Modern flash drives can be used to store collections of high-quality films, images, games, and archives. If you tried to transfer something to such a flash drive, and the “File is too large for the destination file system” window or the message “No disk space” popped up, this does not mean that the flash drive is faulty or damaged. Most likely there is a limitation on it. And you won’t be able to transfer a file larger than 4 GB to it. Even if the media memory is 32 GB. At the same time, you can easily upload 10 videos of 3 GB each to it.
Today we will tell you how to copy large data to flash memory
Why is this happening?
This occurs due to the file system (FS) and is associated with some of its features. Typically, flash drives have one of the versions of FAT - File Allocation Table. It is this that prevents you from writing a large file to an external drive. Even on a 128 GB flash drive.
There is another FS - NTFS or New Technology File System. It is widely used in Microsoft Windows. And it does not block downloading if the file exceeds 4 GB. In NTFS, the size of each cluster is much smaller - this is a certain area into which information is added.
Before attempting to write a file larger than 4 GB, check the file system type of the flash drive.
To make an analogy, imagine a piece of paper with a tic-tac-toe board on it. One cell equals a cluster. If you put a cross in it, you will fill it out entirely (that is, you will no longer be able to write any data there). Even if there is still room left in it. For both file systems, the total size of this field is the same - for example, one notebook sheet. In FAT, it fits 9 cells (3 by 3 field). And in NTFS - 49 (field 7 by 7). Because in the second case the clusters (cells) are smaller.
In addition, in NTFS you can configure quotas and set access rights. There is logging, which increases reliability.
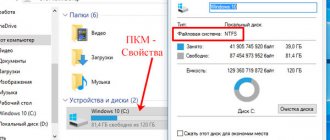
If, when copying, you see the warning “The file is too large for the destination file system,” then the drive is set to FAT. To check this:
- Insert the flash drive into the USB port.
- Open My Computer. Your flash drive should be displayed there.
- Right-click on it.
- Select Properties. The information you need will be there.
It’s easy to find out the file type - to do this, go to Media Properties
If "FAT" is indicated, it means that only data up to 4 GB in size can be written to the disk. But what if you downloaded a video and want to watch it on TV? Or do you need to transfer an archive of photos?
You can remove the maximum volume limit. Before copying a large file to a flash drive, change the FS. If the drive is a boot disk, you must leave FAT.
Why can't I transfer a large file to a flash drive?
Apparently, there is little point in talking about which files in most cases are so large that it is simply impossible to transfer them to a regular flash drive. As a rule, most often the copying problem arises with files of modern video formats, which, depending on the quality of the material, can be quite impressive in size. Just remember the volumes of data that are stored on the same Blu-ray discs. And regular DVD movies, with high quality and duration, can take up no less space. The same can be said about some installation distributions, which may contain specialized databases in the form of a single or several large files. Very often this applies to libraries of virtual synthesizers, which are widely used today in music computer sequencers and studios.
For example, the instrument file of the popular Omnisphere 2 synthesizer takes up more than 50 GB. And transferring such an object to removable media can be not only time-consuming, but also impossible (and not at all due to the limited capacity of the flash drive itself). The main problem is that all flash drives use the FAT32 file system by default, which has its own limitations due to the fact that it cannot work with file sizes larger than 4 GB. The actual size of the file is, of course, determined, but it is impossible to move or copy such objects in it.
Formatting
The easiest way is to format the USB drive and immediately set it to the desired settings. But absolutely all information, even encoded and hidden, will be erased from it. Therefore, you need to transfer everything that is there to another medium. Then you can return your documents to the formatted drive.
Here's how to write a large file to a flash drive:
- Plug in its USB port.
- Open My Computer
- Right-click on the name of the flash drive.
- Click Format.
- Select "NTFS" from the drop-down list.
- Click "Start".
- Wait.
Once the procedure is complete, you will be able to copy large files to the media
This will clear the "File is too large for target file system" warning.
If there is no “NTFS” line in that menu, do the following:
- Open Control Panel. You can enter it through “Start”.
- You need "Device Manager". It is in the Hardware and Sound category. Open it.
- Expand the "Disk devices" list.
- Find your flash drive in it.
- Right-click on its name.
- “Properties” item.
- "Politics" tab.
- Place a marker next to the line “Optimize for execution.”
- Click OK.
Try formatting the flash drive to NTFS again. And you can drop a large file on it.
What file system should I format the flash drive with?
Let's start by deciding on the type of file system. The priority choice today can be considered: NTFS and FAT32.
The main thing here is to understand the positive qualities of each of these systems. So if you need to format a flash drive with a capacity of more than 16 Gigabytes, then the choice will most likely fall on NTFS. Let me explain why, this file system has some advantages over FAT32; it allows you to load large files onto the drive. It will be useful for users who use the transfer of media content, in particular large video files (HD movies).
A small drawback is the mandatory use of the “safely remove devices” function, since the NTFS file system has a caching property and if it is abruptly disconnected, a failure or damage to the stored data may occur. This is why users are afraid of power outages in their homes, since computer hard drives are formatted in the NTFS system, which can make it difficult to restart the operating system, even leading to the loss of personal data!
If you are using a small flash drive to transfer office documents or graphic information, then it will be enough to format the USB drive to the standard FAT32 system (FAT, exFAT).
Either of the two systems can be installed using standard Windows operating system tools. Thanks to modifications in Windows 7, the NTFS file system has become available!
Note! It is worth remembering that in the process of formatting a flash drive, all existing information will be deleted permanently! First, make sure that important data will not be lost!
Conversion
The drive can be converted to the desired file system. To do this, Windows has an option “File System Conversion Utility” or “Convert.exe”. There is no need to launch it manually. It is controlled through commands.
Here's how to transfer a large file to a flash drive:
- Go to “Start - Run”.
- In the input field, write “cmd” without quotes. A window will open with a black background and white characters. This is the command line.
- Insert the drive into the USB slot.
- Open My Computer.
- Find your flash drive there. Look at the name of the disk (external devices are assigned names with the letters “F:”, “L:”, “H:”).
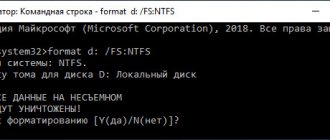
- In the command line you need to enter or copy the command “convert [drive name] /fs:ntfs /nosecurity /x”. Instead of “drive name,” write the letter of the flash drive. And after it put a colon. That is, it should look something like “convert G: …”.
- Wait until the "Conversion Complete" message appears.
Now try writing a large file to the drive.
When converting, nothing is erased from the media. But still, before changing the file system, clean the flash drive and create a backup copy of the data. There must be free space on the USB drive for successful conversion.
If during conversion the error “Enter a volume label for the disk” appears, write the label (the full name of the disk). Or uncheck it in the “Properties” menu in the “General” section. Just remove what is written in the input field at the top.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
With the development of technology, PC users are able to transfer more and more information between PCs using different media.
One of these media is flash memory (hereinafter referred to as a flash drive ), which is connected via a USB port.
“I can’t write a large file to a flash drive. What to do?" .
This question arises when working with flash drives larger than 4GB and writing files larger than 4GB onto them. In this case, the OS displays a message that there is no recording space on the flash drive.
Our support team recently received a similar question:
Hello, I have the following question: I have a flash drive with a capacity of 8 GB, empty, formatted. When I try to upload files (for example, a game image with a capacity of 4.7 GB), the mdf or other extension shows that there is not enough disk space, I tried to upload a large archive, somewhere up to 5 GB it shows that there is not enough disk space. I upload small files, everything is fine up to 7 GB. What could be the problem? Thank you.
Therefore, I decided to write this note in which I will explain why this happens and how to solve such a problem.
The thing is that during production, flash drives are formatted in the FAT32 . And this system does not support files larger than 4GB .
To record larger files, the flash drive must use the NTFS - this system can work with files up to almost 16TB .
I found three ways to make an NTFS . Now I will tell you in detail about each of the methods.
First, connect the flash drive to the PC; if necessary, wait until the OS recognizes and installs it in the system.
Method number 1. Formatting a flash drive.
To do this, you need to open “My Computer”, select the flash drive, open the context menu by right-clicking, and select “Format...”.
A window for settings and formatting the flash drive will appear.
In Windows 7, you can select NTFS , but in Windows XP this value may not be available , as shown in the picture below.
To make this value available in Windows XP, you must do the following:
Click the “Start” and then select “Settings - Control Panel - System”.
In the System Properties , open the Hardware tab and click the Device Manager button.
In the “ Device Manager ” window, expand the “Disk devices” item, double-click to open the properties window of the connected flash drive.
Open the "Policy" tab, select the " Optimize for execution " radio button, click the "OK" button.
Close all windows.
Now again call up the window for settings and formatting the flash drive.
In the “File system:” menu, you can select the value NTFS , as shown in the picture below. The same menu is natively available in Windows 7.
After this, you can configure other formatting options, for example, set the volume label and select quick format.
Now you can format the flash drive in NTFS format.
After formatting the flash drive in Windows XP, select the “ Optimize for quick removal ” switch on the “Policies” tab. Method number 2. Converting a flash drive. To do this, you need to use the file system conversion program “ convert.exe ” (File System Conversion Utility, the description can be read here, located in the C:\WINDOWS\system32\ folder).
Click the Start button, select Run..., type cmd , and click OK.
A command handler window should appear.
In it you need to type the following command:
" convert <flash_letter>:/ fs: ntfs/ nosecurity/ x ".
In my example, you would type " convert r:/ fs: ntfs/ nosecurity/ x ".
Press "Enter", after the conversion is complete, enter the command " exit " and press "Enter", or simply close the window.
In the picture below I showed an example of using this command.
If the flash drive is already in NTFS , then there will be no conversion. And so it happened, because... After the first method, my flash drive was already in NTFS . I formatted it again to FAT32 , and ran the “ convert ” command again.
As a result, I saw this message and received a flash drive in NTFS .
For this command, there are the following recommendations for its use:
- Although the convert.exe allows you to convert the file system of a flash drive without losing data, it is recommended that you copy all the data on the flash drive to your computer’s hard drive before performing the conversion;
- There must be free space on the flash drive to convert the file system. Otherwise you will receive an error message. In this case, free up the required space on the flash drive by deleting unnecessary files, or copy some of the files to your PC’s hard drive;
- If the flash drive is labeled “Volume Label”, then when you try to convert, the message “ Enter the volume label for the drive <flash drive letter>: ” will appear. In this case, enter the label of your flash drive, otherwise you will not be able to convert the flash drive - the message “ Invalid disk label specified ” will appear. Or, before starting the conversion, remove the checkmark in the Properties on the General tab.
Method number 3. Using the free HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool.
Download the program from the Internet (you can download it, for example, from here: version 2.2.3.0).
Run the HPUSBDisk.exe . A window should appear as shown in the picture below.
The program is in English, however, it is easy to understand:
- If several USB devices are connected, in the “ Device ” drop-down list, select the one you need (the flash drive you want to format);
- In the “ File system ” menu, select NTFS (or, if necessary, FAT/FAT32 );
- You can specify a label in the “ Volume label ” text field (optional);
- For quick formatting, check the “ Quick Format ” checkbox;
- Click the " Start " button;
- A dialog box will appear warning (in English) that all data on the flash drive will be destroyed. Click the “ Yes ” button;
- Wait for the formatting process to complete and in the dialog box that appears with the formatting results, click the “ OK ” button.
General recommendations when changing the file system on a flash drive:
Be careful when choosing a device to format so that you don't accidentally format the wrong removable drive.
Before changing the system, be sure to copy all the data on the flash drive to your computer’s hard drive.
It is not recommended to format a flash drive to NTFS if you are using it as a boot device.
After converting the file system of a flash drive to NTFS , you can write files larger than 4GB .
You can also check an external drive or flash drive for errors... You can do this... Just click on the name of the program
The article uses materials from the sites ru.wikipedia.org, support.microsoft.com, netler.ru.
https://www.pc-user.ru/
HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool
To convert a flash drive, use the HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool application.
- Search the Internet and download this utility. There should be only one executable file "HPUSBDisk.exe".
- Right-click on it.
- Select "As Administrator".
- Find your flash drive in the “Devices” list. It should already be inserted into the USB connector.
- In the "File system" field, enter "NTFS".
- You can set a label (“Volume Label”).
- During the conversion, all data on the drive will be erased. It makes sense to copy them to a PC and then return them to a flash drive.
- Click "Start". Before doing this, make sure that you have selected the correct media. So as not to accidentally format something else.
After this, try writing the necessary data to the drive.
Now you know how to transfer a large file to a flash drive. We need to transfer it to another file system. Then the size limitation will disappear. Choose any method you like.