reason will be completely different. But, nevertheless, since my method described below helped me personally, and more than once, I decided to write about it on my website.
So, if you have Windows 10
(or any other
ISO image
) doesn’t
want to boot from a USB drive
, then you need to work with this flash drive on any computer with Windows 7, 8 or 10 installed. What’s especially attractive to me personally is that all manipulations with our removable storage we will carry out this exclusively using the built-in tools of the Microsoft operating system itself, that is, without downloading and installing any third-party programs, and therefore without the threat of catching something painful, which, of course, we don’t need. It is also IMPORTANT that it is NOT NECESSARY to delete the ISO image already recorded on the flash drive!
Inconsistency of hardware and problems with its performance
First of all, let's look at one of the typical situations, which, according to most experts, does not allow installing the tenth modification on a specific computer device. We are talking specifically about the hardware. Despite the assurances of Windows 10 developers about the minimum system requirements, which are practically no different from those recommended for Windows 7, they are often much higher. The fact is that in a configuration with minimal compliance, initially it was possible to install only the very first versions of the system, and over time, although this is not advertised, the requirements have become quite stringent. Besides, why bother installing Windows 10 from a flash drive on a laptop that will obviously slow down? Please note that two Gigabytes of RAM and a mid-price dual-core processor are clearly not enough to install the latest builds today.
Another problem with Windows 10 not being installed from a flash drive is that the user initially incorrectly selects the bit depth of the future system. In this case, you should clearly understand that a 64-bit system will not work on computers or laptops with processors that support only the x86 (32-bit) architecture, no matter how much you might want it. But on the contrary - no problem. That is why you initially need to determine the characteristics of the hardware, and only then select the desired modification of the operating system.
But we can assume that the configuration is fully consistent, but the installer does not start. It is quite possible that Windows 10 does not load from a flash drive as an installer due to the fact that the port into which the media is inserted simply does not work. A similar situation can occur when you insert a flash drive designed for a USB 3.0 interface into a 2.0 port.
The most obvious solution is to reconnect the device to the correct connector.
Note: in order to avoid unexpected errors when starting the installer or at the OS installation stage, it is recommended to completely disable all additional peripheral devices for a while, leaving only the most necessary ones (mouse, keyboard, etc.), since during installation messages may be displayed indicating that that the system cannot find any suitable drivers.
Security issues on devices with ARM processors
Finally, let's look at another fairly serious situation that most computer and laptop users may not be aware of. The point is that quite often Windows 10 is not installed from a flash drive on tablets equipped with full USB ports. An error as such is not issued, but it may be impossible to boot from removable media. Why is that? Despite the fact that some types of tablets (for example, the Surface Pro and RT series) seem to have a pre-installed OS like the eighth version or its modification 8.1 and, in theory, should support updating to Windows 10, installing an OS of a lower rank or even other systems oriented for devices equipped with ARM processors, it’s not so simple either. The main problem concerns the fact that in such models, protection against unauthorized change of the pre-installed OS is installed directly in the primary system. To bypass it, if possible, you must first disable the so-called Secure Boot feature. However, this is not all.
In particular, on the Surface RT series tablets, even this does not help, since there is a TPM module built right into the motherboard, which cannot be bypassed even in principle (unless you unsolder it if it is impossible to disable it in the primary system, but it is possible that after such action, the device itself will not turn into a “brick”). Among other things, there is no normal version of Windows 10 for ARM processors. There is, of course, scant information that some of the XDA Developers group of enthusiasts were running Windows 10 Pro on such devices, which is believed to run natively on an ARM processor, but the technical details were not particularly disclosed. You can also find some modifications like Windows 10 IoT or even entire unofficial builds 1703, however, their use is also questionable, even though all the actions resemble the most common installation of Windows 10 from a flash drive to a laptop (Microsoft tablets are really are in many ways similar to ordinary transformable netbooks with touchscreen support). And not only the presence of the highest level of control over violations of the integrity of the system plays a negative role. In such systems, even standard x86 applications usually do not run, so the utility described above for upgrading to “ten”, downloaded from the official website, also turns out to be completely useless.
Why doesn't my computer boot from a flash drive?
Booting a computer from a flash drive is quite simple: in the BIOS you need to enter the appropriate section and set this media as the priority device. However, alas, things are not always simple. What difficulties can you encounter when trying to start a PC or laptop from an external USB drive? Some BIOS versions may provide for storage media a single item from the number of devices from which the computer can, in principle, boot.
Separate media list in BIOS
For the media themselves - flash drives, HDD, SSD, SD cards, etc. – in such cases, priority is configured in a separate list. The latter is not always displayed in the same section as other boot devices (usually called “Boot”) . Such a list may be contained separately, in another BIOS settings tab. For example, in the section for installing a priority storage medium (named “Hard Drive” or something similar) .
UEFI media
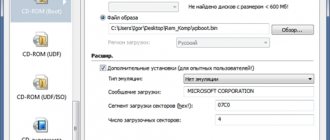
If the computer runs on BIOS UEFI - modern firmware that offers certain advantages, in particular, working with GPT disks, the process of installing Windows using such advantages will have its own nuances. The installation flash drive must contain program codes that adapt it to the new format of the base firmware. Not every program that writes bootable media can yet create one that is compatible with UEFI software. The software that can do this includes, for example, the official utility for downloading and burning the Windows 10 distribution from Microsoft, as well as the third-party program Rufus .
Selecting the correct loading point
It is not enough to create a UEFI flash drive as such; you must not make a mistake in choosing it in the BIOS. On UEFI computers, among the possible boot devices, it will be displayed twice - with the usual name and the same name (same manufacturer, same marking), but also with the prefix “UEFI” . Selecting a flash drive with such an annotation and the enabled UEFI interface are two conditions that make it possible to install Windows 8.1 and 10 on a GPT .
Secure Boot
Secure Boot technology supplied with the UEFI BIOS interface is a mechanism to prevent the launch of unauthorized software. The technology has been developed primarily to prevent malicious software codes from entering a computer. And it is precisely this that can become an obstacle to booting from external media if the latter contains, for example, an installer for a pirated build of Windows or a makeshift Live disk. In such cases, the technology must be disabled.
USB port
The installation flash drive for Windows 7 and older versions of the system must be connected to a USB 2.0 port. The distribution kit of older versions does not contain drivers compatible with USB 3.0 ports. The same applies to LiveDisk, the creators of which did not provide the ISO image with USB 3.0 drivers. But there are exceptions to this rule.
So, on certain computer devices, in particular, on some models of Acer with BIOS UEFI, on the contrary, you need to insert the Windows 8.1 and 10 installation media into the USB 3.0 port. Otherwise, the installation process will either freeze for no reason or generate errors.
No matter what situation we would be dealing with, if at a certain stage of the system installation process a failure occurs, we need to try connecting the flash drive to the USB port of a different version.
What should I do if the installer does not start from a flash drive, but the flash drive is visible in the primary system?
Despite the correctness of the steps described above, you can encounter another problem: Windows 10 cannot be installed from a flash drive, which is somewhat incomprehensible to many users. The device seems to be detected in the primary system, but when you try to start from it, the installer does not start. Why? As mentioned above, initially, when creating bootable media, two types of bootloader are assigned to it, and you can often see two flash drives appear in the list of available devices, one of which has an EFI prefix before the main name. If the BIOS is used as the primary system, you need to select regular media, and not one that is marked as an EFI boot loader.
How to install Windows 10 with 32 bits from a flash drive if UEFI is used as the primary system?
Here it is strongly recommended to change the main boot mode by simply switching it from UEFI to Legacy.
Note: one of the symptoms of an incorrect start may be damage to the file system, for example, if the flash drive is incorrectly removed from the port after recording the image. In this situation, it is better to check the disk using standard tools of the system itself or the command line, and if the firmware is damaged, download it from the official website and reinstall it. Low-level formatting programs are also a good idea, after which the image will need to be rewritten.
Reason 3: Inappropriate hard drive partition structure
During the installation of "tens", a message may appear stating that installation on the selected disk is impossible, since it has an MBR partition style. We wrote about this problem and ways to solve it earlier.
Read more: Resolving MBR disk errors during Windows 10 installation
The opposite situation also happens when installing Windows 10 is impossible because the disk has a GPT partition structure. You can learn how to solve this problem from the article provided at the link below.
Read more: Solving the problem with GPT disks when installing Windows
Burning an image
In addition to loading, the image must also be recorded correctly. Media Creation Tools will help with this again, which can immediately download and burn the image to a USB drive. But if suddenly MCT doesn't work, you can try other options.
One of the main mistakes that results in a laptop or PC not seeing a bootable Windows 10 flash drive is simply unpacking the image onto a disk or USB drive.
The ISO image can be unpacked using any archiver, but this is not recommended, since you will simply copy the files, but the flash drive will not be bootable and as a result, the Windows 10 installer will not see the flash drive.
To create a bootable flash drive, it is better to use other software - Rufus, USB/DVD Tools, UltraISO and many others.
Windows 10 won't boot - how to restore bootloader
Good time!
Despite the fact that Windows 10 has become a very reliable system (at least compare with Windows XP.), however, it is not immune to various problems. One of the most common and painful is refusal to boot. Most often, Windows 10 does not boot after you have installed a second OS on another disk partition, perhaps updated the system, or connected another hard drive (or SSD). In rare cases, the problem occurs due to incorrect operation of the antivirus.
In this article I will show you several ways to restore the bootloader and bring Windows 10 back to life. I think the information will be relevant for most novice users.
You might find this article about ways to restore Windows 10 (a kind of mini-instruction) useful. Link to it: https://ocomp.info/vosstanovlenie-windows-10.html