When a Windows system fails to read an instruction from the specified memory, the user will receive an error that the memory cannot be read or written. This error is rare in Windows 10; most often it could be found in Windows XP or Windows 7 with code 0x00000000. An error occurs when a program, system file or driver accesses the physical RAM memory with its instructions and cannot read the necessary actions in certain memory fragments. The culprit when memory cannot be read or written may be damaged system files, damaged RAM sticks, insufficient virtual memory, or the program itself was installed crookedly. Let's look at how to fix an error with reading memory read or written.
Damaged system files
Damaged system files that access physical memory may generate this error, since the address of the system file will be modified and will not be read in RAM. Run Command Prompt as an administrator and enter two commands in turn to restore system files.
- sfc /scannow
- DISM /ONLINE /CLEANUP-IMAGE /RESTOREHEALTH
Diagnostics using Windows
You can also check using the built-in capabilities of Windows. To do this, open Search and look for Windows Memory Diagnostics. Select the first option “Reboot and check”.
The computer will begin to restart and the diagnostic screen will appear. You don't need to touch anything, and you don't even have to monitor the process, since the scan results will appear after the computer is fully turned on.
Often you have to look for them yourself, since they rarely appear on their own after the system starts. Search for Event Viewer again. In the left menu, open the “Windows Logs” folder, select “System” in it. Next, “Find” and “Memory diagnostics”.
Defender Core Isolation
The kernel isolation feature may prevent programs, drivers, or system files from accessing memory, resulting in a "Memory cannot be READ or WRITTEN" error. Open the built-in antivirus “Windows Security” and go to the “Device Security” column. Next, disable “Memory Integrity” if it was enabled.
Diagnostics MemTest86
Windows built-in tools are not able to detect all problems. Therefore, for a more thorough check, you will have to install third-party, more professional programs. For example, "MemTest86".
To get started, prepare additional removable media – it’s most convenient to use a flash drive. After downloading the archive with the program, which can be done on many platforms, open the file “imageUSB.exe”. Select an external device from the menu and click “Write”.
For further work you need to open the “Boot menu”. To do this, you need to press one of the keys: F2, Del, Esc, F12 immediately after turning on the computer or during reboot. You can press several keys or all in turn.
After opening the menu, the scan will begin automatically. It will be looped, that is, it will start again every time. It is best if it goes through 5-10 times.
Any errors found will be displayed at the bottom of the screen. After completing the test, press "Esc".
Virtual memory
Insufficient virtual memory can cause an error where the memory cannot be read or written if you run a power-hungry program or game. In this situation, increasing virtual memory can solve this problem.
the Win+G keyboard shortcut and enter sysdm.cpl to quickly open system properties. Go to the “Advanced” tab, click “Options” and in the new window, going to the “Advanced” tab, click “Change”.
Next you have two options:
- If you do not have the “Automatically select paging file size” checkbox checked, then check the box. Drive C, where Windows is installed, must be set to the system's choice.
- If method 1 did not help solve the problem, then manually set the memory, taking the values from below.
If you want to thoroughly understand how to properly configure and what sizes to set virtual memory, then read this guide on the paging file.
Problems with virtual memory
Problems with the paging file also sometimes lead to all sorts of errors. In certain cases, this type of memory may simply not be enough, the size of the paging file is too small. Therefore it is necessary to increase it.
In other cases, problems may arise after installing programs (especially games) that require more powerful resources than those on the computer. Let me give you an example: for the game to run adequately, you need 2 GB of RAM, but this PC has only 512 MB. After launching such a game, it is quite natural that a memory access error may occur.
Autoload
If there are many programs running when you start your computer, there may be a lack of memory. In Windows 10, open the task manager by pressing the Ctrl+Shift+Esc button combination and go to the “Startup” tab. Next, select programs that you do not really need and click “Disable”.
In Windows 7 and XP, press Win+R and enter msconfig , go to the “Startup” tab.
Third method
It is necessary to pay attention to, and without using various programs, which, moreover, are very dubious. Each motherboard has its own signals. And in order to find out what this or that signal means, you need to read the instructions from the manufacturer of this board. For example, when the computer boots, the BIOS emits one short beep. This means that the system has been tested and is working properly. And computers with BIOS AMI, with a working system, do not make any sounds at all. And one short one indicates a malfunction. In addition, it is RAM.
RAM diagnostics
Errors in RAM can cause a "memory cannot be written or read" error. Follow this RAM diagnostic guide to check for errors and fix them.
If the error is not resolved, then the problem may be physical in the RAM stick itself. Try swapping the strips and inserting them one by one into different connectors.
See also:
- How to find out how many RAM slots are free and occupied
- Why Ntoskrnl.exe System is using CPU and Memory in Windows 10
- Video RAM: How to increase allocated video memory in Windows 10
- How to increase RAM using a ReadyBoost flash drive
- How to find out the NET Framework version in Windows 10
comments powered by HyperComments
Key Concepts
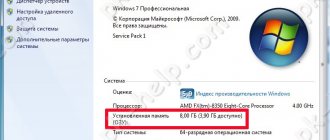
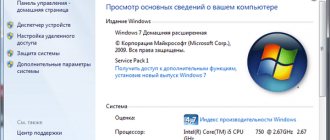
RAM is the “official” name for random access memory. A chip located in a special connector on your computer or laptop. In the first case, its dimensions are larger, in the second - smaller.
The RAM strip is the chip that represents the RAM. I must say that this is the most reliable hardware component of your PC. It breaks less often. Manufacturers establish a warranty period for planks of at least 4 years. It's all about the simplicity of the microcircuit design. It does not heat up, which is why it does not need a cooler (fan in a computer system). True, sometimes powerful gaming PCs install a radiator to cool the RAM. It also makes the RAM bar structurally stronger.
From here you can identify that different RAM will work differently. However, the reasons for failure for all varieties are identical.
How RAM problems manifest themselves
The “clinical” picture of memory failures, regardless of the reasons, is very, very diverse - from the complete inoperability of the computer to errors in the operation of applications that occur haphazardly and without connections with any action.
Typically, RAM problems manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- The PC or laptop does not respond at all when pressing the power button.
- When you press the power button, the system speaker beeps when POST fails. Moreover, codes (combinations of short and long beeps) do not always indicate memory problems.
- The computer turns on and immediately turns off or restarts cyclically at any stage of boot.
- After switching on, error messages are displayed on the screen. For example: “ CMOS checksum error ”, “ CMOS checksum bad ”, etc.
- During startup and operation, the operating system crashes with critical errors (blue screens). PAGE_ FAULT_ IN_ NONPAGED_ AREA , UNEXPECTED_ KERNEL_ MODE_ TRAP , DATA_ BUS_ ERROR , PFN_ LIST_ CORRUPT , KERNEL_ STACK_ INPAGE_ ERROR , UNEXPECTED_ KERNEL_ MODE_ TRAP are especially typical , but there may be others. Very often - different.
- The image on the screen disappears or is distorted (video memory defects). In the absence of discrete video with its own memory, the latter is allocated from the RAM.
- The computer slows down or freezes until the user restarts it.
- The functions of transferring and copying files stop working.
- Errors occur when launching and running applications. For example, “ Memory cannot be read\written ” and others.
- Programs are not installed or uninstalled.
- Files stop being saved. Or after saving they cannot be opened.
- Operating system components are damaged.
As you can see, this list contains almost everything that can happen when a computer malfunctions. And this is just because of the broken RAM!
This is interesting: How to force Windows 32 bit to see more than 3 GB of RAM
By the way, memory problems are often disguised as other problems and manifest themselves in the most bizarre ways. There have been cases when they were manifested by constant crashes of the antivirus program (giving reason to “sin” for elusive viruses), an unstable connection to Wi-Fi, loss of device drivers (after installation, the driver only works until the computer is rebooted), etc.
Sometimes the same failure appears constantly, sometimes they alternate. Often there is a combination of several errors, for example, blue screens of death and system function failures.
What consequences can result from using a faulty RAM? To the most deplorable ones. Namely, to the loss of data that you work with on your PC. As files are opened and rewritten, they will accumulate errors that will sooner or later render them unreadable and possibly unrecoverable.
Identifying RAM errors using programs
Software diagnostics of RAM are carried out under the same conditions under which failures occur.
When you are not sure that the problems are caused by the memory, and you want to find out, leave all RAM modules connected in the configuration in which they were installed. If you need to determine which strip has failed, check them one at a time. If you're using memory acceleration technology, select the profile that's causing the problem for the first test. If there are errors, do another check with XMP disabled.
Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
The RAM diagnostic tool built into Windows, Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool , may not be the most popular tool for such tasks, but it is the most accessible.
Versions of the utility included in Windows 7, 8.1 and 10 support DDR-DDR4 generations of RAM with a capacity of up to 64 GB (but in fact, perhaps less). Myths that the system tool is capable of detecting only obvious problems, but not hidden and subtle ones, are created by users who have not bothered to figure out how to work with the utility correctly. Yes, by default it runs a quick scan and a minimal set of tests, but if you change the settings, its sensitivity will increase significantly.
To launch the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool, press the Windows + R key combination and enter the mdsched command in the “ Open ” .
Then confirm your consent to restart. To have access to the entire RAM space, the utility will reboot the computer into DOS mode.
The scan will begin immediately after the restart. As I already said, this will be a superficial scan that will only reveal obvious errors. F1 settings key .
This is interesting: More powerful, faster, more convenient: pros, cons and features of USB Type-C
The program has few settings, and they are intuitive.
- The first option is a test suite. For in-depth diagnostics, select " Wide ". To move to the next item, press Tab.
- Next is the use or non-use of the processor cache. To ensure that the utility only accesses RAM, it is advisable to disable .
- The last option is the number of passes. The more there are, the higher the likelihood of detecting hidden errors, so if time is pressing, bet no less 8-15.
To exit the setup menu, press F10.
A full, deep check of RAM by any means always takes a long time. As practice shows, the bulk of defects are detected already in the first hour of testing, but some emerge only after multiple passes - 6-8 hours from the start of the test.
Messages about errors found appear on the same screen in the “ Status ” section.
Memtest86
The utility (not to be confused with Memtest86+, which has ceased development since 2013) is a classic of the genre.
Its first algorithms were developed more than 20 years ago. To date, they have been improved and comply with all memory standards and platforms currently produced. Memtest86 is the seventh version (latest), available in a free version - Free Edition, and two paid editions. The Free edition does not have the ability to save test reports to disk, create configuration files that can be used to set testing parameters for the program, or exclude the processor cache from testing. In addition, some tests were cut from it, in particular, the use of instructions for reading/writing 64- and 128-bit data and error modeling to test the correction function (ECC) of server memory.
Despite the limitations, the capabilities of Memtest86 Free Edition are sufficient for the vast majority of home users. Searching for hacked paid versions or purchasing them is completely useless.
Unlike the Windows tool, Memtest86 is optimally configured by default, so it's fairly easy to run. But before that, the downloaded file (iso image) will have to be written to an external medium - DVD or flash drive, and the computer booted from it. The tool for creating bootable USB flash drives, along with the utility itself, is also available for free download on the latter's official website.
Memtest86 interface is in English. The green dot in the screenshot above outlines the source data: information about the processor - frequency, size, cache speed, and information about memory - speed and size.
The area on the right - in a yellow frame, displays the current execution of the program: the serial number of the test, the percentage of its completion, as well as the percentage of completion of the entire cycle ( Pass ).
The orange frame contains information about the time that has passed since the start of the check ( Time ), the number of passes ( Iterations ), the addressing mode ( AdrsMode ), the sequence number of the cycle ( Pass ) and the errors found ( Errors ).
Error details, if any, are listed below. It is impossible not to notice them, since this area is highlighted in red.
At the very bottom of the screen are options for managing the program.
Information about testing methods and procedures, descriptions of tests, rules for creating configuration files and much more is available on.
GoldMemory
The utility is another powerful RAM testing tool built on alternative algorithms.
It often reveals errors that cannot be detected either by Memtest or other means, but, unfortunately, it is a paid solution. You can only use a 30-day demo version for free, which is essentially useless. This is interesting: How to set the BIOS to boot from a drive or flash drive
The full – registered version of GoldMemory allows you to test all types of modern DDR-DDR4 RAM up to 64 GB. It has 4 scanning modes - fast (the only one available in the demo version), normal, advanced and custom. Supports batch batch files. Saves reports and inspection history. Can operate continuously until manually stopped.
Like the previously discussed utilities, GoldMemory works in a DOS environment - it is launched from a bootable DVD or USB flash drive (the distribution of the paid version also includes media creation tools). Testing begins immediately after downloading.
The program interface, like Memtest 86, is English. At the top of the screen are the version and license information. The block in the orange frame in the screenshot above displays information about the current execution of tasks and settings.
The settings menu is surrounded by a red frame. Here:
- The "T" key controls the selection of the test mode.
- “C” – enables and disables continuous checking mode.
- “M” – allows you to change the method for determining the RAM size.
- “B” – enables and disables the benchmark test.
- “F” – determines whether to save the report file or not.
- “A” – turns on and off the sound notification about found errors.
- “X” – determines whether to complete testing if errors are detected.
- “E” – controls the transition to an accelerated verification mode, which saves up to 50% of time while maintaining normal efficiency.
By pressing the "T" key in Custom mode, you can select from a list of test groups to identify specific problems.
After the scan starts, a list of errors found will be displayed in the area where the menu is located. It’s also impossible not to notice them.
What to do first
Because RAM failure has so many faces, it should be ruled out for any unclear computer problems.
In cases where the computer does not turn on, shuts down, or restarts before loading the operating system, and before testing memory using programs, do the following:
- Turn off the power to the system unit - unplug the cord from the outlet or press the power button on the power supply/surge protector. Open the case cover and make sure that the RAM sticks are correctly and completely installed in the slots. If even one module is not inserted completely, the computer will not turn on.
- Remove the strips from the slots and clean their contact groups with a school eraser. If the problem is an oxide deposit that disrupts contact, it will be solved.
- Reset the BIOS settings to default by removing the flash memory battery for 15-30 minutes or closing the Clear_CMOS jumper contacts (other names CLCTRL, CLR_CMOS, JBAT1, etc.).
If a failure prevents your computer from starting, try turning on the computer with one RAM module in different slots. If there are several modules, check them one by one.