For some reason, most computer users have a very firmly ingrained opinion that the system disk is the partition of the hard drive in which the operating system was originally installed (which one plays absolutely no role in this case). But more advanced users understand this term more deeply. Why there might be such a difference in opinions, we next propose to consider in a little more detail, and at the same time we will try to find out what is actually meant when it comes to system drives.
The system disk is...
Yes, of course, in most cases, a system disk or partition refers to an area of the hard drive allocated for files and folders of the operating system.
As a rule, if the system is not installed, say, as a second OS, in a logical partition, in Windows this is drive “C” (everyone knows this). But let's see what other interpretations of the described term are found, and we will start not only from the user's understanding of the essence of the issue, but also from the knowledge of many computer scientists and experts who, as they say, ate the dog on such questions.
“Crutches” for GPT
To boot from GPT, Windows systems need:
- BIOS UEFI
- 64 bit system bit depth
And what should we do if we have a powerful server (we need a lot of disk space) - but only hardware with BIOS is available?
That's right - use a crutch!
In a nutshell:
- install Windows on a disk with MBR (the system will not allow installation on a disk with GPT on the BIOS)
- using a third-party utility to convert the disk layout to GPT
- In total, our Windows system is installed on GPT
- but of course there is no download - because... there is no MBR boot sector (more precisely, it exists - but is blocked from writing)
- but we really need it - and we have a flash drive or other disk with MBR
- we create an MBR boot sector there (which was where the BIOS should go to start) and transfer control to the OS boot loader (which is already on the GPT disk)
Bingo!
Here's more details:
https://winitpro.ru/index.php/2014/03/11/zagruzka-windows-7-s-gpt-na-bios-bez-uefi-2/
Attention! There is a lot of confusion in the names. The “hidden partition” is not visible to the system and cannot be booted from it, even if it is active. The Win7 System Recovery partition is not actually hidden (the system boots from it), it simply does not have a letter and therefore is not visible in Explorer.
Types of system disks
In general, if we approach the issue under consideration objectively, we can safely say that a system disk is a drive or, if you like, a memory area of a certain device that allows you to run the operating system itself, its installation tools, and recovery or error correction tools.
Thus, among all that is called system disks, the following devices can be distinguished in the classification:
- hard disks;
- logical partitions;
- removable boot and recovery devices;
- bootable antivirus applications.
How to prevent system reserved partition
During Windows installation
- When you run Windows Setup, you are prompted to create a primary partition for system files.
- Once you have created a new partition for your Windows installation, a System Reserved Partition is created automatically
- Select the primary partition, click "Delete", then click "OK" to confirm the pop-up window.
- Select the partition reserved for the system and click the Expand button. Now you can expand this partition by giving it all the unallocated space.
- Click on the latest format, then select this partition to install Windows.
System hard drive
As for this definition, this concept means either the entire hard drive with the operating system installed, if it is not divided into several partitions, or a dedicated (reserved) area of physical memory (volume) that is used by the OS to store its own files and folders necessary for its operation. correct operation.
In most cases, if you do not take into account the installation of a second system or virtual machine, the Windows system disk is partition “C” (this is the default, since previously the letters “A” and “B” were used for floppy disks, and for optical media - “E”, for bootable media – “X”, and for removable USB and other devices – all the rest). That is, it turns out that the system unit defines drive C by default. In the case of RAID arrays that combine several hard drives into one system, a special boot tool is used to select a partition from which to start.
Partitioning disks without losing data
Typical situation: you bought a computer with the OS installed, happily installed all the necessary software, transferred photos and videos, and then thought: why is there only one section? It's not too late, you can increase the division of the disk into virtual parts.
Rule #1 : Before doing anything with your hard drive or SSD, create a copy of it (BackUp). If there is too much information, keep at least the most important ones.
To create partitions on a HDD with Windows already installed, you can use a disk partitioning program. More precisely, software that can do this, among other things. These can be paid or free. Of the latter, we recommend Paragon Backup & Recovery Free.
You can do without third-party software, using the existing capabilities of the OS. How to partition a hard drive using Windows? The instructions won't be that complicated.
- Open the “Start” menu and right-click on “Computer” and find the “Manage” option in the context menu.
- In the window that opens, select “Disk Management” from the list on the left.
- Right-click on the C: drive area , and then in the context menu that appears, click “Shrink Volume.” The system will analyze the disk and suggest the maximum possible size to reduce the system partition. Specify the compression size so that the size of drive C is at least 150 GB.
- After shrinking the system partition, an “Unallocated” area will appear on the disk. Right-click on it and select “Create simple volume” from the context menu. If you want to create one logical disk, then confirm the proposed volume size.
- Do you need two or more sections? Specify your size for the first logical drive you create. Then confirm to format the partition—NTFS is suggested by default—and optionally specify the desired drive letter. Do the same with the next remaining area. Click Next and Finish.
Main files and folders
But what is located in the system partition by default immediately after installing the system? It goes without saying that these are OS files (the Windows directory containing the system disk files and additional directories).
Software components that are present initially or are installed by the user during operation are usually placed in the Program Files folder. But these are only the objects that the user sees. If you dig deeper, in the system partition you can also find folders related to a specific user if there are several accounts on the computer.
It is impossible to see all objects. The main thing here is that they are available for viewing only when you go to the Users directory on the local disk; some folders like AppData are not displayed even in the local user directories. However, setting the parameters for displaying all hidden objects is not so difficult, using the view menu with a checkmark on the corresponding line.
How to recover lost files?
If at any stage the user made a mistake and valuable information was deleted, we recommend using a specialized data recovery program RS Partition Recovery . This utility is able to quickly return important information that has been deleted, formatted, or destroyed by viruses. This way you can recover photos , video files , audio tracks , documents , program files and any other data.
Note that RS Partition Recovery has advanced operating algorithms that allow for in-depth analysis of the disk and recovery of long-deleted files . We recommend that you familiarize yourself with all the features and functions of the RS Partition Recovery utility for quick data recovery on the official RS Partition Recovery page.
On computers with x86 processors, the MBR partition can be marked as active using the Diskpart command line utility. This means that the computer will start booting from this partition. You cannot mark dynamic disk volumes as active. When you convert a basic disk with an active partition to a dynamic disk, that partition automatically becomes a simple active volume.
Can a logical partition be a system one?
This question is relevant only if not one, but several operating systems are installed on the computer. It doesn’t matter at all that one of them is Windows, and the other, say, Linux.
Even if there are two OSes from the same developer, they will never be installed on the same logical partition. Accordingly, when you turn on the computer and after checking the functionality of the equipment in the primary BIOS/UEFI systems, control of the computer is not transferred to the system kernel immediately, but only after a special boot loader is activated, in which you can select your preferred OS. If the system is installed on the “D” drive, say, the tenth version of Windows, the Windows 10 system drive will be defined as the specified virtual partition to start.
Do I need to partition the disk?
Each user decides whether to partition the hard drive independently. In some cases, for example, new laptops may already have additional partitions created by the device manufacturer.
Dividing a disk into partitions is not a necessary operation. Many computers run on one system partition, which takes up the entire physical hard drive.
Typically, the hard drive has several service partitions necessary to boot or restore the system. On systems with UEFI BIOS there are several such partitions, and on PCs with Legasy BIOS there is 1 partition with the MBR (Master Boot Record).
In addition to service partitions, the device may have a recovery partition created by the laptop manufacturer. We do not consider these additional service sections in this article.
Whether it is worth partitioning the disk into partitions, you will decide for yourself after thinking about the current situation on your PC. Check out the reasons for creating an additional partition on your computer's hard drive.
You can divide your hard drive into partitions in Windows in the following cases:
- To separate the operating system and installed software from other user data.
- For more efficient PC work and faster system maintenance.
Often, users separate the operating system from their other data: music, videos, photos, documents, etc. Windows with programs is located on one system partition of the disk, and the rest of the data is located on another partition. Typically, these are local drives: “C” for the system and “D” for all other data.
If, as a result of failures and malfunctions on the computer, the user reinstalls the operating system, then all information from the system partition will be deleted, and the data located on another partition of the hard drive will be saved.
If you put things in order on your computer, it will be much more productive to work because it is easier for the user to find the necessary files located on certain sections than in a situation where all the information is jumbled together in one place. System maintenance programs will perform their work faster on the system partition without unnecessary data, because the disk size will be smaller.
In addition, viruses are more likely to infect the C drive, so data on the D drive has a better chance of avoiding infection from malware.
Based on the above, decide for yourself whether you need to partition your hard drive or not. You can not change anything and continue to use the hard drive without creating new partitions on it, especially if your PC has a small hard drive.
Some laptops and desktop PCs use a hybrid design of two physical drives: an SSD (solid-state drive) and an HDD (hard drive). In this configuration, the Windows operating system and application programs are installed on the SSD, and other user data is located on the HDD. In this case, there is no need to create additional partitions on the computer's SDD disk.
Bootable removable media
Installation media can also be equally designated by the term described. For example, a removable system disk of Windows 7 or any other OS is a medium that contains an installation distribution or recovery tools.
Using such tools, you can perform many actions that may not be available in a loaded OS. For example, the same command line, when the entire stationary system, roughly speaking, “crashes,” allows you to use standard commands to restore its functionality, even though the console itself is launched from removable media.
Separately, it is worth noting operating systems of the so-called portable type, for which installation exclusively on the hard drive is not required.
The simplest example is the same version of Windows 7, the files of which are written to an optical DVD disk, and after installing it as a priority boot device, you can work with the system as easily as if it were installed directly on the hard drive.
The main and logical partitions of the hard drive: their essence and conversion from one type to another
Hard disk partitions (also called volumes, also known as partitions from the English partition) can be primary or logical. Another name for the main type of disk partition is primary. Primary (or primary) disk partitions are used to run the operating system. This is the system partition C, where Windows is directly installed, and a small partition with reserved space (100 MB, 350 MB or 500 MB), which, starting with version 7, is created for the needs of the operating system. Logical disk partitions are functionally no different from the main ones. Both on the main and on the logical partitions of the disk - both there and there information is stored. The difference is that Windows cannot be started from a logical disk partition. If you turn the system partition C from primary to logical, Windows, not in all cases, but in most cases, will be able to fully function.
But in all cases it will not want to boot if it is logical to make it a technical small partition with reserved space, where, in particular, the download data is stored.
Below we will talk in detail about the essence of the main and logical partitions of the hard drive, and also consider ways to convert their type from one to another and vice versa.
Content:
- Limit on the number of primary partitions on a disk;
- Formation of main and logical partitions;
- Why change the logical disk partition to the primary one and vice versa;
- Installing Windows on a logical disk partition;
- Acronis Disk Director 12 program for solving assigned tasks;
- Converting a primary disk partition to a logical partition and vice versa;
- In conclusion.
Limit on the number of primary partitions on a disk
One hard drive should have no more than 4 main partitions, if there are no logical ones. If there is a need to create more than 4 disk partitions, the created 4th partition and all subsequent partitions must be logical. So, after the three main sections have been created, the 4th section, called additional or extended, will be something like a container, which, in turn, can be divided into many logical sections.
Formation of main and logical partitions
The standard Windows disk management utility does not provide the user with the ability to select the type of disk partition. The utility itself provides the optimal layout for most cases. The first 3 sections it creates are the main ones by default. And, starting from the 4th, all partitions created by the utility are automatically created as logical.
A third-party disk space manager, the AOMEI Partition Assistant program, works on exactly the same principle. The first three sections with default settings are created as main ones, and starting from the 4th – as logical ones. But, unlike the standard Windows utility, AOMEI Partition Assistant provides an advanced settings mode for creating disk partitions, where you can manually select a primary or logical type for the first three partitions to be created.
Another fan of template presets is the Paragon Hard Disk Manager program. Its default settings for creating disk partitions are also designed to create the first three partitions as the main ones. And, as in the previous program, when creating the first three sections, you can manually change the preset main type to logical, which is significant in the program as an extended one.
But Acronis Disk Director does not adhere to template parameters. The default form for creating a new disk partition involves creating a logical partition. The partition type parameters must be reassigned manually - to create the main partition, respectively, check the boxes next to the “Primary” inscription and next to the “Active” inscription if a partition is being created for Windows.
Why change the logical disk partition to the primary one and vice versa?
In what cases may it be necessary to change the logical type of a disk partition to primary and vice versa? The need to carry out the first operation is, as a rule, those very cases of unsuccessful experiments with converting Windows system partitions from primary to logical. These are also cases of problems with Windows installation when only logical partitions were initially created on the hard drive.
The need for the reverse operation - to convert the primary partition into a logical one - arises when there are more primary partitions on the disk than are needed for specific situations. For example, in the case of restoring Windows from a backup to a partition different from the original one. We are talking about transferring the system to another, already distributed hard drive, where it is necessary to preserve the structure and data of non-system partitions, and restore the “lived-in” Windows to the system partition from a backup copy. If the hard drive has 4 primary partitions with no logical partitions, or 3 primary partitions and all the others are logical, backup programs will in some cases refuse to perform the Windows restore operation. Since the backup copy may contain more than one system partition C, but also the technical partition mentioned above with reserved space for Windows needs. This small partition and the system partition C, upon completion of the recovery operation, if it were possible, would divide the main destination partition into two partitions, also the main ones. And thus the rule would be broken - either 4 main sections without logical ones, or 3 main sections, and all the rest are logical. In this case, the problem is solved like this: one of the non-system partitions where user data is stored is converted from primary to logical, which, in fact, is what it should be.
Installing Windows on a logical disk partition
If there are primary partitions on the hard drive, even if Windows is purposefully installed on a logical partition, the operating system itself converts it into the primary partition during the installation process. Windows will even get out of a situation when the main partition limit is reached. It will simply set up a technical section for itself on any available main section.
But if there are only logical partitions on the hard drive, Windows will not want to be installed at the stage of selecting a disk partition. Things will be easiest if there is no data on the disk or if it is not important. In this case, the problem can be easily solved using the available tools on the operating system installation disk itself. Existing logical disk partitions are deleted using the “Delete” button,
and in their place new sections are formed using the “Create” button.
On the Windows 7 installation disk, to access these buttons you need to click the “Disk Setup” option.
If you don’t need to partition the disk, for example, when it’s a 60 GB SSD, you can not create any partitions and install Windows directly on the “Unallocated Disk Space”.
But when there is a large amount of data on the hard drive, then you cannot do without special programs for working with disk space. It is necessary to convert the partition on which you plan to install Windows from logical to primary.
Acronis Disk Director 12 program for solving assigned tasks
The primary or logical type assigned when creating a partition cannot subsequently be changed using the standard Windows Disk Management utility. To do this, you will need to resort to more functional solutions in the form of third-party programs for working with computer disk space, which will be able to carry out the operation without deleting the partition, while preserving its data. Compared to competitors in terms of assigning disk partitions of the main or logical type, Acronis Disk Director 12 compares favorably with the presence of “fool protection”. While, for example, Paragon Hard Disk Manager will thoughtlessly agree to an experiment to convert a technical Windows partition from a primary to a logical one, Acronis Disk Director will carefully warn you about all the negative consequences of the planned operation.
Acronis Disk Director 12 is such a smart program that even if this operation is confirmed, only the effect of the operation will occur, so to speak, a deception for the “especially persistent”. Nothing will really change, and after rebooting Windows, the technical partition of the system will remain the main one, as before.
For critical cases when Windows does not boot or is simply not installed yet, Acronis Disk Director 12 provides for the creation of bootable media in its interface.
After the welcome window, select “Windows-like presentation” of the bootable media.
We skip the step with Linux kernel parameters.
We choose bootable media with UEFI support for computers based on this BIOS or limit ourselves to the regular version for 32-bit systems. The choice is only important for BIOS UEFI.
Next, we determine the media type and follow the appropriate steps of the wizard to complete the process.
Finally, set the boot priority from the selected media in the BIOS and launch Acronis Disk Director 12.
Converting a primary disk partition to a logical partition and vice versa
In the Acronis Disk Director 12 window, be it a desktop program window or an installation media interface, select the desired disk partition. You can choose either in the disk partition table at the top or in their visual representation below. Call the context menu on the section. If this is the main partition, select the “Convert to logical” function.
We confirm the decision.
Apply a pending operation.
Once again we confirm the decision by clicking the “Continue” button.
The partition has been converted to logical.
The operation to convert a logical disk partition into a primary one occurs in a similar way. On the selected logical partition, in the context menu, select the “Convert to primary” function.
In some cases, returning the Windows technical partition to the main type in this way will require additional recovery of the boot sector.
In conclusion
I would like to end this article with a parting word for beginners who are going to experiment with computer disk space. It is not necessary to check the potential of professional software in this area on the physical disk of the computer. For these purposes, using Windows tools (in the same disk management utility), you can create a virtual VHD disk, initialize it and conduct various kinds of experiments with it.
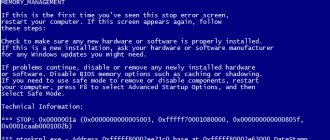
Problems when loading the system and methods for solving them
In general, I think it is already clear that a system disk is a very flexible concept, and it cannot be attributed to any one type. But let's look at some possible system startup errors, when the standard recovery tool (rolling back to the previous state point) does not work or simply does not have an effect.
Usually you can use a special boot menu, which is called up when the computer starts by pressing the F8 key and selecting to load the last working configuration. If this does not help, you should use the safe mode call.
The best option is to start from removable media and then call the command console. There are quite a lot of tools here, but the main ones include the system file checker with sfc /scannow recovery, online system recovery when loading DISM network drivers, as well as resuscitation of boot records and even complete rewriting of the bootloader using the Bootrec.exe tool, which uses several additional parameters.
... and user habits
And then it turned out that many users who skipped Windows Vista are trying to squeeze Windows 7 onto the same partition where XP was installed, or a similar one in size. But after installing the system, it suddenly turns out that there is very little space left on the partition!
Of course, because the size of the distribution has grown 3-4 times, from 600 MB Windows XP to 2.1 - 2.4 GB Windows 7, depending on the bit depth. But that's not so bad! The amount of RAM has grown from the “luxurious” 512 MB for XP to 2-4, or even 8 GB, which immediately affected the size of the paging files (1.5 RAM volume) and hibernation files (0.75 RAM volume).
Paging and hibernation are usually dealt with quickly, but very soon they discover that there is still not enough space.
The operating system is constantly updated, increasing in size to the point of obscene size. People's anger turns to the winsxs folder, which for particularly indignant users is punished through castration (and some of the executions occur on a system that has been cut off by someone else's hands).
But this doesn’t help either! Distributions of your favorite programs have grown fat over the years from Big Macs, and after installation they eat up precious space. Office 2003 managed with a modest 400 MB of disk space, while Office 2010 requires 3 GB for itself, brazenly storing installation files in the gigabyte MSOCACHE folder.
It would seem that in such a situation the idea arises of allocating as much space on your disk for Windows as it needs, fortunately terabyte drives allow this!
Even netbooks from one and a half to two years ago already had 320 GB disks installed. What can we say about the market of drives for desktop systems, where the “1 TB and above” segment is dominant for 7200 rpm drives (the offer of the leading American online seller newegg.com is shown)
Antivirus programs
Finally, it can be noted that the anti-virus system disk is one of the main tools with a built-in bootloader, which allows you to neutralize most known threats even before the main OS starts.
In this case, we mean that the Rescue Disk utility is first loaded from the removable device, in which you can choose to use a graphical interface similar to that presented in Windows, and then mark all the necessary areas for scanning and perform the most complete scan for threats . By the way, it is precisely such programs that allow you to get rid of viruses that in a working system cannot be detected by any means at all and are located exclusively in RAM.
conclusions
As already understood, it is impossible to call the logical partition on the hard drive selected for installing the OS a system disk, since, based on the information above, there can be quite a lot of varieties. In addition, here it is also worth paying attention to some well-established stereotypes: users call the system disk partitions with the OS on the HDD, system specialists tend to identify system disks with removable media on which there are recovery or development tools, so you won’t immediately understand which one them right. As it turns out, both are right. But I would like to hope that even such a brief consideration of the issue will still give some idea of what it is.
Creating an EFI partition on an empty hard drive in the command line
So, we have a medium initialized as GPT without markup and data.
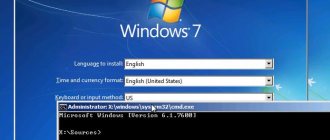
Launch the command line.
Be sure to do this on behalf of the administrator.
We enter one by one:
diskpart lis disk sel disk 1 (instead of 1, indicate the number under which the hard drive you need is listed above) creat par efi size=100 format fs=FAT32
In the disk management utility we see that a 100 MB EFI partition has appeared on the second hard drive. Now we can create a regular partition to indicate it to programs like WinNTSetup or WinToHDD as a system partition C.