What is backup?
I’ll try to describe in simple terms what backup is:
Backup
or “
backup
” (from English backup copy) is creating a copy of your files and folders on an additional storage medium (external hard drive, CD/DVD drive, flash drive, cloud storage, etc.).Backup is necessary to restore data if it is damaged or destroyed in its primary storage location (on the internal hard drive of a computer or the flash memory of a mobile device).
For simplicity, the English word “ backup”
”, which reads “
back-up
” and is literally translated as “
reserve
” (can be translated as “reserve” or “duplicate”).
Please note that in the definition I specified that the copy must be on additional media
information, this is an important point. Why? Let's find out!
Reservation Plans
Both file backup and image backup can be performed in three main plans: full, differential and incremental backup.
- Full backup : in this case, all data to be protected is copied at a certain period according to a particular policy. Data recovery in this case occurs by completely backing up a full backup copy of the data to its original location. Everything is simple here, but the approach has its drawbacks: the need for a large amount of space to store backup data, as well as a long time for both the backup itself and the recovery of the backup copy.
- Differential backup , which periodically backs up only the differences that occurred between the current version of the data and the last full backup. Restoring from a differential backup requires both a full copy of all data and a differential backup. This copying is fast, but also requires a lot of space on the backup drive.
- Incremental backup , which copies only the differences that occurred between the current version of the data and the last differential, incremental, or full backup. The advantage of such a backup plan is the speed and low requirements for the volume of backup media. The downside is that data recovery requires all data from the last full backup and data from every incremental backup between the full backup and recovery to the RPO (recovery-point objective).
Why do you need backup?
As you may have guessed, a computer is not the most reliable device. Data can get corrupted quite easily
or even collapse.
If you do not have a copy, then restore important documents, family photo albums and videos
It can be very difficult or completely impossible!
Backup serves as a lifeline to help you recover your data!
Also, a backup will be useful if the device itself is unavailable (you took your computer to a service center, lost your phone (pah-pah-pah) or simply forgot your laptop at the dacha).
What is backup? This is your salvation!
In addition, using a backup, you can quickly restore your computer’s operation.
after a failure (by making a copy of the system partition). At the same time, your data will not be touched if you do not store your documents on drive C. We will talk about this in detail later, so as not to miss it, subscribe to the site’s news.
Why is data lost?
If you think about it, backup wouldn't be necessary if data weren't lost. But there are many ways to lose important information.
Let's look at the most common reasons for data loss:
- Failure of computer components
. A hard drive can fail at any time for various reasons (defective defect, power surge, accidental shock or fall, etc.). Flash memory is also not a very reliable storage medium. You should never trust important data to one device! - Software glitch
.
Programs are written by people, and people make mistakes. Due to a software glitch, the operating system may not load and you will not be able to use the contents of your computer. Errors in programs can damage or delete files. More examples can be given, but I think the point is clear: programs can accidentally cause harm
. - Attackers
. Unfortunately, our society is not ideal either, and there are those who want to take advantage of someone else’s work by stealing a device with information on it. There is another method of sabotage, which is described in the following paragraph: - Malicious programs
. Various viruses can corrupt/delete your files or encrypt them in order to extort money from you. Antivirus does not always help (we will talk about this in the following IT lessons). - Computer user
. Yes, it’s not surprising, the user is very often the one to blame for the loss of his important documents. Inadvertently deleted or overwrote a new version of a document with an old one, accidentally deleted the contents of a file, forgot what it was called and where it was put... etc.
I myself have encountered each of the listed points and, if it were not for backup, it’s scary to imagine how much time it would take to restore data each time.
AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition
AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition is a utility for managing hard disk partitions. In the application, you can resize the partition, format the disk, and merge multiple partitions. There is a built-in tool for transferring the operating system to an SSD or HDD and a function for converting the FAT file system to NTFS. The software is completely free, compatible with the Windows operating system (32 and 64 bit) and translated into Russian.
In the main application window, you need to select the “SSD or HDD OS Transfer” tool in the “Wizards” section.
The System Transfer Wizard will open. In this tool, you need to select the disk to which the program will transfer the OS. To perform the operation, the target disk must have enough free space for Windows system files.
After this, the utility will begin transferring the system. Once the process is complete, you can boot the systems from the new storage device.
Advantages of AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition:
- simple and convenient interface with Russian language support;
- free distribution model;
- bootable CD creation tool;
- function to delete all partitions;
- built-in partition recovery wizard;
- support for file system conversion function;
- the ability to create backup copies of disks, files and folders.
Flaws:
- no built-in task scheduler;
- There is no benchmark for testing the disk for errors.
What should you copy?
Before making a backup, let’s figure out what needs to be copied.
your personal files need protection
:
- photographs and family videos;
- work documents;
- browser bookmarks;
- important stored information from the Internet;
- notes;
- contacts;
- settings files for the necessary programs;
- other data that is difficult to recover.
Secondly, you can backup the operating system and programs
, but we will talk about this later, at a higher level of complexity.
There is no need to back up those files that you can easily restore (for example, a movie that you downloaded from the Internet for two viewings, music that you will delete in a week, etc.)
Preparing to clone a disk
It is important that the cloning process is not interrupted, therefore:
- If you are copying data from a laptop's hard drive (or SSD), charge the device in advance and connect it to a power source.
- If your computer has recently shut down or restarted on its own, troubleshoot these issues.
- If you have important data on your device that you don't want to lose, make a backup just in case. In the event of a failure, you can restore information from this copy.
To clone a disk, you will need an additional destination disk.
Tip: when using SATA 6 (also relevant for higher speed versions), the cloning process is faster. If you are unable to connect both devices this way, use the USB interface.
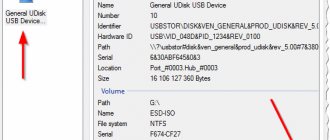
Where should I make a backup?
Keep a backup copy in a safe place. Such a reliable place can be considered an external storage medium, i.e. one that is not directly connected to your computer most of the time.
1. External hard drive
. The device is quite reliable, but requires careful handling (does not like falling from a table or shelf). By the way, I advise you to periodically monitor the health of both the external hard drive and the main internal one.
2. DVDs _
. They have a different nature of storing information, they are not so afraid of falling, but they do not have the highest speed and ease of recording, and reliability depends on the quality of the disks (“blanks”).
3. Flash drive
(USB flash drive). The small size and ease of use are attractive, but can be misleading in terms of reliability, which is far from ideal. I’ll say right away that a flash drive can only be considered as an addition to the main backup drives (note that it was originally created for data transfer).
4. Cloud storage
. Nowadays people are increasingly talking about “clouds”; indeed, using such storage facilities is very convenient if the Internet speed is high enough. But this information carrier also has disadvantages, we will talk about them in the corresponding lesson (in which I will reveal the secret of how to get rid of these shortcomings, don’t miss it, subscribe to the news of the IT lessons site).
You may ask, “What should I choose for backup?” Believe it or not, my answer is EVERYTHING!