Content
People in their early 30s today remember very well a device attached to a telephone wire that made strange grinding sounds. While it was running, it was impossible to call anyone, but it was possible to use the global network very slowly. These were the first modems that provided a connection over a telephone line. What a modem is today is something so familiar that few people think about the meaning of the device and how it differs from other Internet equipment.
Modem. Definition. Purpose. Main characteristics.
⇐ PreviousPage 5 of 14Next ⇒The modem performs the functions of both input and output devices. It allows you to connect to other remote computers using telephone lines and exchange information between computers. The modem converts digital signals into sounds when transmitting, and vice versa when receiving.
Modem is a device for converting digital signal information into analog (Modulation) for transmission over analog communication lines, and converting the received analog signal back into digital (DEModulation).
Why is this needed? Since computers can only exchange digital signals, and communication channels are such that analog signals pass best through them, this is why a bridge is needed that converts the signal - a modem. But the modem also has quite a few other functions, the main ones being error correction and data compression. The first mode provides additional signals through which modems check data at both ends of the line and discard untagged information, while the second mode compresses the information for faster and clearer transmission, and then reconstructs it at the receiving modem. Both of these modes significantly increase the speed and purity of information transmission, especially in Russian telephone lines.
Main characteristics of modems
Modems differ in many characteristics: design, supported data transfer protocols, error correction protocols, voice and fax data transfer capabilities.
According to their design (appearance, placement of the modem in relation to the computer), modems are: internal - inserted into the computer as an expansion card; desktop (external) have a separate case and are placed next to the computer, connecting with a cable to the computer port; the modem in the form of a card is miniature and is connected to the laptop computer through a special connector; the portable modem is similar to the desktop modem, but has a reduced size and is self-powered; rack modems are inserted into a special modem rack, which increases ease of use when the number of modems exceeds a dozen.
Modems also differ in type: an asynchronous modem can only perform transmission over an analogue telephone network and works only with asynchronous communication ports of terminal devices (in its pure form it is not currently used);
fax modem is a classic modem with added fax capability, which allows you to exchange faxes with fax machines and other fax modems;
a voice modem is a modem capable of not only performing the functions of a fax modem, but also receiving voice messages from the telephone network, recording them to a file;
modem with backup of a dedicated dial-up line - these modems are used when reliable communication is required. They have two independent line inputs (One connects to a leased line and the other to a dial-up line);
SVD modem (simultaneous voice and data) allows you to simultaneously (and not alternating) with data transfer carry out a conversation using a handset connected to the modem;
synchronous modem - supports synchronous and asynchronous transmission modes;
four-wire modem - these modems operate over two dedicated lines, one is used only for transmission, the second only for reception) in duplex mode. This is used to reduce the influence of echo;
cellular modem - used for mobile radiotelephony, which includes cellular communications;
ISDN modem - combines a regular modem and an ISDN adapter in its case;
a radio modem uses the air as a transmission medium instead of telephone wires;
network modem - these are modems with a built-in LAN network adapter for sharing on a local network;
cable modem - these modems allow you to use cable television channels for transmission. At the same time, the speed can reach 10 Mbit/s.
Modems are also characterized by data transfer speed. It is measured in bps (bits per second) and is set by the manufacturer at 2400, 9600, 14400, 16800, 19200, 28800, 33600, 56000 bps.
Drives for CDs. Purpose. Main characteristics.
Operating principle of a CD-ROM drive. The surface of the optical disk moves relative to the laser head at a constant linear speed, and the angular speed varies depending on the radial position of the head. The laser beam is directed onto the track and focused using a coil. The beam penetrates the protective layer of plastic and hits the reflective layer of aluminum on the surface of the disk.
When it hits the protrusion, it is reflected onto the detector and passes through a prism, which deflects it onto a light-sensitive diode. If the beam hits the hole, it is scattered and only a small part of the radiation is reflected back and reaches the photosensitive diode. On the diode, light pulses are converted into electrical ones, bright radiation is converted into zeros, and weak radiation into ones. Thus, the pits are perceived by the drive as logical zeros, and the smooth surface as logical ones.
CD-ROM capacity is 640-700 MB. The information carrier on a CD is a relief polycarbonate substrate, on which a thin layer of light-reflecting metal is applied.
CD-ROM discs are designed for reading information only, not writing.
CD-ROM drive performance. It is usually determined by its speed characteristics during continuous data transfer over a certain period of time and the average data access time, measured in KB/s and ms, respectively. There are one-, two-, three-, four-, five, six and eight-speed drives that provide data reading at speeds of 150, 300, 450, 600, 750, 900, 1200 KB/s, respectively. An important characteristic of the drive is the buffer fill level, which affects the quality of playback of animated images and videos.
Design features of CD-ROM drives
As you know, most drives are external and built-in (internal). CD drives are no exception in this sense. Most CD-ROM drives currently offered are built-in.
The front panel of each drive provides access to the CD loading mechanism. One of the most common is the CD-ROM loading mechanism using a caddy.
CD-R. A disk drive with the ability to write information once onto a special disk. Recording on CD-R discs is carried out due to the presence of a special photosensitive layer on them, which burns out under the influence of a high-temperature laser beam.
The speed of writing information to CD-R discs on modern drive models can reach up to 20 times. However, it is very important to select discs for recording, the markings of which coincide with the speed marking of your drive (4x, Sx, 10x, 12x, 14x, etc.). Most blanks sold today should support at least eight times the write speed.
CD-RW. Today, CD-R drives have virtually disappeared from the scene. They have been replaced by new standard drives that can burn not only CD-Rs, but also rewritable discs - CD-RW. When recording these discs, a completely different technology is used, different from CD-R, and they are designed differently.
A CD-RW disc is like a layer cake, where the working, active layer rests on a metal base. It consists of a special material that changes its state under the influence of a laser beam. Being in a crystalline state, some parts of the layer scatter light, while others - amorphous - transmit it through themselves, onto the reflective metal substrate. Thanks to this technology, information can be written to the disk, and not just read.
Speed characteristics are usually indicated in the name of the drive - for example, 12x8x32, where the lower value corresponds to the CD-RW write speed, and the maximum corresponds to the read speed.
ROM. Purpose. Compound.
Read-only memory (ROM) stores information that does not change during computer operation. This information is made up of test-monitor programs (they check the functionality of the computer when it is turned on), drivers (programs that control the operation of individual computer devices, for example, a keyboard), etc. ROM is a non-volatile device, so the information in it is saved even when the power is turned off.
Read-only memory (ROM—read-only memory) is non-volatile memory used to store data that will never need to be changed. The memory contents are specially “hardwired” into the BIOS chip during its manufacture for permanent storage. ROM can only be read.
BIOS is the basic input/output system. BIOS is a complex system consisting of a large number of utilities designed to automatically recognize the equipment installed on a computer, configure it and check its operation.
This system includes various input-output programs that provide interaction between the operating system, application programs on the one hand, and devices included in the computer (internal and external) on the other.
Originally, BIOS was intended to test the computer when it was turned on. Currently, BIOS is a complex system consisting of a large number of utilities designed to automatically recognize the equipment installed on a computer, configure it and check its operation. The most promising way to store a BIOS system is flash memory (removable memory cards). It allows you to modify functions to support new devices connected to the computer. The BIOS system is inextricably linked with CMOS RAM .
CMOS ( semi-permanent memory ) is a small area of memory for storing computer configuration settings, which is controlled using the CMOS Setup Utility. Has low power consumption. The contents of CMOS memory do not change when the computer's power is turned off because it uses a special battery to power it. It is used to store information about the configuration and composition of the computer’s equipment, stores information about floppy and hard drives, about the processor, as well as readings from the clock system.
RAM. Purpose. Compound.
Random access memory (also random access memory, RAM) - in computer science - memory, part of the computer memory system, which the processor can access for one operation (jump, move, etc.). It is designed to temporarily store data and instructions necessary for the processor to perform operations. RAM transmits data to the processor directly or through cache memory. Each RAM cell has its own individual address. RAM can be manufactured as a separate unit or included in the design of a single-chip computer or microcontroller.
Random access memory (RAM) is used for short-term storage of variable (current) information and allows its contents to change as the processor performs computational operations. This means that the processor can select a command or processed data from RAM (read mode) and, after arithmetic or logical processing of the data, place the result in RAM (write mode). New data can be placed in RAM in the same places (in the same cells) where the original data was located. It is clear that previous commands (or data) will be erased.
RAM is used to store programs compiled by the user, as well as initial, final and intermediate data resulting from the operation of the processor.
RAM uses either flip-flops (static RAM) or capacitors (dynamic RAM) as storage elements. RAM is a volatile memory, so when the power is turned off, the information stored in the RAM is lost forever.
Today, the most common types of RAM are SRAM (Static RAM). RAM collected on flip-flops is called static random access memory or simply static memory. The advantage of this type of memory is speed. Since the triggers are assembled on gates, and the gate delay time is very short, switching the trigger state occurs very quickly. This type of memory is not without its drawbacks. First, the group of transistors that make up a flip-flop is more expensive, even if they are etched in the millions on a single silicon substrate. In addition, a group of transistors takes up much more space because communication lines must be etched between the transistors that form the flip-flop.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
A more economical type of memory. To store a discharge (bit or trit), a circuit consisting of one capacitor and one transistor is used (in some variations there are two capacitors). This type of memory solves, firstly, the problem of high cost (one capacitor and one transistor are cheaper than several transistors) and secondly, compactness (where one trigger, that is, one bit, is placed in SRAM, eight capacitors and transistors can be accommodated). There are also some disadvantages. Firstly, capacitor-based memory works slower, because if in SRAM a change in voltage at the trigger input immediately leads to a change in its state, then in order to set one digit (one bit) of capacitor-based memory to one, this capacitor must be charged , and in order to set the discharge to zero, discharge accordingly. Memory on capacitors got its name Dynamic RAM (dynamic memory) precisely because the bits in it are not stored statically, but “drain” dynamically over time. Thus, DRAM is cheaper than SRAM and its density is higher, which allows more bits to be placed on the same space of the silicon substrate, but at the same time its speed is lower. SRAM, on the contrary, is faster memory, but also more expensive. In this regard, conventional memory is built on DRAM modules, and SRAM is used to build, for example, cache memory in microprocessors.
⇐ Previous5Next ⇒
Why and when do you need a modem?
Modulator-demodulator - that’s what this equipment is called. In English, the word sounds similar - modem. A modern modem is a device whose main purpose is to transmit information from one source to another, simultaneously converting it.
This is done as follows:
- The analog data received at the input is processed by the device and transformed into a digital format.
- The request is processed, and the received response is converted back into information that the user can understand.
Roughly speaking, a modem can be called a translator between the digital and analog worlds, harmonizing their communication. The operation of a wired telephone or telegraph is based on the principle by which equipment processes information. For a modern person, the obvious and most important advantage of a modem is access to the World Wide Web.
How the modem works
Initially, such devices were used to create computer networks using telephone lines. All information processed in computers is in digital form, and is transmitted via telephone cable in the form of an analog signal. Therefore, devices were needed that could connect PCs at different ends of the line.
The word "modem" is a derived form of "modulator-demodulator". Before transmitting data, it transforms the signal into a form that meets the requirements of the communication channel used (it modulates the signal), and changes the received signal into a form suitable for processing by the user’s computer (it demodulates the signal).
The modem is used to transform the signal into a form suitable for processing by a computer
What is the difference between a modem and a router
Some users believe that a router and a modem are the same equipment, differing only in name. Yes, today many manufacturers combine these two devices into one, but initially the principle of their operation and the functions they perform are different.
What is the modem used for? The converter in its pure form can be connected to only one receiving equipment, for example, a computer, and provides access to the Internet only to it. But one PC is not enough for people. They need Wi-Fi, which will not only provide access to the virtual world for all gadgets, but also connect them to a local network. For this you need a router. The equipment performs complex tasks of sending and receiving data between users and the World Wide Web simultaneously.
For example, in one second, several requests were created within the same wireless network - a purchase was made from a laptop in an online store, a news feed was opened from a tablet, and a social network was accessed from a smartphone. The router will not only process each request, but also ensure that the necessary information is output to a specific device. The situation is exaggerated, but in general the principle of operation and the device is clear.
Thanks to the router, there was no need to connect a modem to each gadget, and it was also possible to connect all devices together. For example, send files for printing from any office computer, manage the Smart Home system, and so on. However, for all its functionality, a router without a modem is absolutely useless.
Modem and its functions
The main function of the modem is to ensure communication between devices during data exchange. In simple terms, this device is designed to encode, transmit, receive and convert signals. The areas of application of such devices are very wide: they are used in civil and military communications. Among ordinary consumers, the most popular are modems, which are used to provide an Internet connection. Let's take a look at how they work.
The most popular among users are modems that provide Internet access.
History of the device
It is understandable that the first rudiments of data transmission based on the modem principle appeared at the beginning of the last century. It was then that people were able to use telephone wire, and the great-grandfather of the modern modem was designed to transmit voice messages. In the 50s of the last century, signal conversion technology was actively developed by engineers of the American telecommunications company AT&T. But this was not done for civilian purposes - the equipment being developed was supposed to become a mechanism for connecting the command headquarters with military terminals.
The real discovery was the first device that could be used to convert data for a PC. It was introduced to the general public in 1977. It was called Micromodem II. The device was capable of delivering speeds from 110 to 300 bps. The hardware development was owned by Hayes. A year later, the Apple brand released its version of the device. But both inventions did not fully solve the problem of equipment interaction, so an ellipsis was put in the question of the development of the Internet era.
The problem was resolved three years later. Hayes engineers have released a new creation - Smartmodem. The speed of processing and issuing information was not too different from the previous model, not exceeding 300 bps, but the unique command system has become a world standard for Internet communications, used to this day.
Since 1981, a boom in modem production began. Today, the pace of release of new types of devices is off the charts. Users are presented with wired and wireless devices, economy and business class devices, models with a fax function, devices that act as a data converter, router, network bridge, and so on. But the main purpose of the modem remains the same - signal modulation.
What are modems used for?
What is a voice recorder on Android and what is it used for?
This issue has already been partially discussed in previous sections. However, the purpose of the device will be discussed in more detail below.
Purpose of the device
Such equipment was created in the 50s of the last century and was originally intended to transmit information through telephone lines to computers. At that time, modems were used exclusively in military institutions.
Later, they were used by people at home to provide a desktop PC or laptop with Internet. Now these devices are practically not used. They have been replaced by Wi-Fi routers, which are distinguished by advanced functionality and low cost.
Some routers have a built-in device that allows them to access the Internet using a telephone line. Currently, such models are rare.
Principle of operation
The description of the operation of this device can be divided into several points, each of which deserves detailed consideration and study:
- The computer sends a signal to the modem, which it subsequently converts. This procedure is carried out automatically after connecting the device to the PC. The digital signal will consist of zeros and ones.
- The signals converted by the device are sent to the external network.
- The signal from the network goes back to the modem, which it, in turn, once again converts into a form understandable to the computer.
Old-style external modem for a personal computer
Important! Many signal converter models can be used as a telephone. This option is activated in the gadget settings.
What does the device consist of and how does it work?
A modern modem consists of the following elements:
- A processor that transforms incoming information and performs the inverse operation on the output. The standard depends on the data transfer protocol used.
- Controller. This component is responsible for exchanging information with the computer.
- Input/output ports through which connections to other devices occur.
- ROM memory chip. This is the brain of the device where the software (firmware), protocols and firmware are stored.
- NVRAM is a memory compartment designed to store hardware settings that can be changed by the user.
- RAM is a “RAM” designed for processing information, compressing it and transmitting it.
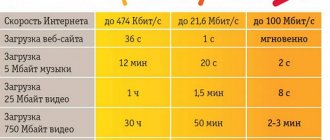
Does Internet speed depend on the modem?
In reality, the speed of the device depends on the capabilities of the provider. However, each modem model has its own throughput, which also has a strong impact on this indicator. Estimated throughput capacities are usually indicated in the accompanying documents for the equipment.
But we should not forget about such factors as the number of end consumers using the Internet, or the load on the system with various programs running in the background. In addition, providers do not always provide the declared indicators. Don’t forget to timely optimize your system, update your antivirus software, and periodically clean your computer with utilities such as Glary Utilities.
Of all the variety of existing types and types, the most interesting for ordinary users are modems that provide wireless access to the Internet from anywhere in the signal coverage area. As the capabilities of cellular operators grow, this method of connecting to the network is gaining popularity. Soon, the speed of wireless Internet will be equal to the capabilities provided by high-speed cable connections.
What types and types of modems are there?
The field of telecommunications is developing rapidly. New communication standards, data exchange protocols, updated device configurations, and so on are constantly emerging. Along with the supporters of everything new, there are still enough supporters of the classics, using slightly outdated but reliable network equipment. And in some regions there is simply no possibility of using technological innovations - progress has not yet been made. Therefore, the modem market is saturated with all kinds of device models for all occasions.
By type of supported networks
If we talk about this classification, the differences between the devices are obvious. Modems are:
- Wired. That is, to connect them you need to insert a cable (fiber optic, television, telephone) into a special connector.
- Wireless. Another name is GSM or USB modem. Today even a schoolchild knows what it is, a USB modem. A wireless modem is a device that allows you to receive a signal from a cellular operator. No cable is needed; the devices receive the signal from the nearest tower. Initially, portable devices provided access to only one device and looked like standard flash drives. Now the equipment includes a router that allows you to distribute Wi-Fi.
By method of execution
The equipment also differs in the method of execution. The following types of modems are distinguished:
- External, that is, independent devices connected to the necessary equipment.
- Built-in. Such modems are called boards mounted in a PC or laptop. The device cannot be removed; it is part of the machine. But you can turn it off.
- Internal modems. The device interface involves connecting to a PC through special slots on the motherboard.
Connection method that determines Internet speed
Now let’s take a closer look at which connection method and modem type to choose to get a good bit rate:
- Via fiber optic cable. Today, a fiber optic modem is a device that allows you to use the Internet in a village at a speed of up to 1 Gb/sec. But there is one thing - this service is not provided by all providers.
- Via ADSL connection. The modem simultaneously connects to the telephone cable and to the computer, allowing you to simultaneously make calls and surf the Internet. A significant disadvantage is the low speed and possible connection breaks.
- Wireless connection 3G and 4G, the speed of which can reach 300 Mbit/s, but it all depends on the quality of the coverage.
- DOCSIS connection via cable television network.
Selecting, connecting and setting up an ADSL modem
ADSL modems are most often used when connecting to telephone networks.
The cheapest connection option is a modem equipped with a USB interface. Such devices are small in size and easy to set up. Unfortunately, not all computers are compatible with such modems.
Modem with USB interface is easy to use
Modems equipped with an Ethernet port are universal and connect to all computers and laptops. If you intend to use a desktop computer, and there is no need to create an internal Wi-Fi network, it makes sense to choose such a device.
Modems with Wi-Fi are the most popular. They provide for connecting devices both wired and wireless. Such a modem can work as a bridge or router. It provides Internet distribution via Wi-Fi network. These are the kind of multifunctional devices that you should choose for use. The main evaluation criterion when choosing them is the power you need. The price of the modem and the range of the Wi-Fi signal depend on it. Accordingly, for small rooms a cheaper option will suffice; in case of requirements for covering a large area, it is necessary to choose a higher power.
A Wi-Fi modem will help you create a home network
To configure such devices, information from the provider is required - DNS and IP address, PVC, login and password assigned to the subscriber. These parameters are entered manually. Many operators provide a disk with the necessary settings. In such cases, special knowledge and skills are not required to configure the modem.
If the modem has been used before, the best solution would be to reset it to factory settings. This function is mainly used when changing providers or in case of losing the access password.
To return the settings to the default ones:
- Connect the ADSL modem to a power source.
- Find a button or hole (depending on the model) labeled Reset on the modem body.
- Press the button for about 30 seconds.
- If a hole is provided in the device for these purposes, you need to insert a thin metal object such as a paper clip into it and hold it there for some time.
If the manipulations are performed correctly, the device will reboot and return to factory settings.
Directly connecting the modem is done in the following way:
- Connect the modem to the power supply.
- Connect the telephone cable to the modem.
- Connect the Internet cable leading to the computer to the LAN connector.
- If the modem can distribute Wi-Fi, and your device is equipped with a Wi-Fi receiver, you do not need to connect the cable. Find the network on your device and enter the password specified in the instructions for the modem.
- When connected correctly, the network indicator on the modems should blink.
Setting up a modem usually does not raise any questions even for the most inexperienced users if you have an installation disk. Everything happens automatically.
Video: how to set up an ADSL modem
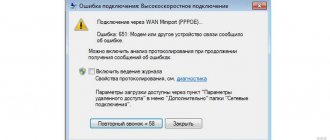
Possible problems on the line and how the modem deals with them
Traffic speed depends not only on the type of modem. It is influenced by a number of factors:
- A package of services provided by the operator.
- Technical capabilities of the service provider.
- Network congestion.
- Weather.
- Operator coverage density when it comes to using a wireless device.
- Distance from the telephone exchange when it comes to ADSL connection.
If there are connection problems, the first thing that can help is rebooting the modem. Sometimes this is enough for the equipment to work at full capacity. If this does not help, you can reset the device to factory settings.
Sometimes the modem is not in the list of PC devices. You can check this through the Control Panel. If the device is not visible in the list or there is a “!” next to it, then the equipment needs to be reinstalled. The problem may also lie in a poor-quality cable or a breakdown in the modem itself. If everything is in order with the device, all of the above factors are excluded, then the cause of constant Internet failures at the dacha is most likely the service provider, or rather the poor quality of the equipment used to transmit traffic.
What is a modem?
In simple words, this is a digital device that is necessary to connect a computer or laptop to the Internet through a certain type of connection.
Anyone who took computer science classes can also say that it is designed to convert signals from telephone or cellular communications. If you figure it out, then the modem receives Internet from the provider one way or another. It can be via cable or 3G/4G cellular. Its essence is to convert the signal and transmit it to the main device, which can be a computer, laptop or router.
Modems - there are different types
Therefore, the first modems for those email data rates of 2400 bps, and then 14.4 Kbps and 28.8 Kbps were just “toys”.
Since the beginning of 1998, most new personal computers have switched to 56 Kbps modems, although the telephone line could carry up to 128 Kbps of information. And finally, we came to a digital subscriber line (DSL) with a twisted-pair bandwidth in the range of 512 Kbps and megabits. And this has become possible thanks to digital technology.
Bit, megabit, gigabit - what is it?
It will be useful to know what a bit is and their larger units. In data communications, bits per second (abbreviated bps or bps) is a common measure of data transfer speed for computer modems. The term implies a bit rate equal to the number of bits sent or received every second.
Larger units are sometimes used to indicate high data rates. One kilobit per second (kbit) is equal to 1000 bits per second. One megabit per second (Mbps) is equal to 1,000,000 bits or 1,000 Kbps.
Computer modems for twisted pair telephone lines typically operate at 57.6 Kbps or, with digital subscriber line (DSL) services, 512 Kbps or faster. So-called “cable modems” designed for use with cable television networks can operate at 1.5 Mbit/s. Fiber optic modems can transmit and receive data at many megabits.
Choose the right modem
So which modem should you choose? Armed with the knowledge gained here, any of us, based on the characteristics of the modem, will be able to choose the best one that will correspond to our ideas about the optimal price/quality ratio of the device.
(Copying material without an active hyperlink to the source is prohibited and prosecuted).
Is the article useful? Then let others know about it by clicking on the social media buttons (Twitter, Facebook, etc.) below. Most likely, you will be interested and useful in the following posts: Internet and health, no serious curable disease Tablet, phone, what is better to buy. Subscribe.
What does a modem consist of?
Almost the only external hardware components are the input and output ports. This also includes universal, signal and modem processors , read-only memory, RAM and device status indicators.
The functions that the device can perform are determined mainly by the activities of the universal processor and the program located in the ROM. If you update the ROM or reprogram it, you can improve the functions of a particular device.
The signal processor converts incoming and outgoing signals into those needed by the device that is connected to it. RAM buffers incoming and outgoing data, performs compression algorithms and other functions. Adapters allow you to exchange data, on the one hand, between the modem and the Internet line, and on the other hand, between the computer and the modem.
Methods for connecting a network drive in Windows