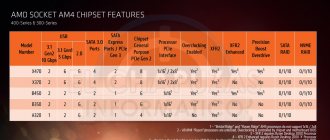
Chipset and its main characteristics
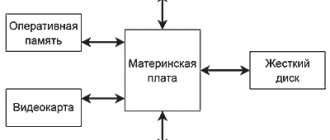
First, let’s look at what is hidden behind the word “chipset”. This is a set of chips that is installed on the computer's motherboard. Its second name is a set of system logic. Until recently, it necessarily included two components: the north and south bridges. Now the north bridge is integrated into the central processor. The south bridge remains on the motherboard, which ensures the interaction of computer system components with peripheral devices and expansion cards in PCI and PCI Express slots. The main parameters of any chipset are the following: socket, list of supported processors, set of interface ports and type of supported RAM.
For servers and workstations
All server chipsets do not have a built-in video core due to their uselessness. To display images on a monitor, they sometimes use discrete video cards or those directly built into the motherboard (processor). Processor index values: UP/EN/W - single-processor configurations, 3xxx/C2xx/C4xx chipset family DP/EP - dual-processor configurations, 5xxx/C6xx chipset family MP/EX/SP - multi-processor configurations, 7xxx/C6xx chipset family
Early chipsets
3000, 5000 and 7300 series for Core 2 processors
| Chipset (northbridge) | Codename | Type | release date | South Bridge | Tire | PCI Express support | RAM support | Maximum amount of RAM |
| Core-UP | ||||||||
| 3000 | Mukilteo | MCH | 2006/8 | ICH7, ICH7R | FSB (533/800/1066 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | 1 PCI-Express x8 1.0a | DDR2 533/677 | up to 8 GB |
| 3010 | Mukilteo 2 | MCH | 1 PCI-Express x16 1.0a | |||||
| 3200 | Bigby | MCH | 2007/11 | ICH9, ICH9R | FSB (800/1066/1333 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | 1 PCI-Express x8 1.1 | DDR2 677/800 | |
| 3210 | MCH | 1 PCI-Express x16 1.1 | ||||||
| Core-DP | ||||||||
| 5000V | Blackford | MCH | 2006/5 | 6311ESB, 6321ESB | FSB (800/1066/1333 MHz) ESI (2 GB/s) | No | FBD DDR2 533/677 | up to 32 GB |
| 5000Z | MCH | |||||||
| 5000P | MCH | 3 PCI-Express x8 1.0a | up to 64 GB | |||||
| 5000X | Greencreek | MCH | ||||||
| 5100 | San Clemente | MCH | 2007/10 | ICH9, ICH9R | DDR2 533/677 | up to 48 GB | ||
| 5400 | Seaburg | MCH | 2007/11 | 6311ESB, 6321ESB | FSB (1066/1333/1600 MHz) ESI (2 GB/s) | 4 PCI-Express x8 2.0 | FBD DDR2 533/677 | up to 128 GB |
| Core-MP | ||||||||
| 7300 | Clarksboro | MCH | 2007/11 | 6311ESB, 6321ESB | FSB (800/1066 MHz) ESI (2 GB/s) | 3 PCI-Express x8 1.0a 1 PCI-Express x4 1.0a | FBD DDR2 533/677 | up to 256 GB |
3400, 5500 and 7500 series for Nehalem processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support | FDI support |
| Nehalem-EP | |||||||||
| 3400 | Ibex Peak | PCH | 2009/9 | DMI (2 GB/s) | 6 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 8 USB 2.0 | 4 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) | No | No |
| 3420 | PCH | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 12 USB 2.0 | 6 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) | Yes | ||||
| 3450 | PCH | 14 USB 2.0 | HDMI, DVI, VGA, SDVO, DisplayPort | ||||||
| Chipset (northbridge) | Codename | Type | release date | South Bridge | Tire | PCI Express support | RAM support | Maximum amount of RAM | |
| Nehalem-EX | |||||||||
| 5500 | Tylersburg | IOH | 2009/5 | ICH9, ICH9R ICH10, ICH10R | QPI (25.6 GB/s) ESI (2 GB/s) | 1 PCI-Express x16 2.0 2 PCI-Express x4 2.0 | No | No | |
| 5520 | IOH | 2 PCI-Express x16 2.0 1 PCI-Express x4 2.0 | |||||||
| 7500 | Boxboro | IOH | 2010/3 | ICH10, ICH10R | 2 PCI-Express x8 2.0 1 PCI-Express x4 2.0 | ||||
C200 and C600 series for Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support | FDI support |
| Sandy Bridge-EN and Ivy Bridge-EN | |||||||||
| C202 | Cougar Point | PCH | 2011/4 | DMI 2.0 (4 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 12 USB 2.0 | 6 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) | Yes | No |
| C204 | PCH | 4 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 2 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | |||||||
| C206 | PCH | 14 USB 2.0 | HDMI, DVI, VGA, eDP, DisplayPort | ||||||
| C216 | Panther Point | PCH | 2012/5 | 10 USB 2.0 4 USB 3.0 | |||||
| Sandy Bridge-EP and Ivy Bridge-EP | |||||||||
| C602 | Patsburg | PCH | 2012/3 | DMI 2.0 (4 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 14 USB 2.0 | 4 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 2 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) 8 SAS (3 Gbit/s) | Yes | No |
| C602J | PCH | ||||||||
| C604 | PCH | ||||||||
| C606 | PCH | ||||||||
| C608 | PCH | ||||||||
C220 and C610 series for Haswell and Broadwell processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support | FDI support |
| Haswell-EN | |||||||||
| C222 | Lynx Point | PCH | 2013/6 | DMI 2.0 (4 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 8 USB 2.0 2 USB 3.0 | 4 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 2 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | Yes | No |
| C224 | PCH | 8 USB 2.0 4 USB 3.0 | 2 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 4 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | ||||||
| C226 | PCH | 8 USB 2.0 6 USB 3.0 | 6 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) | VGA | |||||
| Haswell-EP and Broadwell-EP | |||||||||
| C612 | Wellsburg | PCH | 2013/9 | DMI 2.0 (4 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 8 USB 2.0 6 USB 3.0 | 10 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) | Yes | No |
C230, C420 and C620 series for Skylake and Kaby Lake processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support |
| Skylake-S/EN and Kaby Lake-S/EN | ||||||||
| C232 | Sunrise Point | PCH | 2015/8 | DMI 3.0 (8 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 6 USB 2.0 6 USB 3.0 | 6 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) | Yes |
| C236 | PCH | 20 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 4 USB 2.0 10 USB 3.0 | 8 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) | ||||
| Skylake-W | ||||||||
| S422 | n/a | PCH | 2017/7 | DMI 3.0 (8 GB/s) | 24 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 4 USB 2.0 10 USB 3.0 | 8 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) | Yes |
| Skylake-SP | ||||||||
| S621 | Lewisburg | PCH | 2017/7 | DMI 3.0 (8 GB/s) | 20 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 4 USB 2.0 10 USB 3.0 | 14 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) | Yes |
| S622 | PCH | |||||||
| S624 | PCH | |||||||
| S625 | PCH | |||||||
| S626 | PCH | |||||||
| S627 | PCH | |||||||
| S628 | PCH | |||||||
C240 series for Cascade Lake processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support |
| Cascade Lake-EN | ||||||||
| C242 | n/a | PCH | 2018/7 | DMI 3.0 (8 GB/s) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| C246 | PCH | |||||||
| Cascade Lake-SP | ||||||||
Which socket is this set of system logic designed for?
A socket is a processor socket on a motherboard. A central processing unit is installed in it. As a rule, the designation indicates the number of contacts. Any Intel H81 motherboard is focused on processor solutions based on socket 1150. Moreover, only the Haswell and Haswell Refresh generations of CPUs are supported. In the latter case, it may be necessary to update the BIOS so that the system logic set begins to detect the central processing unit. But the most productive solution for socket 1150, BroadWell, cannot be installed in such motherboards: they are not supported by this set of system logic.
LGA 1150 socket overview
Socket LGA 1150, also known as Socket H3, is a processor socket designed to accommodate Intel processors with Haswell and Broadwell architecture.
Haswell is an architecture that was introduced in 2013 and is the next step after the Ivy Bridge architecture. Following the Tick-Tock strategy, Haswell's architecture was built on a 22nm process technology. This architecture brought changes to the processor cache memory, support for AVX2 instructions, as well as improved energy efficiency. Haswell is the fourth generation in the Core processor line; therefore, the index of Core processors with this architecture begins with the number 4. For example, Core i3-4130.
Broadwell is the next architecture after Haswell. According to the Tick-Tock strategy, the Broadwell architecture was built on a new 14 nanometer process technology. Broadwell is the fifth generation in the line of Core processors; accordingly, the index of Core processors with this architecture begins with the number 5. For example, Core i7-5775C.
Below is a table listing all processors that are compatible with Socket 1150. You can use this information to help you select a processor, but you should be aware that matching the socket on your motherboard and processor does not guarantee compatibility. If you are planning to purchase a processor, then you need to additionally check on the motherboard manufacturer's website whether this particular processor is supported by your motherboard. Otherwise, you run the risk of buying a processor and then discovering that it refuses to work on your existing board.
Chipset niche
As noted earlier, H81 is the base chipset of the 1150 processor socket, which is inferior in functionality even to the Intel B85. Accordingly, the niche of this set of system logic is the most affordable computer systems with a low level of performance by today's standards. That is, CPUs of the Celeron and Pentium series can most often be found in such motherboards, and much less often - Cor I3. Such PCs are used in offices, educational institutions and in other cases where there are no special requirements for the computing power of the computer.
Motherboard socket
The socket is the set of pins and security mechanism that holds the processor in place and connects the motherboard to the available processing power. There are different sockets depending on which processor is supported. If a situation arises where the processor and socket are incompatible, the best case scenario is that the component will not be physically able to connect to the socket, while the worst case scenario could be irreparable damage to any part of the system.
Luckily, it's easy to find out and check whether the processor you're considering will work with a particular motherboard. It's generally a good idea to first select a processor that provides you with the socket you need, which makes buying a motherboard a little easier. For example, the Ryzen 5 3600X will require an AM4 motherboard, and the Intel Core i5-9600K will require an LGA 1151.
Estimated cost of solutions based on this set of system logic
Since H81 is the most affordable set of system logic, its cost is relatively low. Even Intel B85 costs much more. The most affordable H81-based motherboards can be purchased for $50. But there are also slightly more functional solutions that can be purchased for $63. Well, it is not practical to make more expensive motherboards based on this chipset. The niche above $63 is occupied by more functional system logic sets, the capabilities of which are significantly better than those of the H81.
Peculiarities
Intel H81 boasts the following list of technical specifications:
- Only the processor and graphics accelerator can be overclocked. But support for increasing the RAM frequency is not implemented. Therefore, it will not be possible to maximize the potential of any Intel CPU with the “K” index (that is, with an unlocked multiplier). And installing something more productive than budget Celerones or Pentiums into such a motherboard is completely impractical.
- The motherboard is equipped with only 2 slots for installing RAM. Accordingly, the maximum amount of RAM in such a computer system is 16 GB (2 modules of 8 GB each). The supported RAM type is DDR3. The maximum permissible operating memory frequency is 1600 MHz. You can, of course, try to install faster modules on such a motherboard, but this will not give a significant performance gain. The RAM frequency will automatically drop to 1600 MHz and the performance level will remain exactly the same as if the PC had 1600 MHz RAM.
- The maximum number of USB 2.0 ports is 8, and USB 3.0 is 2.
- There are two SATA 2.0 ports for connecting a hard drive, a solid-state drive, and an optical drive. Exactly the same number of SATA 3.0 ports for similar purposes.
- 6 PCIe version 2.0 ports for installing expansion cards are provided in the H81 Express.
- The semiconductor chip of the system logic set is manufactured using exactly the same technological process as the CPU (14 nm).
- The thermal package of the chipset is 4.1 W.
For mobile computers
960 and 4 series for Core 2 processors
| Chipset (northbridge) | Codename | Type | release date | South Bridge | Tire | PCI Express support | RAM support | Maximum amount of RAM | Built-in video core support |
| GL960 | Crestline | GMCH | 2007/6 | ICH8M | FSB (533 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | No | DDR2 533 | up to 2 GB | Intel GMA X3100 |
| GLE960 | GMCH | ||||||||
| PM965 | MCH | 2007/5 | ICH8M, ICH8M-E | FSB (533/667 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | 1 PCI-Express x16 1.0 | DDR2 533/667 | up to 4 GB | No | |
| GM965 | GMCH | Intel GMA X3100 | |||||||
| GME965 | GMCH | 2007/6 | |||||||
| GL40 | Cantiga | GMCH | 2008/8 | ICH9M | FSB (667/800 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | 1 PCI-Express x16 1.0 | DDR2 667/800 DDR3 667/800 | up to 4 GB | Intel GMA 4500MHD |
| GS40 | GMCH | 2009/6 | ICH9M-SFF | FSB (800 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | |||||
| PM45 | MCH | 2008/6 | ICH9M, ICH9M-E | FSB (667/800/1066 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | DDR2 667/800 DDR3 667/800/1066 | up to 8 GB | No | ||
| GM45 | GMCH | DDR2 667/800 DDR3 667 | Intel GMA 4500MHD | ||||||
| GS45 | GMCH | 2008/8 | ICH9M-SFF | FSB (800/1066 MHz) DMI (2 GB/s) | DDR2 667/800 DDR3 667/800/1066 |
5 series for Nehalem processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support | FDI support |
| PM55 | Ibex Peak | PCH | 2009/9 | DMI (2 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 14 USB 2.0 | 6 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) | Yes | No |
| HM55 | PCH | 6 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 12 USB 2.0 | 4 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) | No | HDMI, DVI, VGA, SDVO, DisplayPort, eDP | |||
| HM57 | PCH | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 14 USB 2.0 | 6 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) | Yes | ||||
| QM57 | PCH | ||||||||
| QS57 | PCH |
- Like chipsets for desktop computers, mobile versions also took over the functions of the “southern” one and became a PCH bridge. According to the manufacturer Intel, the reduction of two chipsets to one has significantly simplified the board layout and reduced overall power consumption, which is very important for mobile computers to increase their autonomy.
6 and 7 series for Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support | FDI support |
| Sandy Bridge-M | |||||||||
| HM65 | Cougar Point | PCH | 2011/1 | DMI 2.0 (4 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 12 USB 2.0 | 4 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 2 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | No | HDMI, DVI, VGA, SDVO, DisplayPort, eDP, LVDS |
| HM67 | PCH | 14 USB 2.0 | Yes | ||||||
| QM67 | PCH | 2011/2 | |||||||
| QS67 | PCH | ||||||||
| UM67 | PCH | No | |||||||
| Ivy Bridge-M/U/Y | |||||||||
| HM70 | Panther Point | PCH | 2012/4 | DMI 2.0 (4 GB/s) | 4 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 6 USB 2.0 2 USB 3.0 | 3 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 1 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | No | HDMI, DVI, VGA, SDVO, DisplayPort, eDP, LVDS |
| HM75 | PCH | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 12 USB 2.0 | 4 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 2 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | |||||
| HM76 | PCH | 8 USB 2.0 4 USB 3.0 | |||||||
| HM77 | PCH | 4 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 10 USB 2.0 4 USB 3.0 | Yes | |||||
| QM77 | PCH | 2012/6 | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | ||||||
| QS77 | PCH | ||||||||
| UM77 | PCH | 2012/4 | 6 USB 2.0 4 USB 3.0 | 3 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 1 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | HDMI, DVI, SDVO, DisplayPort, eDP | ||||
8 and 9 series for Haswell and Broadwell processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support | FDI support |
| Haswell-H/M/U1/Y1 and Broadwell-H/M/U1/Y1 | |||||||||
| HM86 | Lynx Point | PCH | 2013/6 | DMI 2.0 (4 GB/s) | 8 PCI-Express x1 2.0 | 12 USB 2.0 2 USB 3.0 | 2 SATA 2.0 (3 Gb/s) 2 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) | No | VGA |
| HM87 | PCH | 10 USB 2.0 4 USB 3.0 | 2 SATA 2.0 (3 Gbit/s) 4 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbit/s) | Yes | |||||
| QM87 | PCH | ||||||||
| HM97 | Wildcat Point | PCH | 2014/5 | ||||||
- 1 They are a system on a chip (SoC) consisting of a processor and a chipset integrated on a single substrate.
100 and 200 series for Skylake and Kaby Lake processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support |
| Skylake-H/U1/Y1 | ||||||||
| HM170 | Sunrise Point | PCH | 2015/10 | DMI 3.0 (8 GB/s) | 16 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 6 USB 2.0 8 USB 3.0 | 4 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbps) | Yes |
| QM170 | PCH | |||||||
| CM236 | PCH | 20 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 4 USB 2.0 10 USB 3.0 | 8 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) 3 SATA Express (8 Gb/s) | ||||
| Kaby Lake-H/U1/Y1 | ||||||||
| HM175 | n/a | PCH | 2017/1 | DMI 3.0 (8 GB/s) | 16 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 6 USB 2.0 8 USB 3.0 | 4 SATA 3.0 (6 Gbps) | Yes |
| QM175 | PCH | |||||||
| CM238 | PCH | 20 PCI-Express x1 3.0 | 4 USB 2.0 10 USB 3.0 | 8 SATA 3.0 (6 Gb/s) 3 SATA Express (8 Gb/s) | ||||
- 1 They are a system on a chip (SoC) consisting of a processor and a chipset integrated on a single substrate.
300 series for Coffee Lake and Cannon Lake processors
| Chipset | Codename | Type | release date | Tire | PCI Express support | USB support | Drive support | RAID support |
| Coffee Lake-H/U1 and Cannon Lake-U1/Y1 | ||||||||
| HM370 | n/a | PCH | 2018/2 | DMI 3.0 (8 GB/s) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| QM370 | PCH | |||||||
| CM246 | PCH | |||||||
- 1 They are a system on a chip (SoC) consisting of a processor and a chipset integrated on a single substrate.
Motherboards from Asus
Many entry-level motherboards are based on the Intel H81. Asus, for example, offers 6 similar solutions based on this set of system logic. The most affordable of them is H81I-Plus. This motherboard is manufactured in the mATX form factor. It has 2 slots for RAM, one slot for a video card and is very small in size, which allows it to be used in compact computer systems.
The Asus H81M-Plus has a similar layout, but the size is increased and there are three additional PCI Express 1.0 slots. But the form factor is the same - mATX. This motherboard can no longer be used in compact systems. Three more motherboards - H81M-A, H81M-C and H81M-E - differ from the H81I-Plus only in the set of wired interface ports. Otherwise, these are almost identical solutions based on Intel H81, mATX format and with the same level of functionality.
The Asus H81-Plus, which is manufactured in the ATX format, differs significantly from all previously listed motherboards. It additionally has three PCI slots.
Review and testing of ASRock H81 PRO BTC, Asus H81-Plus and MSI H81-P35 motherboards
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Specifications
- Packaging and equipment
- Design and features of motherboards
- Cooling system
- Processor and RAM power subsystems
- Connectors and additional controllers
- PCI-Express, PCI: expansion slots and additional controllers
- Hardware implementation of BIOS
- Setup BIOS: ASRock H81 PRO BTC
- Setup BIOS: Asus H81-Plus
- Setup BIOS: MSI H81-P35
- Testing methodology
- Test results
Introduction
Recently, our portal began publishing group reviews of budget-class motherboards, for each of which three or four models were selected.
In addition to the price segment, they were united by the used system logic sets and price. At the moment, only five such materials have been published - four are dedicated to AMD platforms and one to Intel:
- AMD A88X and mATX: review of Asus A88XM-A, Gigabyte GA-F2A88XM-HD3 and MSI A88XM-E35 motherboards;
- Two pairs of twins: review of ASRock FM2A78M-HD+ and FM2A88M-HD+ motherboards, Microstar A78M-E45 and A88XM-E45;
- AMD A55 and mATX: review of ASRock FM2A55M-HD+, Asus A55BM-K and MSI A55M-E35 motherboards;
- AMD A78 and mATX: review of Asus A78M-A, ASRock FM2A78M-DG3+ and MSI A78M-E35 motherboards;
- Review of ASRock Fatal1ty H97 Performance, Asus H97-PLUS and MSI H97 Guard-Pro motherboards.
Thanks to our partner, the Regard company, the subject of a new review will be three motherboards based on the H81 system logic set, designed to install LGA 1150 processors.
Specifications
announcements and advertising
2080 Super Gigabyte Gaming OC for 60 rubles.
Compeo.ru - the right comp store without any tricks
RTX 2060 becomes cheaper before the arrival of 3xxx
Ryzen 4000
series included in computers already in Citylink
The price of MSI RTX 2070 has collapsed after the announcement of RTX 3xxx
Core i9 10 series is half the price of the same 9 series
The price of memory has been halved in Regard - it’s more expensive everywhere
To begin with, we present a table of technical specifications, the differences in characteristics are highlighted (photos in the table are clickable, clicking will open a full-size photo).
| Parameter | ASRock H81 PRO BTC | Asus H81-Plus | MSI H81-P35 |
| Weighted average price* | 3 000 | 3 150 | 3 050 |
| Package | |||
| Motherboard | |||
| back side | |||
| Link | Motherboard page on the manufacturer's website | Motherboard page on the manufacturer's website | Motherboard page on the manufacturer's website |
| Processors | The fourth and fifth generation of Intel Core, Intel Pentium and Intel Celeron processors designed for installation in the LGA 1150 processor socket | ||
| System logic set | Intel H81 Express Chipset | Intel H81 Express Chipset | Intel H81 Express Chipset |
| RAM | 2 x DDR3 DIMM sockets Supported memory capacity - up to 16 GB (unbuffered, non-ECC) Supports dual channel mode and Intel XMP Supports DDR3 1066/ 1333/ 1600 MHz | 2 x DDR3 DIMM sockets Supported memory capacity - up to 16 GB (unbuffered, non-ECC) Supports dual channel mode and Intel XMP Supports DDR3 1066/ 1333/ 1600 MHz | 2 x DDR3 DIMM sockets Supported memory capacity - up to 16 GB (unbuffered, non-ECC) Supports dual channel mode and Intel XMP Supports DDR3 1066/ 1333/ 1600 MHz |
| Audio | Realtek ALC662 (up to 6 channels) | Realtek ALC887 (up to 8 channels) | Realtek ALC887 (up to 8 channels) |
| Net | 1 x Realtek RTL8111GR (10/100/1000 Mbps) | 1 x Realtek RTL8111G (10/100/1000 Mbps) | 1 x Realtek RTL8111G (10/100/1000 Mbps) |
| Expansion slots | 1 PCI Express x16 2.0 slot, physically like x16 5 PCI Express 2.0 x1 slots | 1 PCI Express x16 2.0 slot, physically like x16 2 PCI Express 2.0 x1 slots 3 PCI slots | 1 PCI Express x16 3.0 slot, physically like x16 (PCI_E2) 5 PCI slots 1 PCI Express 2.0 x1 slot |
| Support for graphics tandems | No | No | No |
| Disk subsystem | Intel H81: - 2 SATA 6 Gb/s ports (black) 2 SATA2 3 Gb/s ports (gray) Supports ACHI, NCQ (RAID build is not available). | Intel H81: - 2 SATA 6 Gb/s ports (yellow) 2 SATA2 3 Gb/s ports (black) Supports ACHI, NCQ (RAID build is not available). | Intel H81: - 2 SATA 6 Gb/s ports 2 SATA2 3 Gb/s ports Support ACHI, NCQ (RAID build not available) |
| USB | Intel H81: - 6 USB 2.0/1.1 ports (2 connectors on the board for connecting 4 ports, 2 ports on the rear panel of the board) - 2 USB 3.0/2.0/1.1 ports (2 ports on the rear panel of the board) | Intel H81: - 8 USB 2.0/1.1 ports (3 connectors on the board for connecting 6 ports, 2 ports on the rear panel of the board) - 2 USB 3.0/2.0/1.1 ports (2 ports on the rear panel of the board) | Intel H81: - 8 USB 2.0/1.1 ports (3 connectors on the board for connecting 6 ports, 2 ports on the rear panel of the board) - 2 USB 3.0/2.0/1.1 ports (2 ports on the rear panel of the board) |
| Connectors and other functionality on the motherboard | 1 x 24-pin ATX 1 x 8-pin ATX 12V 2 PCIe Power Connector (standard Molex) 2 x SATA 6 Gb/s 2 x SATA2 2 connectors for connecting CPU cooling fans (1 * 4-pin; 1 * 3pin) 3 connectors for connecting additional fans (1 * 4-pin; 2 * 3pin) 1 header for the front panel of the case 1 header for audio connectors for the case 1 header for SPDIF 2 headers for USB 2.0/1.1 for connecting 4 ports CMOS reset jumper | 1 x 24-pin ATX 1 x 4-pin ATX 12V 1 PCIe Power Connector (standard Molex) 2 x SATA 6 Gb/s 2 x SATA2 1 connector for connecting CPU cooling fans (1 * 4-pin) 1 connector for connection additional fans (1 * 4-pin) 1 header for the front panel of the case 1 header for audio connectors of the case 3 headers USB 2.0/1.1 for connecting 6 ports CMOS reset jumper | 1 x 24-pin ATX 1 x 8-pin ATX 12V 6 x SATA 6 Gb/s 1 x M.2 sizes 2260 and 2280 2 connectors for connecting a CPU cooling fan (2 * 4-pin) 3 connectors for connecting additional fans (1 * 4-pin; 2 * 3-pin) 2 headers for the front panel of the case 1 header for audio connectors of the case 3 headers USB 2.0/1.1 for connecting 6 ports 1 header for a COM port 1 header for a TPM CMOS reset jumper |
| Connectors and other functionality on the rear panel | 2 PS/2 ports for connecting a keyboard and mouse 1 LPT connector 1 COM connector 1 D-Sub connector 2 USB 2.0/1.1 ports 2 USB 3.0/2.0/1.1 ports 1 HDMI connector 1 RJ-45 network port 3 audio jacks | 2 PS/2 ports for connecting a keyboard and mouse 1 LPT connector 1 COM connector 1 D-Sub connector 2 USB 2.0/1.1 ports 2 USB 3.0/2.0/1.1 ports 1 RJ-45 network port 3 audio jacks | 2 PS/2 ports for connecting a keyboard and mouse 1 LPT connector 1 COM connector 1 D-Sub connector 2 USB 2.0/1.1 ports 2 USB 3.0/2.0/1.1 ports 1 HDMI connector 1 RJ-45 network port 3 audio jacks |
| I/O controller | Nuvoton NCT6776D | Nuvoton NCT6791D | Nuvoton NCT6779D |
| BIOS | 32 Mbit Winbond 25Q32FVAIQ; removable AMI EFI BIOS Supports multilingual interface localization (Russian is present) | 64 Mbit GigaDevice GD25B64BP1G; removable AMI EFI BIOS Supports multilingual interface localization (Russian is present) | 64 Mbit (MXIC 25L6473FM2I-10G) one non-removable AMI EFI BIOS chip Support for multilingual interface localization (Russian is present) |
| Dimensions, mm | 305 x 178 | 305 x 188 | 305 x 214 |
| Form factor | ATX | ATX | ATX |
*According to Yandex.Market data at the time of publication of the material.
The MSI website contains an error: the description indicates the presence of four USB 3.0 ports, while in reality there are only two on the motherboard - there are no declared ports for the front panel of the system unit case.
Packaging and equipment
Each of the three boxes contains the motherboard itself, packed in an antistatic bag, but the order is different: somewhere it lies on top, somewhere on the bottom.
By the way, the ASRock model is packaged most carefully: a thick antistatic bag and a polyethylene foam backing.
The participants are identical:
- Two or three booklets and instructions;
- DVD with software;
- Two SATA cables with latches;
- Blank strip for the rear panel of the system unit case.
The envelope with the DVD disk of the Asus motherboard contains a small sticker with the manufacturer's logo, intended for sticking to the body of the system unit.
Solutions from MSI
Another leading motherboard manufacturer, MSI, has a similar situation with the Intel H81 chipset. Most of them are made in the mATX form factor. The most affordable of them are H81M-E33 and H81M-R33, which can now be purchased for $50. The difference between them lies in the graphics ports installed on the motherboard. The first has DVI-D and D-Sub, and the second has HDMI instead of DVI-D. Otherwise, these are identical motherboards. The most affordable ATX board is the H81-P33. It differs from the previously reviewed H81M-P33 only in size and three additional slots for PCI expansion cards.
Gigabyte and its motherboards
Intel chipsets have always made it possible to find various solutions based on one set of system logic. But another leading manufacturer of Gigabyte motherboards for some reason makes all of its H81-based motherboards almost identical. All of them are designated GA-H81M (for mATX form factor) and GA-H81 (ATX motherboards). At the end of the designation, a prefix is added that characterizes the BIOS version and the presence of additional wired interfaces. Otherwise, the level of functionality of H81-based solutions from this manufacturer is similar to Asus and MSI.
Reviews
Intel chipsets of the last few generations are strictly tied to certain market segments. Likewise, the hero of this article is an entry-level solution. It is perfect for budget computer systems.
You shouldn't expect anything unusual from him. The same can be said about the performance level of solutions based on this set of system logic. As a result, reviews from owners highlight primarily the availability of such motherboards and their low cost. At the same time, the level of functionality is sufficient for any educational or office PC based on the H61 motherboard.