- 6shared
- 1Facebook
- 5Twitter
- 0VKontakte
- 0Odnoklassniki
Computer performance is a combination of several factors, or better yet, the technical characteristics of hardware devices, among which the main role is played by the processor, hard drives and, of course, RAM or RAM for short. On a computer, RAM serves as a kind of intermediate link between the processor that performs all the calculations and the storage device - the HDD or SSD. The processes of all programs and the Windows 7/10 operating system itself are loaded into it, but if the volume of application data exceeds the capacity of RAM, the data is cached, for example, in the page file. But in any case, a lack of RAM will cause the computer to run slowly and applications to become less responsive. And on the contrary, the more RAM there is on a PC, the faster data exchange occurs, the faster the system, the more powerful applications you can run.
What are the main characteristics of RAM and why know them?
So, the more RAM, the better, and that is why users often install an additional RAM module on their PC. However, you can’t just go to the store, buy any memory and connect it to the motherboard. If it is chosen incorrectly, the computer will not be able to work, or worse, it will lead to the fact that the RAM will simply fail. Therefore, it is so important to know its key characteristics. These include:
- Type of RAM . Depending on performance and design features, DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4 modules are distinguished.
- Memory . The parameter is characterized by the amount of data that can fit in memory cells.
- RAM frequency . The parameter determines the speed of operations performed per unit of time. The bandwidth of the RAM module depends on the frequency.
- Timing . These are time delays between sending a memory controller command and its execution. As the frequency increases, the timings increase, which is why overclocking the RAM can lead to a decrease in its performance.
- Voltage . The voltage required for optimal operation of the memory stick.
- Form factor . The physical size, shape of the RAM stick, as well as the number and location of pins on the board.
If you install additional memory, it must have the same size, type and frequency as the main one. If the RAM is completely replaced, attention should be paid to the support of the replaced RAM by the motherboard and processor with only one nuance. If the PC uses Intel Core i3, Intel Core i5, Intel Core i7 processors, matching the memory frequency and the motherboard is not necessary, because for all these processors the RAM controller is located in the processor itself, and not in the northbridge of the motherboard. The same goes for AMD processors.
Explanation of symbols
Manufacturers of RAM often use their own markings to designate models, but they still try to indicate the characteristics in a single format. For example, the following information can be extracted from the Crusial strip.
4GB DDR3L-1600 UDIMM 1.35V CL11
Standard DIMM, UDIMM and SODIMM strips
These abbreviations denote the standard of planks. DIMMs are strips for personal computers, and SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module) - for laptops - are shorter and taller in size.
You can also find the following designations:
- U-DIMM - without buffer;
- R-DIMM - with buffer;
- LR-DIMM - with a buffer and reduced power consumption;
- FB-DIMM - fully buffered.
U-DIMM is a type of DIMM memory used in 99% of home PCs. “U” means that the bar does not have protection against errors when accessing cells. This allows it to work faster and cost less. For everyday tasks, the lack of protection is not critical. The letter “U” is often not written in the markings, leaving only DIMMs.
R-DIMM, LR-DIMM and FB-DIMM are brackets for servers and computing systems that require maximum operational reliability. They are more expensive and are not recommended for purchase for regular computers.
Memory type: DDR4, DDR3 and DDR3L
Memory types differ in many technical characteristics. For example, DDR4 operates at higher frequencies and has better energy efficiency. Read about the difference between DDR4 and DDR3 here. I note that types 3 and 4 generations are incompatible.
The only difference between DDR3 and DDR3L is energy efficiency. "L" is short for "Low". Memory with such a marker consumes 1.35V, while regular memory consumes 1.5V. Both types are compatible and can be used together on a computer. Lower power consumption will not save on electricity, but will provide the memory with slightly less heat.
Operating frequency: 1333, 1600, 1866, 2133 MHz
The higher the frequency, the better the performance. But there is a nuance. The processor has a maximum frequency threshold at which it can interact with RAM. If the processor has this threshold of 1600 MHz, then buying memory with a frequency of 2133 MHz will not give anything. Everything will work at a frequency of 1600 MHz.
This characteristic is often not indicated on processors and should be looked for on the manufacturer’s website. As an example, I will give a short list of the maximum frequency of interaction with RAM for some processors.
| Processor series | Max frequency |
| Core i3 | |
| Core i3 8 series | 2400 MHz |
| Core i3 7 series | 2133/2400 MHz |
| Core i3 6 series | 2133 MHz |
| Core i3 4 series | 1600 MHz |
| Core i5 | |
| Core i5 7 series | 2400 MHz |
| Core i5 6 series | 2133 MHz |
| Core i5 4 series | 1600 MHz |
| Core i7 | |
| Core i7 7 series | 2666 MHz |
| Core i7 6 series | 2400 MHz |
| Core i7 4 series | 1600 MHz |
| AMD FX | |
| AMD FX-4xxx | 1866 MHz |
| AMD FX-6xxx | 1866 MHz |
| AMD FX-8xxx | 1866 MHz |
| AMD Ryzen | |
| AMD Ryzen 3 1st series | 2666 MHz |
| AMD Ryzen 5 1st series | 2666 MHz |
| AMD Ryzen 7 1st series | 2933 MHz |
Peak baud rate: PC10600, PC12800, PC19200
The maximum data transfer rate depends on the memory operating frequency and is indicated by the prefix “PC”. Next comes the speed, measured in MB/s. The higher the speed, the better.
| Frequency | Speed |
| 2400 MHz | PC19200 |
| 2133 MHz | PC17000 |
| 1866 MHz | PC14900 |
| 1600 MHz | PC12800 |
| 1333 MHz | PC10600 |
Sometimes the prefix "PC3" or "PC4" is found, which indicates a specific type of memory - DDR3 or DDR4.
A letter may be added at the end to indicate the standard of the bar. For example, "PC4-24000U" or "PC4-24000R".
- U - U-DIMM;
- S - SO-DIMM;
- R - R-DIMM;
- L - LR-DIMM;
- F - FB-DIMM.
Rarely found “E” - ECC (error-correcting code) - memory with error correction.
Timing: 8-8-8-24, CL11
Timing is the delay that occurs when the processor accesses memory. Usually indicated as 4 numbers. They describe the speed of reading, writing and executing an action. The fourth indicates the full cycle of these operations. Sometimes only the reading speed is indicated - CL11 (CAS Latency 11).
The lower the delay, the better. But the architecture of modern processors implies the presence of a large cache and it does not often access RAM directly. Therefore, these indicators do not play a big role in performance. The difference between 8-8-8-24 and 17-17-17-42 is almost impossible to notice.
In markings, timing can be indicated by a letter after the frequency. For example, DDR4-2400T or DDR4-2666U.
- P - 15-15-15;
- R - 16-16-16;
- T - 17-17-17;
- U - 18-18-18;
- V - 19-19-19;
- W - 20-20-20;
- Y - 21-21-21.
Memory chip placement: 1Rx8 and 2Rx8
Some memory models have the designation 1Rx8 or 2Rx8 in the marking. This is an indication of the schematic arrangement of chips on the board.
- 1Rx8 - 8 chips on one side of the board;
- 2Rx8 - 16 chips, 8 on each side.
One computer can use memory with different arrangements of chips. This does not affect performance. The manufacturer simply decides how it is more convenient for him to place them on the board.
How to determine the type and amount of RAM visually
Physically, RAM is an oblong board, most often green, with chips located on it. On this board, the manufacturer usually indicates the main memory characteristics, although there are exceptions. Thus, there are memory strips on which nothing is indicated except the name of the manufacturer. If there are markings, it is not difficult to find out what RAM is installed on the PC. After completely turning off the computer and removing the system unit cover, carefully remove the memory module from the slot (the latter may not be necessary) and carefully study the information on the white sticker.
A number with the GB prefix will indicate the memory capacity, a number with the MHz prefix will indicate the frequency, numbers in the XXXX format will indicate timing, V will indicate voltage. But the type of RAM (RIMM, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, etc.) is not always indicated. In this case, you should pay attention to the bandwidth, usually denoted as PC, and check it according to the standards specification in the same Wikipedia on the page ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/DRAM. The number after PC usually indicates the DDR generation, for example, PC3-12800 indicates that the PC has DDR3 memory installed.
Types and characteristics of random access memory (RAM)
New generations of processors stimulated the development of faster SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) with a clock frequency of 66 MHz, and memory modules with such chips were called DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module).
For use with Athlon processors, and then with Pentium 4, the second generation of SDRAM chips was developed - DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM). DDR SDRAM technology allows data to be transferred on both edges of each clock pulse, which provides the ability to double memory bandwidth.
With the further development of this technology in DDR2 SDRAM chips, it was possible to transmit 4 pieces of data in one clock pulse. Moreover, it should be noted that the increase in performance occurs due to optimization of the process of addressing and reading/writing memory cells, but the clock frequency of the memory matrix does not change.
Therefore, the overall performance of the computer does not increase by two or four times, but only by tens of percent. In Fig. The frequency principles of operation of SDRAM microcircuits of various generations are shown.
The following types of DIMMs exist:
- 72-pin SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module) - used for FPM DRAM (Fast Page Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory) and EDO DRAM (Extended Data Out Dynamic Random Access Memory)
- 100-pin DIMM - used for SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) printers
- 144-pin SO-DIMM - used for SDR SDRAM (Single Data Rate...) in laptop computers
- 168-pin DIMM - used for SDR SDRAM (less often for FPM/EDO DRAM in workstations/servers
- 172-pin MicroDIMM - used for DDR SDRAM (Double date rate)
- 184-pin DIMM - used for DDR SDRAM
- 200-pin SO-DIMM - used for DDR SDRAM and DDR2 SDRAM
- 214-pin MicroDIMM - used for DDR2 SDRAM
- 204-pin SO-DIMM - used for DDR3 SDRAM
- 240-pin DIMM - used for DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM and -DIMM (Fully Buffered) DRAM
- 244-pin Mini-DIMM – for Mini Registered DIMM
- 256-pin SO-DIMM - used for DDR4 SDRAM
- 284-pin DIMM - used for DDR4 SDRAM
To prevent installation of the wrong type of DIMM module, several slots (keys) are made in the module’s textolite board among the contact pads, as well as on the right and left in the area of the module fixation elements on the system board.
To mechanically identify different DIMM modules, a shift in the position of two keys in the module’s textolite board, located among the contact pads, is used. The main purpose of these keys is to prevent the installation of a DIMM module with an inappropriate supply voltage for memory chips into the socket.
Additionally, the location of the key or keys determines the presence or absence of a data buffer, etc.
DDR modules are marked PC. But unlike SDRAM, where PC indicated the operating frequency (for example, PC133 - the memory is designed to operate at a frequency of 133 MHz), the PC indicator in DDR modules indicates the maximum achievable bandwidth, measured in megabytes per second.
DDR2 SDRAM
| Standard name | Memory type | Memory frequency | Bus frequency | Data transfer per second (MT/s) | Peak Data Rate |
| PC2-3200 | DDR2-400 | 100 MHz | 200 MHz | 400 | 3200 MB/s |
| PC2-4200 | DDR2-533 | 133 MHz | 266 MHz | 533 | 4200 MB/s |
| PC2-5300 | DDR2-667 | 166 MHz | 333 MHz | 667 | 5300 MB/s |
| PC2-5400 | DDR2-675 | 168 MHz | 337 MHz | 675 | 5400 MB/s |
| PC2-5600 | DDR2-700 | 175 MHz | 350 MHz | 700 | 5600 MB/s |
| PC2-5700 | DDR2-711 | 177 MHz | 355 MHz | 711 | 5700 MB/s |
| PC2-6000 | DDR2-750 | 187 MHz | 375 MHz | 750 | 6000 MB/s |
| PC2-6400 | DDR2-800 | 200 MHz | 400 MHz | 800 | 6400 MB/s |
| PC2-7100 | DDR2-888 | 222 MHz | 444 MHz | 888 | 7100 MB/s |
| PC2-7200 | DDR2-900 | 225 MHz | 450 MHz | 900 | 7200 MB/s |
| PC2-8000 | DDR2-1000 | 250 MHz | 500 MHz | 1000 | 8000 MB/s |
| PC2-8500 | DDR2-1066 | 266 MHz | 533 MHz | 1066 | 8500 MB/s |
| PC2-9200 | DDR2-1150 | 287 MHz | 575 MHz | 1150 | 9200 MB/s |
| PC2-9600 | DDR2-1200 | 300 MHz | 600 MHz | 1200 | 9600 MB/s |
How to find out how much RAM you have using Windows tools
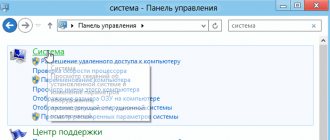
Above, we briefly discussed how to determine what RAM is on a computer by visually inspecting the module; now let’s find out how to find out its volume using the operating system. Windows 7/10 has a built-in utility for this, msinfo32.exe . Press Win+R to open the Run dialog box, enter the command msinfo32 and press Enter.
In the main section of the system information window that opens, find the item “Installed random access memory (RAM)” and see its volume in GB.
Instead of the msinfo32.exe utility, you can use another built-in component to determine the amount of RAM - DirectX . It is launched with the dxdiag , the amount of memory is displayed in megabytes on the first “System” tab.
How to find out the model of RAM in a computer?
You can find out the model names of installed RAM modules using two methods: visual inspection and special software. The second option requires less effort, so let's start with it.
Method 1: Additional software
There are a number of programs designed to view detailed information about your computer. We recommend paying attention to two: HWiNFO64 and AIDA64. They collect the most detailed and reliable information about computer components.
In order to find out the model names of installed RAM modules using the HWiNFO64 utility, download and install it. Those who do not like to install everything can use the portable version. After launch, three windows will open:
We are only interested in one of them (in the screenshot above it is located on the right). In the device tree, expand the Memory . Here you can see the desired model names of the installed RAM modules, and in the window on the right you can see detailed information about them:
In this case, the RAM modules are the same and are called G.Skill F4-3000C16-8GISB.
If the models of installed RAM modules are not identified by the HWiNFO64 program for some reason, you can try to find out information about them using the AIDA64 utility. Download, install and run it. In the window that opens, expand the device tree branch Motherboard (or Motherboard ) and select SPD . The window on the right will show all the necessary information. In the Device Description or in the Module Name the Memory Module Properties section , you can see the exact names of the models of installed RAM modules:
But what should you do if for some reason it is not possible to find out the model names of installed RAM modules using programs? In this case, you should resort to a visual inspection of the modules themselves.
Method 2: Visual inspection of RAM modules
To do this, you will have to remove the side cover of the desktop computer case (the left one when looking at the case from the front) and remove one of the RAM modules from the motherboard. This should only be done after physically disconnecting your computer from the power supply.
In this example, the ASRock B450 Pro4 motherboard was used.
As you can see in the screenshot, the board has four RAM slots located to the right of the processor socket.
It is necessary to remove one of the RAM modules in order to be able to calmly take a closer look at it. There are two types of fastening in the connector: double-sided and single-sided. The type of fastening depends on the number of latches. In the case of single-sided fastening there is one latch, and in case of double-sided fastening there are two.
After removing the module, look for the markings on it. Most often this is a sticker located directly on the memory chips or on the radiator (if there is one). There you will definitely find the full model name of this module.
In the case considered, the module name shown by the HWiNFO64 and AIDA64 utilities is slightly different from the module name indicated on the label. The only difference is a couple of numbers - 16, located in the second part of the module name. In the case of G.Skill RAM, this number simply indicates the total memory capacity of the entire set of modules - 16 GB (2 modules of 8 GB each).
At the end of the procedure, do not forget to place the memory module back into the connector, inserting it properly and closing all the latches as far as possible. Otherwise, the computer may become inoperative.
If you are not sure that the RAM modules are the same, you will have to do the same procedure for all modules in turn.
Third-party programs for determining RAM parameters
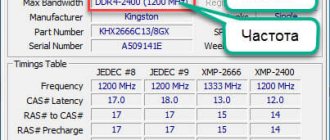
The information provided by the standard Windows utility is sparse. It allows you to find out how much RAM is on your computer, but does not display its other important characteristics. If you need more data, it is better to use special programs. The most famous of them is, of course, AIDA64 Extreme Edition . Information about memory in this program is contained in the Motherboard - SPD menu and includes such characteristics as module name, size and type, frequency, voltage, timing and serial number.
You can also view the RAM using the Speccy from the developers of the popular CCleaner cleaner. General information about RAM in the program is available on the main “Summary” tab, and additional information is available on the “RAM” tab. This includes volume, type, timing, channel mode, frequency and some other, less important information. Unlike AIDA64, the Speccy application is free, but it shows less information.
To view the main memory characteristics, we can also recommend the CPU-Z . The necessary information is located in the “Memory” tab. It includes the type, size, channel mode, ratio of the system bus frequency to the RAM frequency and other additional information. Like Speccy, CPU-Z is free, but it does not support the Russian language, which, however, is not so important.
And finally, we recommend one more program for viewing information about RAM. It's called HWiNFO64-32 . Externally and functionally, it is somewhat reminiscent of AIDA64 and at the same time CPU-Z. On the “Memory” tab, the program shows the module type, capacity in megabytes, channel mode (one-, two- or three-channel), clock frequency, timing and other additional information. HWiNFO64-32 is free, the interface language is English, which, as in the case of CPU-Z, is not fundamentally important.
- 6shared
- 1Facebook
- 5Twitter
- 0VKontakte
- 0Odnoklassniki
How to find out what RAM is on your computer
RAM is one of the most important components of any computer and certainly a guarantee of operating speed. In the modern world, even the frequency of the processor does not affect the overall perception of speed as much as RAM. But in order to replace or add this component, you need to thoroughly know all its characteristics - and RAM has a lot of them. So, how do you find out what RAM is in your computer? In this article.
Why you need to know the type of RAM
Why be interested in computer RAM, its random access memory? The reasons may vary. For example, when installing computer games or programs, recommended system requirements are indicated. These are approximate characteristics that the OS must meet in order for the application to launch and work stably. They might look like this:
- CPU 2.2 GHz
- 1, 5 or 2 Mb RAM
- HDD 25 GB
These system requirements are recommended by the developers for the game World of Tanks. That is, in order to run a tank simulator, the computer’s RAM, RAM, must meet these characteristics, otherwise the game simply will not start or will be very slow.
And if your PC does not meet these parameters, you can increase the RAM by adding another module, or change it to a different size. In this case, the processor and motherboard must support RAM. If you decide not to change the RAM, but to add another stick to the one already on your PC, it must correspond to it. In this case, it is desirable that both the first and second memory modules have the same volume. This is necessary for the computer/laptop to work quickly, without lags or slowdowns.
Visual inspection of RAM
If you have the opportunity to open the computer and inspect its components, then you can get all the necessary information from the sticker on the RAM module.
Usually on the sticker you can find an inscription with the name of the memory module. This name begins with the letters “PC” followed by numbers, and it indicates the type of RAM module in question and its bandwidth in megabytes per second (MB/s).
For example, if a memory module says PC1600 or PC-1600, then it is a first-generation DDR module with a bandwidth of 1600 MB/s. If the module says PC2‑3200, then it is DDR2 with a bandwidth of 3200 MB/s. If PC3, then it is DDR3 and so on. In general, the first number after the letters PC indicates the DDR generation; if this number is not there, then it is a simple first generation DDR.
In some cases, RAM modules do not indicate the name of the module, but the type of RAM and its effective frequency. For example, the module may say DDR3 1600. This means that it is a DDR3 module with an effective memory frequency of 1600 MHz.
In order to correlate the names of modules with the type of RAM, and the bandwidth with the effective frequency, you can use the table that we provide below. The left side of this table shows the names of the modules, and the right side shows the type of RAM that corresponds to it.
| Module name | RAM type |
| PC-1600 | DDR-200 |
| PC-2100 | DDR-266 |
| PC-2400 | DDR-300 |
| PC-2700 | DDR-333 |
| PC-3200 | DDR-400 |
| PC-3500 | DDR-433 |
| PC-3700 | DDR-466 |
| PC-4000 | DDR-500 |
| PC-4200 | DDR-533 |
| PC-5600 | DDR-700 |
| PC2-3200 | DDR2-400 |
| PC2-4200 | DDR2-533 |
| PC2-5300 | DDR2-667 |
| PC2-5400 | DDR2-675 |
| PC2-5600 | DDR2-700 |
| PC2-5700 | DDR2-711 |
| PC2-6000 | DDR2-750 |
| PC2-6400 | DDR2-800 |
| PC2-7100 | DDR2-888 |
| PC2-7200 | DDR2-900 |
| PC2-8000 | DDR2-1000 |
| PC2-8500 | DDR2-1066 |
| PC2-9200 | DDR2-1150 |
| PC2-9600 | DDR2-1200 |
| PC3-6400 | DDR3-800 |
| PC3-8500 | DDR3-1066 |
| PC3-10600 | DDR3-1333 |
| PC3-12800 | DDR3-1600 |
| PC3-14900 | DDR3-1866 |
| PC3-17000 | DDR3-2133 |
| PC3-19200 | DDR3-2400 |
| PC4-12800 | DDR4-1600 |
| PC4-14900 | DDR4-1866 |
| PC4-17000 | DDR4-2133 |
| PC4-19200 | DDR4-2400 |
| PC4-21333 | DDR4-2666 |
| PC4-23466 | DDR4-2933 |
| PC4-25600 | DDR4-3200 |
How do you know if your motherboard has a free slot for a memory module?
It would seem that there is nothing complicated here - open and look. Moreover, to install the modules you still have to do this. Unfortunately, this is often not as simple as it seems. Sometimes you have to disassemble almost the entire laptop to access the memory slots. And if the laptop is not yet out of warranty, additional problems will appear in the form of warranty stickers. To find out whether it has a free RAM slot without disassembling the laptop, you will have to refer to the documentation or the manufacturer’s website.
Recently, manufacturers have been releasing several versions of laptops at once, which practically do not differ in labeling or are even listed as the same model. To find out for sure whether your laptop specifically has a free slot, you can use a free program to determine the characteristics of the motherboard - for example, CPU-Z. In the SPD (“speed”) tab, expand the drop-down list of memory slots. Most laptops have two slots - choose the last one.
Empty? This means the slot is free. And you can double the laptop's current RAM simply by installing a memory module in the second slot, similar to the one installed in the first. But keep in mind that programs do not always correctly determine the number of slots: if the official website says one thing, and CPU-Z says another, you should believe the first.
Important parameters
To correctly select a new bar, you need to obtain a number of information about the old one. Without them, it is impossible to choose the right RAM.
Important characteristics:
- Generation. RAM has a type or generation, they differ in their operating algorithms. The speed, voltage and other parameters depend on the algorithms. Today there are four generations from DDR1 to DDR4, you shouldn’t guess whether ddr2 or ddr3 is in the laptop, it’s better to look and make sure exactly what type is needed.
- RAM capacity. Allows you to understand the maximum volume possible for use in the device.
- Speed or throughput. Characterizes how quickly data is exchanged between the processor and RAM. Typically the designation includes numbers and letters, starting with PC. There are tables on the Internet that indicate speed for a specific designation. Obviously, memory with different speeds will not work correctly.
- Manufacturer and serial number. These are indicators with which you can choose a similar memory card for better synchronization. If we talk about which company is better to choose memory, then it is better to take the manufacturer’s bar that made the one you are already using.
- Delay time. The indicator reports the amount of time required to process a request from RAM to the processor. The lower the number, the better.
Is it possible to increase the memory in a laptop?
Laptops have much fewer upgrade options than regular personal computers: the laptop owner can only dream of replacing a video card or installing an additional pair of hard drives. But things are not so bad with RAM: on many laptops the memory modules are still removable, moreover, sometimes there is a free slot on the laptop motherboard for an additional module.
So the algorithm for expanding laptop memory is quite simple:
1. Find out the maximum amount of memory for your laptop.
2. Find out if your laptop has a free slot for memory modules.
- If there is one, find out the parameters of the installed module and buy a similar one.
- If not, find out which memory modules the laptop motherboard supports and buy more capacious and modern ones.
3. Install or replace memory modules.
However, this algorithm is not suitable for all users. Most modern netbooks and ultrabooks, all Macbooks since 2013, many Acer, ASUS and HP laptops have integrated memory: the RAM chips in them are soldered directly to the motherboard. It is not possible to increase the amount of RAM in such laptops.
How can you find out whether the memory is built-in or not? Find a description of your laptop model on the manufacturer's or seller's website and pay attention to the memory characteristics. If it says “integrated” or “memory is not added,” then, alas, it will not be possible to increase the amount of RAM on this model.
Well, for other laptops we will consider all the points of the algorithm in more detail.