Why are some files and folders not deleted?
If you try to delete some folders or files from your computer’s memory, you may see one of the possible errors with the corresponding reason:
But sometimes it is necessary to delete such objects, for example, when an extra file takes up too much space or a fragment of a virus remains in the folder. Also, some of these files cause errors during system operation.
There are several reasons why your computer may refuse to allow you to delete a folder or file:
- incorrect removal of third-party programs. If the user erased installed applications not through a special utility, but by moving files to the trash, then fragments of this application could remain hanging on the hard drive, which are still considered to be involved in its operation;
- a program is active that uses the file to be deleted in its work;
- the file is needed for the operation of the operating system itself;
- The antivirus suspects the file being deleted of being infected with a virus. Also, the antivirus program can wait for an update that will allow it to correctly get rid of the file with the virus;
- To delete folders related to Windows operation, administrator rights are required;
- if your computer is synchronized with another device over a local network, the file may be used on the second device;
- if the file that needs to be deleted is located on a third-party device (USB flash drive, SD card, DVD, etc.), then you should make sure that the device is not write-protected.
Empty folders appear on the system after you have installed a third-party program and then uninstalled it, cleared the cache, or erased data or settings. The weight of such folders is zero, they do not take up space, but if a large number of them accumulate, the system will begin to get confused and overloaded. An error when deleting them may occur if there is a program on the device to which they belong, or due to incorrect deletion of the program or its data, since the system continues to think that these folders are still needed.
Files in the .dll format store information for the operation of programs, widgets, and pop-up windows. Problems with deleting files of this format can arise for the same reason as with empty folders: they are required for a running program or remained after the application was incorrectly uninstalled. There are also very often cases where a virus disguises itself as a DLL file.
Objects that require special rights: how to delete?
Sometimes it is necessary to delete some objects, but they are not deleted because there are no corresponding rights. Solving this problem is very simple.
First, you need to log into the operating system under the main “Administrator” and re-run the uninstallation process. If the deletion succeeds, it is important not to forget to log out of Windows and log in as “User” - this way you can eliminate the risk of damage to the system.
But there are situations when this is not enough. Then you need to select the desired folder, then open the “Properties” of the folder. Next, for a specific user, you should check the boxes that give full access to the folder. After this, you need to click on the “Apply” button and you can try to delete it again.
This is true for all versions of Windows operating systems, including 7, 8 and 10.
Methods for deleting “undeletable” files and folders
There are many ways that make it possible to get rid of problematic files. For each individual case, you need to select the method that is most suitable and easiest to implement.
Restarting the device
After restarting the computer, all unnecessary processes and programs will be turned off, only those files that are really needed for the system to function will remain, and the rest can be deleted.
Reboot the device
Boot in Safe Mode
Turn off your computer. After it just starts to turn on, a black screen and a greeting will appear, then start pressing the F8 button on the keyboard to open the boot menu. When it appears, select the “Safe Mode” section.
Booting the computer in safe mode
The fact is that in this mode the computer loads only those processes that are necessary for the system to operate. This means that folders and files that do not belong to this list can be deleted. Also, in this mode, the virus will not be able to interfere with you, since the chance that it will be activated is much lower.
Video: how to enter safe mode in Windows 7
By obtaining administrator rights
If you are logged in as a regular user, without administrator rights, you will not be able to delete system elements. To get administrator rights, re-login from your main account or grant administrator rights to your account:
Video: how to delete files as administrator
Through the Unlocker program
There is a special program aimed at unlocking access to editing files - Unlocker. Thanks to it, you can delete, edit, change the name and format of any file and folder:
Video: removal using Unlocker program
By moving
You can try to create a new folder and move files or a folder into it that for some reason are not erased, and then delete them.
Move and delete a folder
Via file manager
There are third-party analogues to Windows Explorer, for example, Total Commander. It will allow you to delete blocked and find hidden files and folders.
Video: how to delete a file using Total Commander
Show hidden files
You may not be able to delete a folder if it contains hidden items. To make them appear and give you the option to erase them, follow these steps:
Using autoload
Perhaps the program or file you want to delete starts automatically when you start your computer. In this case, they should be removed from startup:
Video: how to remove a program from startup
By checking the list of quarantined files
Perhaps the file cannot be deleted because it is quarantined by antivirus software. To check this option, follow these steps:
System Restore
If you know why the undeletable file appeared, you can roll back the system to the moment when it did not exist:
Disabling Tustedinstaller
Tustedinstaller is a process that checks the user for administrative rights when attempting to use system files. That is, if you disable it, the “File cannot be accessed” notification will no longer appear:
Video: TrustedInstaller permission request
Via another operating system
If you have the opportunity to run Windows from a USB flash drive or DVD/CD, then do so, and then delete the file or folder. When using a bootable USB flash drive or Windows 7 installation disk, at any time during the installation (after the language selection window has already loaded and in the following steps), press Shift + F10 to enter the command line. You can also select “System Restore”, a link to which is also present in the installation program.
If you try to move, rename, or delete a folder or file, you see a message that says you need permission to perform this operation, "Request permission from Administrators to edit this file or folder" (even though you are already an administrator on computer), then below are step-by-step instructions that show how to request this permission to delete a folder or perform other necessary actions on a file system element.
I will warn you in advance that in many cases, an error in accessing a file or folder with the need to request permission from the “Administrators” is due to the fact that you are trying to delete some important element of the system. So be careful and careful. The guide is suitable for all latest OS versions - Windows 7, 8.1 and Windows 10.
In fact, we won't need to ask for any permission to edit or delete a folder: instead, we'll make the user "become the boss and decide what to do" with the specified folder.
This is done in two steps - the first is to become the owner of the folder or file and the second is to grant yourself the necessary access rights (full).
Note: at the end of the article there is a video instruction on what to do if you need to request permission from the “Administrators” to delete a folder (in case something is not clear from the text).
Change of owner
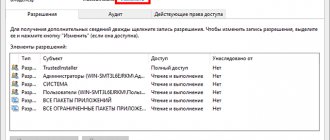
Right-click on the problematic folder or file, select Properties, and then go to the Security tab. In this tab, click the "Advanced" button.
Pay attention to the “Owner” item in the additional security settings of the folder, “Administrators” will be indicated there. Click the "Edit" button.
In the next window (Select User or Group), click the "Advanced" button.
After that, in the window that appears, click the “Search” button, and then find and highlight your user in the search results and click “OK”. In the next window, just click “Ok”.
If you are changing the owner of a folder and not an individual file, then it would be logical to also o (changes the owner of subfolders and files).
Click OK.
Setting user permissions
So, we have become the owner, but most likely we cannot remove it yet: we do not have enough permissions. Go back to “Properties” - “Security” of the folder and click the “Advanced” button.
Notice if your user is in the Permission Items list:
If not, click the “Add” button below. In the subject field, click “Select subject” and through “Advanced” - “Search” (how and when the owner was changed) we find our user. We set it to “Full access”. Also at the bottom of the “Advanced Security Settings” window. We apply all the settings made.
- If there is, select the user, click the “Change” button and set full access rights. A. We apply the settings.
After this, when deleting a folder, a message stating that access is denied and you need to request permission from Administrators should not appear, as well as during other actions with the item.
Quite often, when programs are uninstalled, residual files and folders remain that take up a decent amount of space on the local disk. Everything would be fine if, when trying to delete them, an error did not appear informing us that we must have rights to perform such an operation.
And it seems like I logged in on behalf of the “manager,” but the computer still curses. In this case, we will try to tell you how to liquidate a document with administrator rights.
Setting advanced rights
In principle, you can set for yourself an expanded set of rights to carry out absolutely all actions provided by the system. How to delete files from the disk in this case?
First, in Explorer, in the RMB menu, the properties window is called up, on the security tab, the additional parameters button is pressed, after which the owner is replaced with the current user.
Next, you need to go to the permissions section and check the Full Access option, and then check the boxes for adding and replacing permissions. After saving the changes, you can perform any actions with non-deletable objects.
The simplest methods
The easiest method that will allow you to do this is to restart your computer. The thing is that the error may occur due to the use of file resources by a third-party application. When you reboot, it will turn off, and if you manage to do it before it autostarts, you will be able to send the folder to the trash.
If the first method did not work, then right-click on the unfortunate file, select the “Security” tab, select your name and check the box next to “Full Control”. We save the changes and try to delete the file again as an administrator.
In some cases, you can delete a folder with administrator rights by first moving it to a flash drive or other local drive. The method works quite often.
Deleting files via the command line
Use of the console is recommended for experienced users. If you are not confident in yourself, then it is better to use another method.
- To open the command line, press Win+R and write cmd in the line. Next, depending on the situation, enter several commands:
- del/fc:\FolderName\File.docx—delete a locked file;
- del c:\FolderName\File.docx - deletes a specific file from a folder;
- del/ac:\Folder name\File.docx - deletes all files in the folder in which “File.docx” is located.
- The entire path must be specified. For example, to delete a document from the desktop, the command would be something like this: “C:\Users\Username\Desktop\Microsoft Word Document.docx.” And specify the extension.
- The full name, extension and path to the folder - all necessary entries can be viewed in the file properties. To do this, right-click on it and select “Properties”.
The properties indicate the full name, extension and location where the file is located
Why this method is dangerous: there is a risk of erasing important information. Through the command line, all data is permanently deleted, bypassing the trash can. File names, paths and extensions must be specified accurately. An error in the name may erase the wrong file and cause the system to become unstable.
Using software
There are at least two programs that will help you eliminate the document. These are the Unlocker and Total Commander utilities. The first application removes the lock on behalf of the administrator, and the second expands the user's capabilities.
After installing the Unlocker program, you must:
If a document is blocked as an administrator, you will be prompted to unlock it (including unlocking attached files and folders). After this the program should help.
When using the Total Commander program, the steps change slightly. Launch the installed application. A certain analogue of the standard Explorer program will appear.
Find your document, right-click on it, and select delete from the drop-down list. If nothing happens, then do the following:
- Open the folder and find the previously “invisible” file.
- , find the process with the same name.
- Complete the process and try to destroy the document.
Sometimes there are several such background processes in a directory that interfere with the task. It is necessary to check this and complete each of them. Unfortunately, this method cannot provide a 100% guarantee. In this case, you should make sure there are no viruses or give your PC to professionals.
Hello everyone, today I’ll tell you how to solve the error Request permission from Administrators when deleting a folder in Windows. If you try to move, rename, or delete a folder or file, you see a message that says you need permission to perform this operation, "Request permission from Administrators to edit this file or folder" (even though you are already an administrator on computer), then below are step-by-step instructions that show how to request this permission to delete a folder or perform other necessary actions on a file system element.
I will warn you in advance that in many cases, an error in accessing a file or folder with the need to request permission from the “Administrators” is due to the fact that you are trying to delete some important element of the system. So be careful and careful. The guide is suitable for all latest versions of OS - Windows 7, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10.
In fact, we won't need to ask for any permission to edit or delete a folder: instead, we'll make the user "become the boss and decide what to do" with the specified folder.
This is done in two steps - the first is to become the owner of the folder or file and the second is to grant yourself the necessary access rights (full).
Change of owner
Right-click on the problematic folder or file and select Properties
and then go to the Security
.
In this tab, click the Advanced
.
Pay attention to the Owner
in the additional security settings of the folder, it will indicate
Administrators
.
Click the Change
.
In the next window (Select User or Group), click the Advanced
.
After that, in the window that appears, click the Search
, and then find and highlight your user in the search results and click
OK
. In the next window, just click “Ok”.
If you are changing the owner of a folder, and not an individual file, then it would be logical to also check the Replace owner of subcontainers and objects
(changes the owner of subfolders and files).
Click OK.
Setting user permissions
So, we have become the owner, but most likely we cannot remove it yet: we do not have enough permissions. Go to Properties
- “Security” folder and click the
Advanced
.
If you try to move, rename, or delete a folder or file, you see a message that says you need permission to perform this operation, "Request permission from Administrators to edit this file or folder" (even though you are already an administrator on computer), then below are step-by-step instructions that show how to request this permission to delete a folder or perform other necessary actions on a file system element.
I will warn you in advance that in many cases, an error in accessing a file or folder with the need to request permission from the “Administrators” is due to the fact that you are trying to delete some important element of the system. So be careful and careful. The guide is suitable for all latest OS versions - Windows 7, 8.1 and Windows 10.
System Restore
You can restore the system to a state where the required file was not yet locked. But this method has disadvantages:
- When rolling back, programs that were installed after the restore point was created are removed;
- settings and changes that were created after creating the restore point will be reset;
- there will be no suitable restore points.
Before you start rolling back the system to a previous state, transfer important files to external storage so as not to lose them.
Required steps to start system recovery:
- Open the Start menu and type “System Restore” in the search bar.
- In the window that appears, click the “Next” button.
- Select a restore point from the list.
Select the desired restore point from the list
- Click Next, read the warnings, and click Finish.
How to request administrator permission to delete a folder or file
In fact, we won't need to ask for any permission to edit or delete a folder: instead, we'll make the user "become the boss and decide what to do" with the specified folder.
This is done in two steps - the first is to become the owner of the folder or file and the second is to grant yourself the necessary access rights (full).
Note: at the end of the article there is a video instruction on what to do if you need to request permission from the “Administrators” to delete a folder (in case something is not clear from the text).
Change of owner
Right-click on the problematic folder or file, select Properties, and then go to the Security tab. In this tab, click the "Advanced" button.
Pay attention to the “Owner” item in the additional security settings of the folder, “Administrators” will be indicated there. Click the "Edit" button.
In the next window (Select User or Group), click the "Advanced" button.
After that, in the window that appears, click the “Search” button, and then find and highlight your user in the search results and click “OK”. In the next window, just click “Ok”.
If you are changing the owner of a folder and not an individual file, then it would be logical to also o (changes the owner of subfolders and files).
Click OK.
Setting user permissions
So, we have become the owner, but most likely we cannot remove it yet: we do not have enough permissions. Go back to “Properties” - “Security” of the folder and click the “Advanced” button.
Notice if your user is in the Permission Items list:
After this, when deleting a folder, a message stating that access is denied and you need to request permission from Administrators should not appear, as well as during other actions with the item.
How to resolve the error "Request permission from SYSTEM to edit this folder"
Working with files and directories on your computer can sometimes be accompanied by errors, in particular the appearance of a message with the text “Request permission from SYSTEM to change this folder.” With this development of events, it is not possible to perform any actions with the object. The problem is relevant for the operating systems Windows 7, 8, 10, and an obstacle of this kind was conceived by the developers in order to limit user intervention in system data. Most often, the error is caused by attempts to delete or correct operating system folders and files, which may be vital for the full functioning of the Windows OS, and their elimination can lead to incorrect operation.
Fixing the "Request permission from SYSTEM to edit this folder" error.