08/10/2013 windows | for beginners
The Windows Task Manager is one of the most important tools in the operating system. Using it, you can see why your computer is slowing down, which program is “eating up” all the memory, processor time, constantly writing something to the hard drive, or accessing the network.
Windows 10 and 8 introduced a new and much more advanced task manager, however, the Windows 7 task manager is also a serious tool that every Windows user should know how to use. Some common tasks have become much easier to perform in Windows 10 and 8. See also: what to do if the task manager is disabled by the system administrator
How to call the task manager
You can call the Windows Task Manager in various ways, here are three of the most convenient and fastest:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc anywhere while in Windows
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Del
- Right-click on the Windows taskbar and select “Start Task Manager.”
Opening Task Manager from the Windows Taskbar
I hope these methods will be enough.
There are others, for example, you can create a shortcut on the desktop or call the manager via “Run”. Read more on this topic: 8 ways to open the Windows 10 task manager (also suitable for previous operating systems). Let's move on to what exactly you can do using the task manager.
How to enable the ability to launch Task Manager in Windows 7
Sometimes, after your system is exposed to viruses, you lose the ability to launch the Windows 7 task manager. You have cured your computer of viruses. You can read how to do this here. Now you need to enable the ability to launch the Windows 7 Task Manager.
1. Enabling Windows 7 Task Manager via Group Policy Editor
- Go to the main menu Start
, select
Run
and type
gpedit.msc - In the left area, select Administrative Templates > System > Action options after pressing CTRL+ALT+DEL
- In the right area, select Delete task manager by double-clicking on it
- In the window that opens, select Not configured
or
Disable
and click
OK
Close the Group Policy Editor window and restart the computer. Task Manager for Windows 7 will be available.
2. Enabling the Windows 7 Task Manager using the RegtickPro utility
The program works without installation, similar to AutoRuns.exe, which helps us manage startup.
- Download the RegtickPro.exe utility and run it.
- In the right panel, select System
- On the left side, in the Current User
, uncheck
Disable Task Manager, also known as Task Manager in Windows 7
Click the Apply
then
OK
. Restart your computer and launch Windows 7 Task Manager as usual.
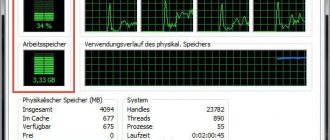
View CPU Load and RAM Memory Usage
In Windows 7, the task manager opens by default on the “Applications” tab, where you can see a list of programs and quickly close them using the “End task” command, which works even if the application is frozen.
This tab does not allow you to see the program's resource usage. Moreover, this tab does not display all programs running on your computer - software that runs in the background and does not have windows is not displayed here.
Windows 7 Task Manager
If you go to the Processes tab, you can see a list of all programs running on the computer (for the current user), including background processors that may not be visible or located in the Windows system tray. In addition, the processes tab displays the processor time and the computer's RAM used by the running program, which in some cases allows you to draw useful conclusions about what exactly is slowing down the system.
To see a list of processes running on your computer, click the "Show processes of all users" button.
Windows 8 Task Manager processes
In Windows 8, the main tab of the task manager is “Processes,” which displays all information about the use of computer resources by programs and the processes they contain.
How to kill processes in Windows
Kill a process in Windows Task Manager
Killing processes means stopping their execution and unloading them from Windows memory. Most often, there is a need to kill a background process: for example, you exited the game, but the computer is slowing down and you see that the game.exe file continues to hang in the Windows task manager and eat up resources, or some program loads the processor by 99%. In this case, you can right-click on this process and select the “End task” context menu item.
Windows processes. How to find and remove a virus process?
Published: 10/21/2012
You can view a list of all programs running on your computer using Windows Task Manager . To do this, press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+Del . You will see a list of processes, and the question will immediately arise: why is each specific process in this list needed? Let's figure out what processes and how you can manage them.
Processes are everything that is happening at a given time in the system. In the Task Manager , the “Processes” tab displays all currently running programs. Processes can be “spawned” either by the user or the system. System processes start when Windows boots; user processes are programs launched by the computer user himself or launched on his behalf. All system processes run under the name LOCAL SERVICE , NETWORK SERVICE or SYSTEM (this information is available in the Task Manager in the “User name” column).
The task manager only allows you to view a list of processes and terminate their work. To do this, select the process name in the list and click the “End Process” button.
This means the program that owns the process is terminated. However, it is not possible to view information about a particular process in the Task Manager.
To manage Windows processes, I would recommend using a more powerful utility called Starter . This is an excellent free program that also does not require installation. Download it here, then run the Starter.exe and select the “Processes” tab at the top.
Starter shows all processes in real time, providing comprehensive information on each of them. By right-clicking on the process of interest to us and selecting “File Properties”, we can find out the manufacturer of the software module, version, attributes and other information. The process context menu also allows you to go to the program folder, end the process, or find information about it on the Internet.
How to get rid of viruses on your computer using Starter?
Very often, viruses and other malicious programs are disguised as various processes. Therefore, if you notice that something is wrong with your computer, run an antivirus scan. If this does not help or your antivirus refuses to start at all, open Task Manager and view all running processes.
If when you press Ctrl+Alt+Del you get the error: “Task Manager has been disabled by the administrator,” read this note of mine.
Pay special attention to a process if it is running as a user and is consuming too many resources (the “CPU” and “Memory” columns). If you find an obviously suspicious process in the list, end it and see how your system works after that. If you are in doubt or don’t know which program the running process belongs to, it’s better to go to Google or Yandex, enter the name of the process in the search bar and find information about it.
The Task Manager built into Windows, of course, allows you to disable processes, but, unfortunately, it provides very little information about them, and therefore it is quite difficult to understand whether a process is viral. The Starter program is much more useful in this regard.
So, to find and remove a virus process from your computer, do the following::
1. Launch the Starter and go to the “Processes” tab. 2. We find a process that makes us suspicious. Right-click on it and select “File Properties”. For example, I chose the file svchost.exe . In the window that opens, look at the manufacturer of this application:
The fact is that almost any process is signed by its developer . But virus applications are usually not signed. In my case, the svchost.exe is signed by Microsoft Corporation and therefore we can trust it. 3. If the selected process turns out to be unsigned by anyone or signed by some strange company, then again right-click on the name of this process and select “Search on the Internet” - “Google” (the Internet on the computer must be connected). 4. If the sites suggested by Google confirm that this process is a virus, then you need to go to the folder of this process (to do this, in Starter, in the context menu, select the item “Explorer to process folder”). Then, having previously completed the process, we delete the file of this process here . If you still doubt whether it is a virus or not (perhaps you were unable to look up information about it on Google due to the lack of Internet), then you can simply change the extension of this file (for example, from .exe to .txt) and move it to another folder .
That's all. Today we learned what Windows processes are and what utilities can be used to manage them. In addition, we now know how to get rid of viruses masquerading as various processes.
Views: 159,488
Category: Windows Tags: virus, processes Leave a comment
Checking computer resource usage
Performance in Windows Task Manager
If you open the “Performance” tab in Windows Task Manager, you will be able to see overall statistics on the use of computer resources and separate graphs for RAM, processor, and each processor core. In Windows 8, network usage statistics will be displayed on the same tab; in Windows 7, this information is available on the “Network” tab. In Windows 10, information about the load on the video card has also become available on the performance tab.
Network and Resource Monitor
The Performance tab includes a Resource Monitor button. This is a logical location where the user can go to the Performance tab to troubleshoot any glitch. usually find problems in the CPU and memory usage graphs. If that doesn't work, you can use the Resource Monitor button to access a variety of monitoring tools.
The Network tab displays a graph of your active network connection, which provides information about network connection usage. The bottom of this tab also contains columns showing communication speed and connection status . The Users tab displays users who are logged in. By clicking on the user name, you can disconnect the one who is remotely connected to the computer, or you can “Log off the local network” itself. Using WTM to shut down a local user:
- Press Ctrl/Alt/Del.
- Open the “Run” tab.
- Go to the “Users” tab.
- Click on the desired username and select “Log out.”
- A warning message will appear asking you to confirm if you want to disconnect the user, and any unsaved data will be lost.
- Click “Logout”, after which the user will be removed from the system.
View network access usage by each process individually
If your Internet is slow, but it is not clear which program is downloading something, you can find out by clicking the “Open Resource Monitor” button in the task manager on the “Performance” tab.
Windows Resource Monitor
The Resource Monitor on the Network tab has all the necessary information - you can see which programs are accessing the Internet and using your traffic. It is worth noting that the list will also include applications that do not use Internet access, but use network capabilities to communicate with computer devices.
Similarly, in the Windows 7 Resource Monitor, you can track the use of the hard drive, RAM and other computer resources. In Windows 10 and 8, most of this information can be seen by being in the Processes tab of the Task Manager.