| Photo | Name | Rating | Price | |||
| The best AMD APU processors on socket FM2 and FM2+ | ||||||
| #1 | AMD A10-7890K | ⭐ 100 / 100 5 — votes | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | AMD A10-5800K Trinity | ⭐ 99 / 100 | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | AMD A8-7680 | ⭐ 98 / 100 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #4 | AMD A8-6600K Richland | ⭐ 97 / 100 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #5 | AMD A6-7480 | ⭐ 96 / 100 | Find out the price | |||
| #6 | AMD A6-7400K | ⭐ 95 / 100 | Find out the price | |||
| #7 | AMD A4-7300 Richland | ⭐ 94 / 100 | Find out the price | |||
| The best AMD processors for socket FM2(+) without integrated graphics | ||||||
| #1 | AMD Athlon II X4 750K Trinity | ⭐ 100 / 100 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | AMD Athlon X4 840 | ⭐ 99 / 100 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | AMD Athlon X4 830 | ⭐ 98 / 100 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
Which fm2 processor would you choose or recommend?
Take the survey
Socket AM3
Socket AM3 is a further development of Socket AM2 (AM2+); the differences are support for DDR3 memory and a higher speed of the HyperTransport bus. Processors for Socket AM3 work on motherboards with Socket AM2+ (less often on Socket AM2), but not vice versa. This is because AM3 processors have a new memory controller that supports both DDR2 and DDR3 memory, thus providing backward compatibility with AM2+ motherboards, but since AM2 processors do not have a new memory controller, it will not work on AM3 motherboards.
Introducing Socket FM2. Review and testing of Gigabyte F2A85X-UP4 on AMD A85X chipset
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Socket FM2
- CPU cooling system
- New A85X logic set
- Packaging and equipment
- Board design and features. Cooling system
- Specifications
- BIOS Setup Features
Introduction
So, the official release of the new AMD platform in the Socket FM2 design took place. Of course, processors themselves are quite interesting, but what is a CPU? A piece of silicon on a substrate, covered with a metal lid, for the price of a certain amount of banknotes. Nothing more. This is just one element of a system called “computer”. But the skeleton that connects and carries almost everything is the motherboard. It largely determines both the functionality that the final system will receive and how fully the potential of the processor will be realized.
Socket FM2
CPU cooling system
A new platform, a new processor is always interesting. Well, almost always. However, in addition to the interest in performance and price, there is the question of compatibility, for example, with older cooling systems.
With the new Socket FM2 connector, AMD did not change its traditions - the mounting of the CPU cooling system remained unchanged and consists of either two separate plastic elements (which appeared on Socket AM3+), or a single plastic frame (an earlier version). On the reverse side, the motherboard is protected from sagging by a plate - plastic with similar latches or metal with bolts (at the manufacturer's choice). The location of the holes has not changed. For comparison, here is a photo of the Socket FM2 and Socket AM3 mounts (Gigabyte GA-MA790XT-UD4P motherboard).
The mount has remained virtually unchanged since Socket 754, which, by the way, celebrated its nine-year anniversary last month. Thus, any cooling system compatible with Socket 754/939/AM2/AM2+/AM3/AM3+/FM1 will be suitable:
announcements and advertising
2080 Super Gigabyte Gaming OC for 60 rubles.
Compeo.ru - the right comp store without any tricks
RTX 2060 becomes cheaper before the arrival of 3xxx
Ryzen 4000
series included in computers already in Citylink
The price of MSI RTX 2070 has collapsed after the announcement of RTX 3xxx
Core i9 10 series is half the price of the same 9 series
The price of memory has been halved in Regard - it’s more expensive everywhere
Thermaltake Big Typhoon 120 VX (2007) from the author’s storage on the Socket FM2 motherboard.
Enviable consistency.
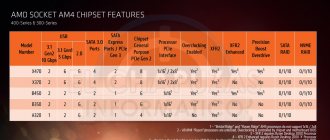
New A85X logic set
Before getting acquainted with the motherboard, it is necessary to at least briefly consider its basis - the chipset. After all, the board's capabilities largely depend on the set of system logic on which it is based. Here it is worth noting one fundamental difference between Socket FM1/FM2 and Socket AM3/AM3+: all FM1/FM2 chipsets are single-chip sets of system logic, actually consisting of a south bridge, since almost the only element of the north bridge is the main PCI-E controller used in primarily for graphics slots, now part of the processor. Why "main"? Yes, because the second PCI-E controller, modest in characteristics (only a few lines), used for peripherals, has not disappeared from the south bridge.
Together with processors codenamed Trinity, AMD also introduced a new set of system logic A85X (codenamed “Hudson D4”), which is a development of the previous generation of AMD chipsets - A55 and A75, without bringing anything revolutionary for the Comal Socket FM2 platform, which can be seen from its characteristics. As a comparison, I will give the characteristics of the leading AMD logic set for Socket AM3+, or more precisely, its south bridge SB950.
| A85X | A75 | A55 | SB950 | |
| Technical process, nm | 65 | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| Thermal package, watt | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 6.0 |
| CPU communication bus | Unified Media Interface 2.0 (UMI 2.0) 2GB/s | Unified Media Interface 2.0 (UMI 2.0) 2GB/s | Unified Media Interface 2.0 (UMI 2.0) 2GB/s | Alink Express III (2GB/s) |
| Support for graphics tandems | AMD CrossFireX AMD Dual Graphics | AMD CrossFireX AMD Dual Graphics | AMD CrossFireX AMD Dual Graphics | AMD CrossFireX NVIDIA SLI |
| Disk subsystem | 8 SerialATA III 6Gbps ports Supports RAID 0, 1, 5, 0+1 and JBOD, AHCI, NCQ, eSATA and port splitters (including FIS-based) | 6 SerialATA III 6Gbps ports Supports RAID 0, 1, 0+1 and JBOD, AHCI, NCQ, eSATA and port splitters (including FIS-based) | 6 SerialATA II 3Gbps ports Support RAID 0, 1, 0+1 and JBOD, AHCI, NCQ, eSATA | 6 SerialATA III 6Gbps ports Support RAID 0, 1, 5, 0+1 and JBOD, AHCI, NCQ, eSATA and port splitters |
| Built-in memory card controller | Secure Digital 2.0 (SDHC) up to 32 GB inclusive | Secure Digital 2.0 (SDHC) up to 32 GB inclusive | absent | absent |
| USB 1.1 support | 2 ports (one UHCI host controller) | 2 ports (one UHCI host controller) | 2 ports (one UHCI host controller) | 2 ports (one UHCI host controller) |
| USB 2.0/1.1 support | 10 ports (three separate EHCI host controllers) | 10 ports (three separate EHCI host controllers) | 14 ports (three separate EHCI host controllers) | 14 ports (three separate EHCI host controllers) |
| USB 3.0/2.0 support | 4 USB 3.0 ports (one xHCI host controller) | 4 USB 3.0 ports (one xHCI host controller) | absent | absent |
| PCI-E for communication with peripheral devices/controllers | 4 PCI-E 2.0 lanes + 4 PCI-E 2.0 lanes by processor | 4 PCI-E 2.0 lanes + 4 PCI-E 2.0 lanes by processor | 4 PCI-E 2.0 lanes + 4 PCI-E 2.0 lanes by processor | 4 PCI-E 2.0 lanes + 6 PCI-E 2.0 lanes via north bridge |
| PCI | 3 slots (can be used for additional controllers) | 3 slots (can be used for additional controllers) | 3 slots (can be used for additional controllers) | 4 slots (can be used for additional controllers) |
As mentioned above, the whole difference between the chipsets for AM3/AM3+ and FM1/FM2 is that in the latter the north bridge of the logic set “moved” into the processor, so the similarity between them becomes even greater than what appears at first glance from the above tables.
If in the case of Socket AM3(+) Hyper Transport 3.1 (6.4 GT/s) is indicated - the connection between the processor and the north bridge, then in the case of FM1/FM2 the actual name of the communication bus between the bridges is given (after all, the north bridge itself is now in the processor) - Unified Media Interface. And for Socket AM3/AM3+, the connection between bridges is called Alink Express. But the point is the same: in both cases these are four PCI-E version 2.0 lanes. Doesn't look like anything? If you look closely, you get a very persistent feeling that under the guise of A**, users actually received a redesigned and slightly modified traditional south bridge of AMD chipsets. Which, however, is not too surprising, given the realities of today.
Something was removed, something, on the contrary, was added to maintain both the technical and marketing level. For example, a built-in SDHC card controller is not at all superfluous for mobile PCs, where, among other things, FM1/FM are positioned, and it would not hurt at all on a desktop computer (if the case manufacturer bothers to implement such functionality). But a special abundance of PCI and PCI-E ports is unlikely to be required, so their number was reduced, which certainly made it possible to both simplify the crystal and save a little in power consumption. To be fair, it is worth noting that despite the functionality of the A55, which is more modest than that of the SB950, the TDP of the former is for some reason noticeably higher.
There is also another noteworthy point in the configuration of PCI-E lines: the competing Intel platform - LGA 1155 - has two PCI-E controllers, they are also located in the processor and chipset, the number of lines is the same - 16 + 8. But Intel's CPU supports there are only sixteen lines used only for the graphics system, and the chipset itself provides another eight lines (which, by the way, is often barely enough for manufacturers to implement all the functionality, and as a result both switches and switches are used). The communication bus between the processor and the chipset is called Direct Media Interface (DMI) and, it’s funny, physically it’s the same PCI-E x4 as AMD’s. With the same bandwidth.
As a result, you can see great similarities between the two platforms. Except for two "buts". The first is that Intel has support for PCI-E 3.0 (the Ivy Bridge processor controller, the chipset itself, even the new Z77, still offers 2.0), and AMD refused 3.0, saying that it doesn’t hurt needed (at the same time, modern AMD video cards fully support this same PCI-E 3.0). Therefore, Socket FM2, despite its novelty, is exclusively PCI-E 2.0. Second, both platforms offer eight PCI-E lanes for peripherals in the form of expansion cards and additional on-board controllers. But for AMD, half of the lines are connected directly to the processor, while for Intel, all eight lines from the south bridge (together with four SATA2, two SATA3, four USB 3.0, fourteen USB 2.0, and others) are tied to a bus with exactly the same bandwidth.
Most likely, it is because of this that Intel has such a variety of SATA versions, and in the end, users must understand the colors of SATA ports, which is the second version and which is the third (by the way, the question is not as easy as it might seem - sometimes color designation back to the opposite) to connect a newly purchased SSD. AMD, as a rule, does not force users of its products to think about such technical nuances.
Well, as in the case of AM2/AM3/AM3+, the set of logic for Socket FM2 is not a constant. The former can have both the 790FX and SB600, or the 790X paired with the SB850. For FM2, A85X, A75, and A55 can be used. They are used: the A75 and A55 will not leave the market, it’s just that now the platform with AMD APUs will be divided into three segments - lower (A55), middle (A75) and high-end (A85X). Accordingly, almost all manufacturers have prepared (or are currently preparing) products on all chipsets. Thus, Gigabyte presented four models:
- Gigabyte GA-F2A55M-DS2 based on A55 for the budget segment;
- Gigabyte GA-F2A75-D3H and GA-F2A75M-D3H based on A75 for the mid-range segment;
- Gigabyte GA-F2A85X-UP4 on A85X for the older segment.
Seemingly complex names are actually easy to decipher and characterize their bearers:
- GA - Gigabyte;
- F2 – Socket FM2;
- A** - chipset used in the board;
- The letter “M” denotes the mATX format, “X” – support for NVIDIA SLI technology (although in this case there is no explicit mention of its support, so, most likely, here “X” is only part of the name of the chipset and, perhaps, left for “ beauty");
- DS2, D3H, UP4 – briefly describe the capabilities and class of the product, for example, “P” indicates that the board belongs to the UltraDurable 5 product family.
In the near future, the release of two more motherboards with the HD2 index at the end is expected. These will be mid-level products. Well, the subject of this review will be Gigabyte’s top-class model for Socket FM2 – the GA-F2A85X-UP4 motherboard on the AMD A85X chipset.
Review of the Gigabyte F2A85X-UP4 motherboard based on the AMD A85X chipset
Packaging and equipment
Despite the new AMD platform, Gigabyte did not make any changes to the box design.
Both the front and back sides of the packaging are replete with references to various technologies, including proprietary ones, used in this product
Let's look at them in a little more detail.
- Most of the space is allocated to the description of the processor power subsystem, based on DrMos chips (the word “DrMos” itself is not mentioned for obvious reasons - it has been used by another motherboard manufacturer for quite a long time). Moreover, it is directly indicated that highly efficient IR3550 microcircuits are used and their advantages are described.
- GIGABYTE Digital Power Engine provides two separate power converters for the processor itself and the integrated GPU.
- Application of copper layers with double thickness.
- 3D BIOS / DUAL UEFI BIOS - the motherboard uses UEFI BIOS, which has two versions of the interface - conventional and pseudo-three-dimensional (3D). DUAL means the presence of two microcircuits: the main one and a backup one in case the contents of the first one are damaged.
- DirectX 11 indicates full support for the integrated graphics core of AMD APUs.
- 333 Onboard Acceleration implies the presence on the motherboard of USB 3.0 ports with triple the current and SATA 6 Gb/s ports.
- Use only Japanese polymer capacitors.
- GIGABYTE On/Off Charge is a technology for accelerated charging via the USB port of Apple products.
- Support for Lucid Universal MVP technology, which allows you to quickly switch between the integrated graphics core of an AMD APU and a discrete graphics card, as well as combine their graphics powers.
- Supports AMD Eyefinity, AMD Dual Graphics and AMD CrossFire technologies.
- Triple-Monitor support means the ability to operate three monitors simultaneously (AMD Eyefinity).
- Dual-link DVI port implies the presence of a Dual link DVI-D port on the rear panel of the motherboard, capable of producing an image with a resolution of 2560 by 1600 pixels, which is important when using large-diagonal monitors.
- Availability of DVI and HDMI ports.
The interior of the box is quite standard for a middle-class product: no transparent windows, nested boxes (one or more) and so on.
The delivery set lies on a cardboard divider, under which the motherboard is hidden in an antistatic bag. It includes:
- Brief assembly instructions in several languages (including Russian);
- DVD with software;
- Plug for the rear panel of the case;
- Detailed instructions for the motherboard in English;
- Six SATA cables with latches.
Socket AM3+
Socket AM3+ (socket 942)
- modification of Socket AM3, developed for processors codenamed “Zambezi” (microarchitecture - Bulldozer).
Some motherboards with socket AM3 have the ability to update the BIOS and use processors with socket AM3+. However, when using AM3+ processors on AM3 motherboards, it may not be possible to obtain data from the temperature sensor on the processor. Also, the power saving mode may not work due to the lack of support for fast core voltage switching in Socket AM3.
all AMD processors on socket FM2+ (A10, A8, A6, A4, Athlon) - characteristics, prices socket FM2+
All processors are FM2+. This page contains: current prices and technical specifications for all AMD processors of the FM2+ socket. The FM2+ connector replaced the FM2 socket.
The FM2+ connector is represented by the following processors:
- Athlon (2-4 cores)
- A10 (4 cores, integrated graphics)
- A8 (4 cores, integrated graphics)
- A6 (2 cores, integrated graphics)
- A4 (2 cores, integrated graphics)
| Processor name | Price | Cores | Frequency | Video card | Cache memory | Power | Technical process | Memory support | Codename |
| A10-7890K | RUB 9,350 RUB 9,350 | 4 | 4.1(4.3) GHz | R7 (866 MHz) | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| Athlon x4 880K | RUB 1,131 RUB 1,131 | 4 | 4(4.2) GHz | No | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| A10-7870K | RUB 4,779 RUB 4,779 | 4 | 3.9(4.1) GHz | R7 (1100 MHz) | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| Athlon x4 870K | RUB 1,377 RUB 1,377 | 4 | 3.9(4.1) GHz | No | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| A10-7850K | RUR 3,518 RUR 3,518 | 4 | 3.7(4) GHz | R7 (757 MHz) | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Kaveri |
| Athlon x4 860K | RUB 1,131 RUB 1,131 | 4 | 3.7(4) GHz | No | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Kaveri |
| A10-8750/A10 PRO-8750B | RUR 3,083 RUR 3,083 | 4 | 3.6(4) GHz | R7 (757 MHz) | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| A10-7860K/A10 PRO-7850B | RUR 3,836 RUR 3,836 | 4 | 3.6(4) GHz | R7 (757 MHz) | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| FX-770K | RUB 2,095 RUB 2,095 | 4 | 3.5(3.9) GHz | No | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3 | Kaveri |
| A10-7800/A10 PRO-7800B | RUB 3,119 RUB 3,119 | 4 | 3.5(3.9) GHz | R7 (720 MHz) | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Kaveri |
| A8-7680 | RUB 3,157 RUB 3,157 | 4 | 3.5(3.8) GHz | R7 (1029 MHz) | 2 MB | 45 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Carrizo |
| Athlon x4 845 | RUB 3,085 RUB 3,085 | 4 | 3.5(3.8) GHz | No | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Carrizo |
| A10-7700K | RUB 3,030 RUB 3,030 | 4 | 3.4(3.8) GHz | R7 (720 MHz) | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Kaveri |
| A8-8650/A8 PRO-8650B | RUB 2,248 RUB 2,248 | 4 | 3.2(3.8) GHz | R7 (757 MHz) | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| Athlon x4 840 | RUB 1,007 RUB 1,007 | 4 | 3.1(3.8) GHz | No | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3 | Kaveri |
| A8-7690K | ? | 4 | 3.7 GHz | R7 (757 MHz) | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3 | Godavari |
| A8-7670K | ? | 4 | 3.6(3.9) GHz | R7 (758 MHz) | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| A8-7650K | RUB 2,446 RUB 2,446 | 4 | 3.3(3.8) GHz | R7 (757 MHz) | 4 MB | 95 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Kaveri |
| Athlon x4 850 | RUB 1,450 RUB 1,450 | 4 | 3.2 GHz | No | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| A8-7600/A8 PRO-7600B | RUR 2,212 RUR 2,212 | 4 | 3.1(3.8) GHz | R7 (757 MHz) | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Kaveri |
| Athlon x4 835 | ? | 4 | 3.1 GHz | No | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3 | Carrizo |
| Athlon X4 830 | 921 RUR 921 RUR | 4 | 3(3.4) GHz | No | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3 | Kaveri |
| A8-7500 | RUB 2,175 RUB 2,175 | 4 | 3 GHz | R7 | 4 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Kaveri |
| A6-7470K | ? | 2 | 3.7(4) GHz | R5 (800 MHz) | 1 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| A6-8550/A6 PRO-8550B | 2_030_rub 2_030_rub | 2 | 3.7(4) GHz | R5 (800 MHz) | 1 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-2133 MHz | Godavari |
| A6-7400K/A6 PRO-7400B | RUB 1,667 RUB 1,667 | 2 | 3.5(3.9) GHz | R5 (800 MHz) | 1 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-1866 MHz | Kaveri |
| A4-8350(B) | RUB 1,240 RUB 1,240 | 2 | 3.5(3.9) GHz | R5 (757 MHz) | 1 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-1866 MHz | Godavari |
| Athlon x2 450 | RUB 1,985 RUB 1,985 | 2 | 3.5(3.9) GHz | No | 1 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3 | Kaveri |
| A6-7480 | RUB 2,175 RUB 2,175 | 2 | 3.5(3.8) GHz | R5 (900 MHz) | 1 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-1866 MHz | Carrizo |
| A4 PRO-7350B | RUR 1,434 RUR 1,434 | 2 | 3.4(3.8) GHz | R5 (515 MHz) | 1 MB | 65 W | 28 nm | DDR3-1866 MHz | Kaveri |
Socket FM2 & Socket FM2+
Socket FM2 is a processor socket for AMD hybrid processors (APU) with 904 pins. Socket FM2 is an update to Socket FM1, but is not backwards compatible.
Socket FM2+ is a processor socket for AMD hybrid processors (APU). Socket FM2+ for APU processors are not compatible with Socket FM2, but FM2 for hybrid processors is compatible with Socket FM2+.
Features of CPU on socket FM2
For a long time, Advanced Micro Devices existed as an affiliate, producing processors under license from Intel. However, in the 90s, the situation in the personal desktop computer market changed: AMD began to develop their own original product on a competitive basis. The results were immediate: the new product was cheaper and had better performance. True, at the same time it consumed a lot of energy and got very hot, which has become a stereotypical opinion about all AMD CPUs. After the impressive success of the first Athlon and Phenom, the company slowed down and began to lose the race. By the end of the 2010s, it was inferior to the giant Intel in all respects. They tried to revive sales by releasing innovative hybrid solutions.
On a note! The hybrid processor combines the CPU itself and the GPU - a graphics chip on one board. The built-in graphics processor allows you not only to run the interface of a personal computer without a discrete video card, but also to process graphics - videos, games, etc.
The FM2 socket was developed for new processor lines. It was designed for a microarchitecture that AMD named after construction equipment - Bulldozer, Pilediver, Steamroller and Excavator. The series turned out to be quite controversial - in addition to problems with the actual performance of the microcircuits, the company was plagued by marketing failures - either the release of the new series would be delayed, or the new line would not live up to expectations.
FM2 socket
The niche where AMD hybrid processors really beat Intel is game consoles and consoles. Profit from this segment allowed the company to stay afloat and release a new generation of Ryzen in 2020.
Among the processors on the FM socket there are also models without a graphics processor, primarily a continuation of the already familiar Athlon line. Most solutions with integrated graphics have the ability to work in hybrid mode.
On a note! Hybrid graphics from AMD is a solution that allows you to use the graphics cores of the processor and discrete video card in conjunction when their performance is combined. In this case, the discrete video chip has its own memory chips, and the built-in one uses RAM resources. This gives a good increase in graphics processing power compared to running devices separately when one of them is turned off. This mode can be configured using special applications.
The Trinity and more modern Richland processor families were based on the Piledriver architecture. Structurally, they had some shortcomings that caused weakness in tasks that required high computing power of tasks when running on a single thread (single-core). But multi-threaded tasks were processed with a bang. With the release of the new Kaveri and Godavari families, the microarchitecture was changed to Steamroller, in which some of the problems were solved, and the process technology was reduced from 32 to 28 nanometers. Finally, filling the segment of budget processors with an integrated graphics core, Advanced Micro Devices updated the line on the old process technology, but with a new Carrizo core and Excavator microarchitecture. Solutions already familiar to users have received a second life at a price that is acceptable to most.
On a note! Overclocking a processor is an increase in its clock frequency and the voltage supplied to the chips by configuring it through special software or BIOS. True, an increase in productivity leads to an increase in heat generation, and therefore increases the noise of the system. Despite the fact that AMD is developing special software for overlocking, the latter is still done at the user’s own risk, as it reduces the stability of operation and shortens the service life of components.
Video - Review of the gaming kit - for socket FM2
Socket AM4
Socket AM4 is a universal processor socket developed by AMD for high-performance AMD Ryzen processors, as well as the AMD Athlon X4 and AMD A-series 7th generation lines. The AM4 platform ensures interaction of the processor with DDR4 RAM in dual-channel mode, allows direct operation with USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 interfaces, supports the PCI-Express bus and the SATA Express controller. Socket AM4 is intended to become a single processor socket for future generations of AMD processors. Regarding the CPU cooling system, the mount is not compatible with previous AM/FM sockets.
Processors for FM2
Sempron
| Processor name | Buy on Aliexpress | Modules (kernels) | Clock frequency | Turbo frequency | L2 cache | Integrated Graphics | Memory | TDP | Socket |
| AMD Sempron X2 240 | 1(2) | 2.9 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 1 MB | N/A | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | FM2 | |
| AMD Sempron X2 250 | 1(2) | 3.2 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 1 MB | N/A | DDR3-1600 | 65 W |
Athlon
| Processor name | Buy on Aliexpress | Modules (kernels) | Clock frequency | Turbo frequency | L2 cache | Integrated Graphics | Memory | TDP | Socket |
| AMD Athlon X2 340 | 1(2) | 3.2 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 1 MB | N/A | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | FM2 | |
| AMD Athlon X2 350 | 1(2) | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 1 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | ||
| AMD Athlon X2 370K | 1(2) | 4.0 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 1 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | ||
| AMD Athlon X4 730 | 770 rub. | 2(4) | 2.8 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 2× 2 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | |
| AMD Athlon X4 740 | 870 rub. | 2(4) | 3.2 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 2× 2 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | |
| AMD Athlon X4 750 | 930 rub. | 2(4) | 3.4 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 2× 2 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | |
| AMD Athlon X4 750K | 2(4) | 3.4 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 2× 2 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 100 W | ||
| AMD Athlon X4 760K | 950 rub. | 2(4) | 3.8 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 2× 2 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 100 W |
A4
| Processor name | Buy on Aliexpress | Modules (kernels) | Clock frequency | Turbo frequency | L2 cache | Integrated Graphics | Memory | TDP | Socket |
| AMD A4 PRO-7300B | 1(2) | 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 1 MB | 8470D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | FM2 | |
| AMD A4-4000 | 1(2) | 3.0 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 1 MB | 7480D | DDR3-1333 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A4-4020 | 1(2) | 3.2 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 1 MB | 7480D | DDR3-1333 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A4-5300 | 1600 rub. | 1(2) | 3.4 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 1 MB | HD 7480D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | |
| AMD A4-5300B | 1(2) | 3.4 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 1 MB | HD 7480D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A4-6300 | 1500 rub. | 1(2) | 3.7 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 1 MB | 8370D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | |
| AMD A4-6300B | 1(2) | 3.7 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 1 MB | 8370D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A4-6320 | 1(2) | 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 1 MB | 8370D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A4-6320B | 1(2) | 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 1 MB | 8370D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A4-7300 | 1(2) | 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 1 MB | 8470D | DDR3-1600 | 65 W |
A6
| Processor name | Buy on Aliexpress | Modules (kernels) | Clock frequency | Turbo frequency | L2 cache | Integrated Graphics | Memory | TDP | Socket |
| AMD A6-5400B | 1(2) | 3.6 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 1 MB | HD 7540D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | FM2 | |
| AMD A6-5400K | 1800 rub. | 1(2) | 3.6 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 1 MB | HD 7540D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | |
| AMD A6-6400B | 1(2) | 3.9 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 1 MB | 8470D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A6-6400K | 2500 rub. | 1(2) | 3.9 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 1 MB | 8470D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | |
| AMD A6-6420B | 1(2) | 4.0 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 1 MB | 8470D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A6-6420K | 1(2) | 4.0 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 1 MB | 8470D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W |
A8
| Processor name | Buy on Aliexpress | Modules (kernels) | Clock frequency | Turbo frequency | L2 cache | Integrated Graphics | Memory | TDP | Socket |
| AMD A8-5500 | 1700 rub. | 2(4) | 3.2 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 2× 2 MB | HD 7560D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | FM2 |
| AMD A8-5500B | 2(4) | 3.2 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 2× 2 MB | HD 7560D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A8-5600K | 2(4) | 3.6 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 2× 2 MB | HD 7560D | DDR3-1866 | 100 W | ||
| AMD A8-6500 | 3500 rub. | 2(4) | 3.5 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8570D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | |
| AMD A8-6500B | 2(4) | 3.5 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8570D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | ||
| AMD A8-6500T | 2(4) | 2.1 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8550D | DDR3-1866 | 45 W | ||
| AMD A8-6600K | 3000 rub. | 2(4) | 3.9 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8570D | DDR3-1866 | 100 W |
A10
| Processor name | Buy on Aliexpress | Modules (kernels) | Clock frequency | Turbo frequency | L2 cache | Integrated Graphics | Memory | TDP | Socket |
| AMD A10-5700 | 2000 rub. | 2(4) | 3.4 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 2× 2 MB | HD 7660D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | FM2 |
| AMD A10-5800B | 2(4) | 3.8 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 2× 2 MB | HD 7660D | DDR3-1866 | 100 W | ||
| AMD A10-5800K | 2800 rub. | 2(4) | 3.8 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 2× 2 MB | HD 7660D | DDR3-1866 | 100 W | |
| AMD A10-6700 | 2300 rub. | 2(4) | 3.7 GHz | 4.3 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8670D | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | |
| AMD A10-6700T | 2(4) | 2.5 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8650D | DDR3-1866 | 45 W | ||
| AMD A10-6790B | 2(4) | 4.0 GHz | 4.3 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8670D | DDR3-1866 | 100 W | ||
| AMD A10-6790K | 2700 rub. | 2(4) | 4.0 GHz | 4.3 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8670D | DDR3-1866 | 100 W | |
| AMD A10-6800B | 2(4) | 4.1 GHz | 4.4 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8670D | DDR3-2133 | 100 W | ||
| AMD A10-6800K | 3500 rub. | 2(4) | 4.1 GHz | 4.4 GHz | 2× 2 MB | 8670D | DDR3-2133 | 100 W |
FX and FirePro
| Processor name | Buy on Aliexpress | Modules (kernels) | Clock frequency | Turbo frequency | L2 cache | Integrated Graphics | Memory | TDP | Socket |
| AMD FirePro A300 | 2(4) | 3.4 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 2× 2 MB | FirePro | DDR3-1866 | 65 W | FM2 | |
| AMD FirePro A320 | 2(4) | 3.8 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 2× 2 MB | FirePro | DDR3-1866 | 100 W | ||
| AMD FX-670K | 2(4) | 3.7 GHz | 4.3 GHz | 2× 2 MB | N/A | DDR3-1866 | 65 W |