Not all users are well versed in configuring the operating system, the author of which is the well-known Microsoft corporation.
Therefore, for many ordinary users, encountering a black screen with some incomprehensible lines when loading the OS on a computer or laptop is tantamount to experiencing stress. They immediately begin to panic, not understanding what happened and how to fix it.
Often, the appearance of previously unseen black screens is perceived as a computer breakdown that requires immediate repair and the purchase of expensive replacement components.
But don't rush to conclusions. Some windows that are unusual for normal Windows booting appear for completely harmless reasons. This also applies to Windows Boot Manager.
What it is
The first thing you need to understand is what Boot Manager is on a laptop or computer and why it appears.
Here we are talking about a special tool that displays a window with options for choosing an operating system when the computer boots.
This is a unified client in Windows OS, which is responsible for loading the operating system. In fact, it is he who prompts the user to choose which modification or version of the operating system should be downloaded. In general terms, this allows you to understand what Boot Manager means and what functions it performs on computers with the Windows operating system.
There is one important feature. Previously, this Boot Manager was solely responsible for offering the user a choice of loading their preferred OS. This was relevant for those cases when several operating systems were installed on the computer. This is a fairly common phenomenon when the same PC or laptop simultaneously runs Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 or earlier versions. This decision is due to the fact that a number of programs work with one OS, but do not run on other generations of operating systems. To eliminate this drawback, 2 operating systems, and sometimes more, are installed on the computer.
But over time, the functionality of this download manager has changed somewhat. In particular, it was turned into a tool for booting the system kernel after an initial check of the hardware components through the BIOS and UEFI. After which control is transferred to the operating system.
When Windows boots in normal mode, which is especially true for the 10th generation of this OS, a selection screen often appears on the monitor. Moreover, the user is prompted to schedule the OS to start or go to tools to troubleshoot system-related problems. This is exactly what Boot Manager is responsible for.
The question of what it is and what it is used for has largely been resolved. But still, users sometimes do not know how to fix problems and errors associated with this OS download manager.
Instead of a total
That's it for the Windows Boot Manager service. What it is, I think, is already clear, as well as what methods are used to eliminate the main failures and errors in its work. If none of the above has any effect, perhaps the reason is the operation of the hard drive or even conflicts when accessing the RAM strips. There shouldn’t seem to be any difficulties with tools applied to hard drives. But you will have to check the RAM using the Memtest86+ utility or, if possible, remove the sticks from the slots on the motherboard, and after identifying a non-working or faulty stick, replace it.
However, if bootloader errors are not related specifically to physical damage to the hardware, you can disable the bootloader in the BIOS or edit the boot.ini file, removing unnecessary lines from it (Windows Vista and below).
Finally, when booting the Shell from removable media, you can use the bcdedit ID line, which disables the bootloader (the bootloader ID can be found by entering only the main command).
I was able to install the rEFInd program on the third try. First, I read posts by other authors on computer topics. I realized that material was being copied almost everywhere, everything was smeared and damp. In the end, nothing worked out. After half a year, I remembered the beautiful Boot Manager and began to take a closer look at the official project (). But I read it one line at a time and not carefully, and in the end it was 2:0 in favor of the software. Another amount of time passed and after hearing the song Argentina - Jamaica 5:0, for some reason I felt ashamed of Jamaica for its own convolutions. Well, really stupid or something :). I took the time to study the material more thoroughly and realized that installing a boot manager for UEFI is easy and has a history of previous defeats, the result of bad training :).
Talk, don't cook cabbage soup.
Advantages of rEFInd over Windows Boot Manager and Grub2. In my humble opinion, this is much more beautiful (you can even throw in a photo of your beloved wife or dog). The boot manager sees all .efi executable files, which means in one window we will have Windows, unix systems (Ubuntu, Gentoo, Fedora, Linux Mint, etc.) and all external drives (bootable flash drive, multiboot external HDD, optical disk, MicroSD, etc.). And what does it mean? That’s right, now, in order to boot from a USB device, we don’t need to “climb” into the boot menu of the laptop/computer, nervously poking F9, F12, or “plunge” into the terrible kingdom of demons with the ominous name of bios. The management utility remembers your last actions. If you logged into Windows 10, then next time you will be offered to log in to this system (20 seconds to think about it). The last attempt was to boot from a multi-boot flash drive, boot from an external drive if you do not use the arrows on the keyboard to select the boot you need, for example, in Linux Mint.
Before I forget, play some magic with themes here (). "A binary zip file" here
(). Here are instructions for installing the “bootloader” on Linux, OS X and Windows ().
What types of bootloaders are there?
Initially, several different boot loaders are used for Windows operating systems. They differ from each other in functionality, capabilities and tasks performed.
Boot Manager is considered a standard boot loader, which is implemented in the form of executable files and system processes. It works exclusively when the operating system starts, giving the user the opportunity to select a specific version and modification if 2 or more operating systems are installed on the computer.
This is also true for cases when virtual machines are used on a PC or laptop. That is, at the start the user is given the opportunity to choose which specific OS he needs to download and run.
If these are operating systems not from the Windows family, then other bootloaders are used. These include BootX, Silo, Lilo, etc. They are used on MacOS, Linux and other platforms.
For Windows, you can use other bootloaders. They are installed using the settings of the primary system, that is, the BIOS. This is a rational solution in situations where different operating systems from different manufacturers are installed on the computer. That is, Windows, Linux, Solaris, etc. can be used simultaneously within one PC or laptop.
Using Visual BCD Editor
If using the command line is not for you
There is a Visual BCD Editor option. Visual BCD Editor implements a huge set of BCDEdit commands in a convenient visual graphical interface. You get the same experience and functionality as using BCDEdit on the command line, but you don't have to worry about typing the exact command.
Deleting an old entry is a simple task. Download and install Visual BCD Editor, then open it. The tool will take a short time to scan your system. In the left option tree you will see Bcdstore > Loaders > [your loader settings] . Select the bootloader you want to remove and click remove at the bottom of the right information panel.
Common mistakes
Faced with Boot Manager, many users have a natural question about what to do next. In fact, the Boot Manager error in Windows is not always terrible and critical. Much depends on the specific circumstances of its appearance. You shouldn’t immediately panic and look for the numbers of service centers for computer equipment repair.
Users often ask questions about how to independently disable this Boot Manager loader in Windows. This can be done, and in the BIOS. But there's no need to rush just yet.
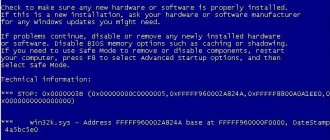
Boot Manager, as a bootloader service, may also encounter errors and crashes during operation. Quite often, users see a picture in the form of a black screen on which a message like “Bootmgr is missing” is written.
So far nothing bad has happened.
If we talk about the reasons for settings failure in Boot Manager for Windows, there are several of them. The setting itself gets lost, or it needs to be configured again if errors occur with the hard drive or the operating system boot manager itself is damaged. Boot records and sectors are also affected.
It is also important to take into account that errors can usually be corrected in 2 ways:
- Simple. Does not involve the use of third-party solutions. You just need to complete a few steps.
- Difficult. Here removable media are used, through which the system is started and the necessary command lines are called.
How lucky a user will be depends on the specific situation.
Primary Actions
First, you need to understand what you need to do first when a failure occurs in the Boot Manager boot loader on Windows OS.
When faced with such a problem, you should first perform a few relatively simple steps:
- The simplest solution, when the download did not occur due to a short-term disruption or random failure, is a banal reboot. This can be done with a keyboard shortcut, or with the Reset button on the system unit or laptop.
- If this method did not work and the situation repeats itself when you restart it, you should try booting using the last known good version.
- An alternative to the previous point is to launch through Safe Mode.
- Then the command console opens to check the hard drive for possible errors. To do this, you need to enter the command chkdsk /x/f/r, or its other variants, depending on the name of the disk.
Only here it is important to understand that the built-in scanning tool available in Windows OS is not very effective. Therefore, sometimes you have to use alternative solutions.
Removing EFI Boot Manager Options Using BCDEdit
I started writing this article because there are a number of old Linux boot loader entries left in my EFI boot manager. Again, they don't cause any problems, but over time they build up and become annoying.
The EFI Boot Manager is part of the UEFI Firmware Management Suite. You might find this if you've ever booted from a USB or other media source and is usually accessible by pressing the function key during the boot process
,
To remove old EFI entries, open an elevated command prompt and type firmware bcdedit /enum, and press Enter. Unlike the command used for the Windows Boot Manager, the "enum firmware" command lists all objects available in the BCD store, including any Linux installations. The following picture shows the list of firmware of my laptop:
There are entries for Ubuntu and openSUSE that are no longer in use. Copy the ID of the firmware entry you want to delete and run the following command bcdedit /delete {identifier} .
Analysis of the state of system components
Before you remove or uninstall the Boot Manager boot loader in Windows, there are a few more steps you should take. Errors in system components may be an obstacle to loading. It’s not difficult to figure out how to check them.
After performing the described steps, there is no guarantee that the bootloader will start working normally. Therefore, the next step is to check all system components.
The command line opens, where the standard command is written. It looks like this sfc / scannow. This can be done in normal OS boot mode, or when using optical disks and USB drives with an operating system.
If it is possible to start the system without using removable media, it is better to start the computer using the administrator username.
Download Manager Features
When the OS starts, the following actions are performed:
- initializing computer components to work as part of the system;
- writing the OS kernel to RAM;
- initial setup of the loaded kernel;
- transfer of control to the kernel.
Next time the manager will be called only at system startup. It will be in standby mode while the computer is turned on.
What is DHCP - how to enable and configure
Disk errors
It's much worse when disk errors appear. When checking with the previous method does not give results, users begin to worry because they do not know what to do next.
If there are software errors on your hard drive, the right solution would be to use a utility like Victoria and scan the system. Moreover, this tool is objectively one of the best. An alternative is HDD Regenerator. It is used in situations where the disk has completely crumbled. This program, according to the developers, is capable of restoring a hard drive using the magnetization reversal method.
Using the Shell
Everything described above concerns rather complex situations. But often the problem can be dealt with using much simpler and more effective methods.
One such solution is to restore boot using certain codes through the command console. In this case, the system will boot through removable media.
Here you will need to use the Bootrec.exe tool. For it, using a space and the / symbol, write the following commands:
- FixMbr, copes with bootloader errors, eliminates record and sector problems;
- FixBoot, performs similar functions;
- RebuildBcd, allows you to overwrite the entire available boot area.
If you don’t want to deal with this, sometimes the only sensible solution is to disable Boot Manager in Windows. It can be done. Therefore, we should talk separately about how to disable this bootloader in the BIOS and not return to it again.
Disabling the bootloader
The desire to disable the Boot Manager bootloader is quite easy to explain. Users don't want to deal with glitches and errors. When the manager is disabled, the system will start smoothly, without any difficulties.
To achieve the desired result, just open the command console and write a few lines here. Namely:
- first comes the c command: expand bootmgr temp;
- the next line attrib bootmgr -s -r -h;
- then del bootmgr;
- followed by the line ren temp bootmgr;
- and finally attrib bootmgr -a +s +r +h.
A truly working method that allows you to cope with this operating system download manager and save the user from errors and possible failures.
It cannot be ruled out that the presented methods for dealing with errors and failures may not work. There is already a high probability of malfunction of the hard drive itself, which will have to be repaired or replaced with a new one. Sometimes it happens that problems arise with access to RAM strips. You can use special utilities to check your RAM. In case of mechanical damage, you will have to dismantle the RAM sticks by pulling them out of the slots and carry out diagnostics.
If there is no physical damage causing the bootloader error, you can simply disable it in the BIOS, as shown above.
Another option is to edit the file. It is called boot.ini. In it, you just need to delete the lines with the operating systems that are offered to choose from when loading, leaving only one operating system. An option for those who are ready to give up additional operating systems and use only one of them.
Interaction between Windows boot manager and BIOS
In general, it can be argued that the functions of the BIOS and bootmgr complexes are interrelated and somewhat similar. The first one starts all the computer components, puts them into operation and configures the ability to exchange commands between the user and the computer. The second one then takes control and launches other system programs, which will be given control later. The following diagram most clearly illustrates the procedure for transferring control of a computer to the operating system.
The start order implies that when the BIOS is initialized, the system disk is turned on (not a disk partition, but the hard disk with the OS), where bootmgr is located, which is unloaded into RAM. Next, under the control of the Windows boot manager, the OS components are launched and control passes to them.