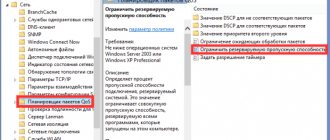
09/01/2017 30174 Share
Cool
Share
Tweet
- internet speed
- best provider
Several months have passed since we launched our new Internet speed test. During this time, it was tested and many Internet providers provided their servers to host our test. Thanks to this, everyone can measure the speed to the point closest to them.
About 3 million Internet speed measurements are made per month through our Internet speedometer. This is a huge amount of data. Therefore, after we achieved the most accurate speed measurements, we decided to conduct a little research and tell you about which providers provide their customers with the highest Internet speed and in which cities the Internet is better (faster).
Below you will see the tops for August 2020. If this data is in demand by our visitors, then we will continue publishing and every month we will inform you about the “fastest” Internet providers and the “fastest cities” in Russia.
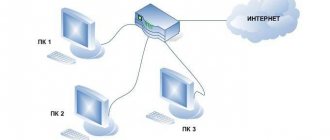
As you probably know, Internet providers can be small, serving a small area of the city, there are large ones that cover most of the city, and there are very large ones that operate in several cities or even in tens and hundreds of cities. In order to give all Internet providers, both small and large, the opportunity to be in the top, we decided to make 2 tops. In one we will show small providers and in the other large ones.
How do we think who is small and who is big? Based on the number of Internet speed measurements carried out by Internet provider clients on our website. If there are less than 1000 measurements per month, we will consider such a provider to be small. And those whose clients carried out more than 1000 measurements per month on our website will be considered large. We will not take into account those whose clients made less than 30 measurements per month.
Fast decision
Friends, one of the fastest ways to choose a provider today is to use free aggregator services. They not only display a list of available operators for your city, but also show reviews with ratings from other people, find optimal rates, and most importantly make this process clear and visual.
There are many services - you can search for them yourself. For the lazy and smart, I recommend immediately going to Provayder.net and starting the selection. I advise the rest to continue studying this article and get to our analytics.
What you need to know before connecting - technology
For those who are completely green, I leave the most important thing for choosing the right technology, so that in the end everything will work well for you for many years. Now there are two options for getting Internet at home:
- By wire (recommended). Here the provider runs a wire into your apartment, from which you receive the Internet (for example, using a Wi-Fi router). The main advantages are excellent speed and stability. I strongly recommend pulling the wire, and resorting to the second option only if it is impossible to install the cable and all providers refuse to connect.
- Wireless Internet. If you are unlucky with the first option (you are in a new area of the city, in a country house, in the remote taiga), but there is good coverage of cellular operators (MTS, Beeline, Megafon, Yota, Rostelecom) - you can choose a tariff from them and choose the final receiving device A USB modem or the same router with support for SIM cards (the worst option is your phone). Cons: relatively low speed (see below) and unstable “jumping” connection.
In this article, I deliberately omit “perverted” methods of connecting to the Internet - from a cable TV provider or via satellite - but sometimes you cannot do without them. Here we will talk about the most common cases, for the rest I invite you to comment.
Now I will dwell in a little more detail on specific connection technologies. With this, you can safely go to the provider, and scary abbreviations will no longer scare you.
For a wired connection (the lower the better):
- ADSL. Connection via telephone cable. It is still a popular connection method in our country and neighboring countries. The downside is the low speed (in practice, up to 2 Mbit/s). But sometimes, especially in remote villages, you can’t live without it.
- FTTx (recommended). Here, a fiber optic cable runs to the entrance, and a twisted pair cable is installed into the apartment. The most popular connection option today. Tariff speeds are usually up to 100 Mbit/s - enough for a home user. Prices for tariffs and equipment are reasonable (you can find a good router for 1000 rubles).
- GPON. The fiber optic cable is routed directly into the apartment or house. The main advantage is speeds up to 1 Gbit/s. The technology is only being introduced in large cities and developed areas. If possible, connect. The downside is that the equipment is still expensive (terminals from 6,000 rubles).
If it is not possible to lay a wire at all, consider the networks of cellular operators. The main recommendation is to choose the operator whose network is good for you specifically. It’s unlikely that anyone can give advice here better than your personal experience. And even with your friends everything may be different. Those. You can see how your phone and other operators receive communications from your neighbors; if it’s really bad, google the “coverage map” for a specific operator (write, for example, “Megafon coverage map”).
Typically, such maps indicate the generations of the cellular network (and this is only the spread of technology, and the level must be measured on site):
- GPRS + EDGE – very slow.
- 3G – national average up to 4 Mbit/s.
- 4G LTE – 20-60 Mbit/s.
- 5G is not in Russia yet, but competition with a wired connection is possible.
Screenshot of a coverage map using Megafon as an example.
Regarding the tariffs of mobile operators - they change every month, you can’t keep track of everything. But on average they remain at the same level. You can try the “average” tariff, and after a month of use, increase or decrease it, or use the same provider catalogs and study reviews.
Which wired Internet is better to connect?
“Wired” types of Internet include:
- — connection using a network cable (twisted pair);
- — fiber optic connection;
- — connection via coaxial (television) cable;
- — connection via telephone line.
However, despite the solid “assortment”, it is quite simple to decide which Internet connection is best for a private home: the “best” option would be to connect using fiber optics or (if this technology has not yet “reached you”) via a network cable.
A communications network based on twisted pair and optical fiber is present in almost all cities of the country, and most large providers provide such services.
— When connecting to the Internet via twisted pair, Ethernet network technology is used (based on TSP/IP protocols). Here, to create an Internet connection, the company’s specialists stretch a cable from the provider’s network equipment (switch) to your home.
Thus, the user receives a dedicated line with high quality and speed of information transfer.
However, over large sections of twisted pair, the signal weakens, and accordingly, the speed of the Internet connection is significantly reduced. Thus, if the switch is located more than 100 meters from your home, you must install additional equipment (or use a different cable).
When using wired Internet, a network cable can:
— connect to the computer directly (when using the Internet only on this PC);
— connect to your home router to create an internal WiFi network (to connect several user devices to the Internet at once).
— The problem of signal attenuation is solved by the use of optical fiber. However, not every user has the money to connect it: not only the fiber itself is expensive, but also all the network equipment used (media converters, SFP modules, routers and switches with optical connectors).
Internet speed when connected via fiber optic is very comfortable.
So, if over a 4-core twisted pair (at a distance of no more than 100 meters from the equipment) you can achieve a maximum of 100 Mbit/s, over an 8-core twisted pair - up to 1000 Mbit/s, then over optical fiber the Internet speed easily reaches 1000 Mbit/s at any distances.
However, 10 Mbit/s is quite enough for household use, so organizations use the Internet via fiber optics more often than the general population. Indeed, in addition to the high cost of connecting to the Internet, the monthly subscription fee also increases proportionally, which is charged even when the equipment is “downtime”.
As for the tariff plan, the Internet here is usually provided unlimited, and the cost of services depends on the limited speed of the Internet connection.
Internet for a summer residence: which one is better?
Optics and twisted pair are, of course, good. But what kind of Internet is better to connect in a village to which these communication networks have not yet “reached”? And it’s irrational to pull an expensive optical cable to some remote place for the sake of a dozen potential subscribers.
And here other “proven” communication technologies come to the rescue: for example, in the private sector you can connect the Internet via coaxial cable (cable television) and telephone cable (here, depending on the “needs”: both a dial-up connection and a leased line) .
Such Internet can be installed in almost any private home: the subscriber has a modem installed that distributes the Internet using one of the network technologies:
— via television cable - using DOCSIS technology. On average, the reception speed here can be 42/38 Mbit/s, the upload speed is 10/9 Mbit/s, however, this speed is allocated for the entire channel, so if in the private sector several subscribers are “sitting” on the same cable at once , then the speed will vary depending on the load on the line.
— via telephone cable using ADSL, Dual-Up and ISDN network technologies (Dual-Up and ISDN connections were once also used, but these technologies are now outdated). In theory, the ADSL connection speed can reach 24 Mbit/s, but in practice these figures are achieved extremely rarely: the real “quality” of the telephone lines affects it.
However, all other things being equal, an ADSL connection will not be the worst solution to the question of which Internet to connect to in a private home. Still, a cable connection to the worldwide information network is much more stable than its wireless counterparts.
What you need to know before connecting - important points
We have decided on the technologies, now I recommend creating clear criteria in your head that you will rely on when choosing a tariff:
- Price . Purely personal perception. For example, “I’m willing to pay no more than 1000 rubles a month,” or “I’m looking for something up to 600 rubles,” or “The price is not important at all.”
- Speed . An important parameter for a wired connection. The settings are as follows: “I want normal 100 Mbit/s”, “If only the price was lower”, “I need maximum speeds and GPON”. For mobile networks this is not so relevant, since there you usually don’t have to choose - just pay and get the maximum possible (occasionally there is a limit on Gigabytes).
- We define personal “features” . For example, if you need IPTV, it’s better to immediately select a package with it, it will be cheaper. Or the availability of technical support - for example, you can call Rostelecom around the clock, and they work promptly, but the local provider can only boast of cheap tariffs. And some people don’t want to buy equipment, then some providers will happily rent it to you.
- Reviews . Yes, rely on them too. Ask your friends, read in catalogs (the link for an example was above). BUT don't look only at negative reviews - of course, the most popular provider will have the most negativity, but that doesn't mean that they are the worst, because... they wouldn't be the most popular.
Main providers in Russia
Currently, the largest Internet providers in Russia are:
- Rostelecom.
- MTS.
- Beeline.
- Megaphone.
At the same time, you should not succumb to stereotypes about the connection method. Thus, Rostelecom, a purebred wireline provider, has recently acquired cellular networks and easily provides access to the mobile Internet. And the same MTS and Beeline successfully entered the market of wired Internet and IPTV. So everything is relative.
Personally, I have been using Rostelecom for a long time and do not experience any problems, no matter how many people scold it, but each region has its own small “outbids”, which are not always inferior to the big four. So they make the choice even more difficult. That's why we have prepared the following ratings and detailed selection instructions for you.
Which operator is the leader in Russia in terms of speed?
Not long ago I personally measured the Internet speed in Moscow and the Moscow region. And then the leader was often the Yota operator, operating on MegaFon’s networks. But this applied only to two relatively small zones across the entire country.
All measurements were carried out through SpeedTest, which guaranteed impeccable results.
Throughout Russia, according to Ookla, MegaFon turned out to be the leader in data transmission quality. The average speed of this operator in the country was 27.31 Mb/sec , which is 7.19 Mb/sec higher than the average of all operators in Russia.
For the third year in a row, MegaFon has been considered the leader in data transfer speeds in Russia.
According to Roskomnadzor, the operator uses more than 235 thousand base stations. This is the best indicator in the country. The closest competitor, MTS, has 180 thousand stations.
▸ 238,527 base stations for MegaFon ▸ 183,250 base stations for MTS ▸ 167,654 base stations for Tele2 ▸ 156,977 base stations for Beeline
In terms of growth rates since the beginning of the year, Tele2 (+13%) and Beeline (+7%) are leading.
It is the base stations that are responsible for the coverage and quality of signal transmission. And the more there are, the better it will be to “catch” the network with the highest speed.
Vlad Volfson, Commercial Director of MegaFon, commented:
Today, a MegaFon client downloads on average over 10 GB per month, and to ensure the highest speed of mobile Internet and the best quality of communication for our clients, MegaFon annually invests significant financial and intellectual resources in the development and configuration of the network.
How to choose your provider in this hustle and bustle?
The main advice is to choose the best in your budget - the best technology (FTTx is a good choice) and the best speed (100 Mbps is a cool speed now). All that remains is to figure out the available providers in your home. With wireless, everything is on average clear, but with wired ones... We ask our neighbors, use aggregators (link at the beginning of the article) or city maps (the same 2GIS).
And for all major cities of Russia, we have already done our own complex analysis of dozens of parameters and identified the three best home Internet providers. I really hope that this table will make your choice of provider at least a little easier.
Table - Rating of Russian providers by city
| City | 1 place | 2nd place | 3rd place |
| Moscow | Rinet | Starlink | Beeline |
| Saint Petersburg | At Home | RSVO-online | E-TELECOM |
| Novosibirsk | Rostelecom | MTS | IP Stream |
| Ekaterinburg | Inetvdom | MTS | A B C |
| Nizhny Novgorod | Samtel | UfaNet | Mosnet |
| Kazan | Beeline | SkyNet | Kazan city network |
| Chelyabinsk | Aizet | Home ru | Rostelecom |
| Omsk | Rostelecom | MTS | Liga-Telecom |
| Samara | Beeline | SamaraLan | Kraft-S |
| Rostov-on-Don | Samtel | Digital Dialogue | Beeline |
| Ufa | Green dot | TV network Ufa | Home ru |
| Krasnoyarsk | Telekta | Rostelecom | Beeline |
| Voronezh | Home ru | NoBuyNo | Beeline |
| Permian | PermTelecom | Innor | U-link |
| Volgograd | Smith34 | NoBuyNo | Alliance connection |
| Krasnodar | South Link | Samtel | Cheetah.Online |
| Saratov | Satellite TV | Home ru | Beeline |
| Tyumen | Sibitex | TV networks | Positive Telecom |
| Tolyatti | InfoLada | Rostelecom | Beeline |
| Izhevsk | MTS | Mark | IzhLine |
| Barnaul | MTS | Dianette | Home ru |
| Ulyanovsk | Beeline | EVO | Home ru |
| Irkutsk | RegionTelecom | Orion Telecom | Rostelecom |
| Khabarovsk | Beeline | Vostoktelecom | Rostelecom |
| Yaroslavl | MTS | LiveComm | Yartelecom |
| Vladivostok | Green dot | Contract | Rostelecom |
| Makhachkala | Intercom | Rostelecom | Samtel |
| Tomsk | Green dot | Home ru | Rostelecom |
| Orenburg | TTK | Rostelecom | Home ru |
| Kemerovo | Good Line | Rostelecom | Skymax |
| Novokuznetsk | Rostelecom | Siberian networks | RCTC |
| Ryazan | Spark | MTS | Vidicon |
| Astrakhan | Real | MTS | TelPlus |
| Naberezhnye Chelny | MTS | Fly | Home ru |
| Penza | PTK | TTK | Home ru |
| Kirov | Home ru | MTS | VerifyNet |
| Lipetsk | Samtel | Green Dot | Beeline |
If we do a summary analysis taking into account the distribution throughout the country and the quality of services provided, we get the following three leaders in Russia:
- Rostelecom and MTS share space.
- Beeline.
- Home ru.
In total, both according to external assessments and according to our research, the best providers retain their positions. Therefore, if you have the opportunity to connect to them in your home, you now know which provider is better to connect to.
Reviews of the largest providers (geography, technologies, approximate prices)
The decision about which Internet to choose depends on the location of the subscriber, because for each Russian region, in addition to the mainline providers, there are also local ones. And sometimes you can find better deals on tariffs.
But the coverage area and quality of connection of backbone Internet companies is most often the reason for choosing them. The largest providers in Russia include:
- Rostelecom;
- Megaphone;
- RetnNet;
- TTK;
- VimpelCom;
- Er-telecom;
- MTS, etc.
And which Internet provider is the best, each user decides independently.
Rostelecom
Rostelecom is the largest Internet provider in Russia.
Geography
Rostelecom has the largest coverage area due to more than 500 thousand kilometers of network highways. For example, in 2016, the construction of a fiber optic system was completed in the area between Kamchatka, Sakhalin and Magadan! The complex of networks that the Internet provider is building throughout Russia (including in the Arctic Circle) on the basis of government orders, perfectly demonstrates Rostelecom’s leading position in the provision of communication services in the Russian Federation.
Internet on the Rostelecom website
Technologies
Rostelecom provides Internet access using optical fiber and Wi-Fi technologies. Fiber access is also divided into:
- FTTx: FTTH (the cable is laid directly into the apartment or house);
- FTTB (fiber optic is delivered to the building and reaches the apartments using other systems);
- FTTN (signal distributed at the node);
- FTTS (the signal arrives immediately to the subscriber’s room);
Approximate prices
Rostelecom's package offers depend on the region where they are provided. For example, in Moscow the minimum cost of connecting to the Internet is 200 rubles per month. But the user will not receive a free Wi-Fi router, and the connection speed is minimal - about 30 Mbit/sec.
Minimum tariff
When the price increases to 449 and 499 rubles per month, the connection speed increases to 100 and 200 Mbit/s, respectively, and subscribers receive a Wi-Fi router.
Tariffs with Wi-Fi router
Beeline
Beeline offers its customers wired and wireless Internet.
Geography
Beeline's 3G Internet coverage area is better in the central and southern parts of Russia; in the eastern regions of the Russian Federation, Internet speed drops, and in the north it is better not to even try to use it at home, but to choose the provider that works locally.
Beeline coverage areas
4G presented in:
- Moscow and Moscow Region;
- St. Petersburg and region;
- some central regions of Russia;
- large cities (if you head to the north and east of the country).
Wired Internet from Beeline transmits a signal at speeds of up to 100 Mbit/sec. The provider builds highways throughout the country. Now more than 140,000 kilometers of networks have been built, but Beeline's main activities are concentrated in the central part of Russia.
Technologies
Beeline wired Internet is provided using FTTB technologies. Mobile Internet is represented by a line of all G, including 4G+.
The device receiving the Internet signal can be a smartphone, tablet or modem. The quality of the connection in the first two cases depends on the gadget itself, but for a USB modem you can amplify the signal in simple ways:
- using a USB extension cable, placing the modem closer to the window or on the balcony;
- by installing a special antenna on the facade of the house (the method is suitable for cottages), which will be connected to the modem device with a coaxial cable;
- by connecting an extension cord, antenna and active amplifier (when living in remote areas with a weak signal from Beeline).
Approximate prices
The cost of Internet depends on the tariff and region. Today there are promotions where you can get home Internet for free.
Home Internet within ALL tariffs
MTS
The length of MTS highways is more than 120,000 kilometers. In Moscow, MTS cooperates with MGTS, the networks of which provider it uses (to reduce Internet rates, it is better to connect a landline telephone to the apartment). The provider has offers for home Internet, even with daily tariffs.
Approximate prices
Prepaid Internet tariffs in Moscow (payment per month):
- 200 Mbit/sec for 490 rubles;
- 60 Mbit for 360 rubles;
- 500 Mbit for 1600 rubles.
Technologies
MTS wired Internet is connected using the following technologies:
- GPON (Moscow and Moscow Region);
- ADSL.
Fiber optic cable is laid into the apartment free of charge. If a subscriber uses MTS services for less than a year, he will be forced to pay a penalty (the amount is discussed individually).
Information from the MTS website
Er-telecom
Er-telecom holding has offices in 56 cities of Russia and provides broadband Internet access as part of the Dom.ru service. The company uses fiber-to-the-home (FTTB) technology.
Internet from Dom.ru
The minimum connection cost is 300 rubles at a speed of 100 Mbit/sec. Simultaneously with the Internet, the user will be connected to 100 television channels (it is better to connect them to a mobile device).
TTK
TransTeleCom services a fiber-optic backbone with a length of about 80,000 kilometers. Despite the relatively small coverage (Rostelecom has the best performance), it was TTK that was the first to build an Internet transmission line to the northernmost city of Lobytnangi (which is located beyond the Arctic Circle!).
In some cities (for example, Moscow) the TTC does not have offers for individuals. Provider tariffs in Yekaterinburg:
Instructions for self-selection
In this section I will show you, for ordinary people, how you can quickly and conveniently choose the Internet. We do everything step by step.
- Go to the website provayder.net (click on the link).
- Let’s scroll a little lower and immediately get acquainted with the list of the best providers. But we are interested in this area:
- I want to connect my Internet and TV, I set the speed to 100 Mbit/s (enough for a long time), the subscription fee is up to 1000 rubles and click the “Choose tariff” button.
- And here are all the tariffs available to us. If desired, you can sort by popularity or cost. Personally, I’m quite happy with the TTK, especially for such a price, and just below there are top-end Rostelecom and MTS (look through it yourself):
That's all. If you like the tariff, click “Connect” and enjoy good internet in your home for many years. Nowadays there is no such thing as the Internet being better in some places and worse in others – competition forces everyone to provide the stated speed according to the tariff. So choose based on price and reviews. And I will end here. Not saying goodbye. If you have any thoughts or questions, feel free to write in the comments - we will discuss, help, and share our experience.
Prices
Prices will likely decrease as we move into the digital age, and average Internet speeds will increase every year.
Providers often offer an optimal speed of 100 Mbps. The highest price for this speed in South Africa is $87/month. Residents of Norway, as well as Iceland, spend about $69/month, and Hong Kong – $29/month.
Speed of 100 Mbit/s is cheapest in Eastern European countries (USD/month):
- Moldova – 10;
- Russia – 8;
- Ukraine - 6.
At the cost of 1 GB of mobile data, the cheapest countries are India - $0.26, Kyrgyzstan - $0.27 and 0.49 in Kazakhstan. See the infographic for other numbers: