Anyone who has ever set up a router on their own from a computer/laptop via wifi or via a wire has come across such concepts as “WAN” and “LAN”. It is to these ports that the provider cable (twisted pair) is connected to access the global Internet or from a router, after which you can open any http address in the browser and establish a connection to sites. The WAN interface, or as it is also called Ethernet Port, and LAN are present on all routers, regardless of the manufacturer - TP-Link, Asus, D-Link, Mikrotik and so on. For some, their number can vary from 2 to 5. We have repeatedly published on the pages of wifika.ru instructions for setting up various types of Internet via wireless - Dynamic IP (DHCP), Static IP, PPPoE and so on. Today I would like to dwell on the very concept of “WAN Network” - how this term is translated, what it means and how it differs from LAN or Wireless LAN.
How WAN and LAN are translated - definition of the term
WAN (VAN) in decoding sounds like “Wide Area Network” - translated into Russian it is a global computer network. We simply call it the Internet. That’s why one of the connectors on the wifi router is marked with the “WAN” icon - this is where the cable for accessing the Internet, which the provider laid into the apartment, is connected to.
LAN (LAN) is by analogy “Local Area Network”, that is, in our opinion, a local network. That is, this is a connection between different devices within a connection to one router. Over such a network, you can transfer files or broadcast video and music from one media to another.
Read more about the difference between a local and global network in a separate article.
Difference between LAN and WAN.
For example, the headquarters could be in Russia, the regional office could be in the UK and the office could be in Italy. Workers in these three buildings - a Wide Area Network - collaborate with each other. The Internet can also be considered a WAN, Ethernet is a classic example global network. Let's look at the differences between these two structures.
Differences
The following amenities are provided: LAN - WAN Speed 1000 Mbps 150 Mbps Transmission Bandwidth - High - Low Data Rate - High - Low Geographic Coverage - Small - Large Equipment Connectivity - 10Base-T Cable - Leased Lines or Satellite Used technologies - Token Ring And Ethernet ATM, Frame Relay, X.25 Transmission errors - Several - More details Installation cost - Low - High Maintenance costs - Less - More details Network topology - Peer to Peer - Client-Server model Security - More secure, than the WAN is open to threats Standard - Ethernet T1 Signal degradation - No - Yes Required equipment - Hub, Switch Router, Modem Expansion using a network card - Using an Additional Router Range 1 km - Up to 10000 km Printer sharing - Yes, if in that same local network - No
Local network structure
In a local area network (LAN), devices are connected to a switch or hub. Common devices are connected to a switch that is located in the city center. In the case of devices that need to be connected to the Internet, the switch connects to the Internet service provider and thus to the Internet. Data common to all devices is stored on servers. If there are multiple devices that need to be added, an additional hub or switch can be added. Local Area Network (LAN) has higher bandwidth and is faster compared to WAN . The maximum speed of the local network can be up to 1000 megabits per second. Since LAN is faster, it is preferred for sharing computers on a network. LANs are easy to install; most computers and laptops are made today with an RJ45 port built into the motherboard, which is used to connect to the network. For older machines that do not have this port, separate NICs (Network Interface Cards) must be installed. This card fits into the PCI slot of desktop computers, and the PCMCIA slot of laptops. The main advantage of using a LAN is its ease of data exchange. The computer, if connected to the same LAN , can even share a printer. The biggest problem that companies face in the process of connecting computers to a local LAN is monitoring traffic for the Internet. If there is too much load on just one computer or on a shared device, it can slow down the LAN . This can be circumvented by using a LAN traffic monitor, which monitors bandwidth usage. Based on setup and operation, the cost of LAN setup is considered cheaper compared to WAN setup .
Wide Area Network
In WAN setup , computers that are present in different places and they are all interconnected. Devices connected to the router are interconnected through the T1 standard. This makes it difficult to expand the use of the WAN. Wide Area Network (WAN) , since it has lower bandwidth, thereby slowing down networks. WAN can reach up to 150 megabits per second. This means that WAN is one-tenth the speed of a local network. Although WAN is slower, it is widely used for data exchange. The best example is global Internet networks .Internet data is available on different continents.However, a WAN cannot share peripheral devices, just like a computer in one country cannot use a printer in another country.To set up a WAN, you need a modem and a router.So, in case if an additional device is to be added to the network, the router must be configured and connected to others on the network. Since the number of devices in the WAN is greater than those connected in the LAN, there is a greater need for monitoring the devices. For this, special devices are used computers whose sole purpose is to send and receive data from the Internet. Leased lines or satellites are used to connect devices on a global network . While each of the two networks has its own advantages and disadvantages, but this is a special factor that helps choose between LAN and WAN setup (WAN setup is a distance). If the places that will be connected are far apart, then there is no point in considering setting up a local area network LAN , despite all the benefits it can offer, it is simply not possible.
WAN port - connector on the router
So, in the broad sense of the word “WAN” is simply the Internet. In the narrow one that we encounter when setting up a network, this is a port on a wifi router for connecting to a wire. It can be indicated by an abbreviation or the words “Internet”, “Ethernet”.
Or just a globe icon
Also, to make it more difficult to confuse it with the LAN interface, it is often distinguished in a different color from other RJ-45 connectors.
LAN connector on your router or computer
Through the LAN connector on the router we connect other devices to it via cable. There are usually many LAN ports for connecting multiple devices at the same time. Most often these are desktop computers or old TVs without a wifi adapter. They are designated by numbers and are always marked with the same color within the same router.
Today, in the wireless era, it is rare to see computers and laptops connected to the router via LAN ports with cables. More often this is done via WiFi, that is, via “Wireless LAN”. To do this, use an 802.11n or ac adapter, which is inserted into the PCI connector on the motherboard or an external USB port. After installing the drivers in Windows, a regular cable signal turns into a wireless signal.
What is the difference between WAN and LAN connection on a router?
A logical question immediately follows: what is the difference between the WAN and LAN ports on a router, if an RJ-45 cable is connected to both? LAN connectors, unlike WAN, are designed to connect other devices to a local network via cable - computers, laptops, printers, IP cameras, and so on.
- There is a cable in the WAN that the provider pulled into the apartment to supply the Internet to the router itself
- In LAN - a wire from another device that needs to be connected to the Internet and local network
As I already said, many of them do not have a wireless adapter (WiFi 802.11ac or 802.11n), and they can only be connected to the Internet using a network cable. Therefore, there are often more LAN ports than WAN ports - usually from 2 to 4.
The speed of the interface may also differ. For example, in inexpensive router models, the Internet speed via WAN will be limited to 100 Mbit/s, although the local network (via LAN) can be gigabyte, that is, reach 1 Gbit/s.
The same applies to the Wireless LAN wireless interface, where the speed depends on the frequency range. At 2.4 GHz (WiFi standard 802.11n) it is usually limited to 150 or 300 Mbit/s, and at 5 GHz (802.11ac) it can reach 900 Mbit/s and higher.
LAN tasks
Now let's talk about why people create these local networks in the first place and why in some cases it is impossible to use a global one.
So, the goals of creating a LAN can be as follows:
Actually, these are all the goals that people pursue when they connect devices into local networks. As you can see, everything turned out to be quite simple and uncomplicated.
There is only one question left to consider: what does using a LAN look like?
It’s very simple - a user who is connected to the network goes to the “Network” folder on his computer and sees the “Users” folder there.
He goes into it, then selects the desired user (opens it like a regular folder) and sees all his shortcuts, folders and other information as if it were on his computer.
Rice. 6. The “Network” folder on a computer connected to the local network.
Of course, before this you need to perform a number of manipulations to configure the LAN, and also make sure that all devices are suitable for use on the local network.
But this, as they say, “is a completely different story.”
You can understand the information presented above even more if you watch the tutorial in the video below.
What is an IP address, mask, host, network address. Basics
Description of the basic principles of addressing in computer networks. An explanation of what an IP address is and what parts it consists of, what a mask is and how to use it, how to determine the number of hosts.
If you have Telegram, you can now download any software or game through our bot, just follow the link and try it!
« Previous entry
WAN port error on router
If you connect another computer through the WAN port on the router, an error will occur and it will not work on the local network. It’s the same thing and vice versa - if you insert an Internet cable into the LAN connector of the router, it will not be connected to the Internet. This will look like an icon with an exclamation mark in the Windows panel and a notification in the browser that “network without Internet access” or “disconnected state”.
Moreover, the WAN or LAN indicator on the router’s LED panel will light up - after all, the cable is connected. But the Internet will of course not work.
However, in some devices, Internet WAN and Ethernet LAN interfaces can be combined due to their specific nature. The simplest example is on the PCI network card of a computer, laptop or TV. After installing the native driver through this connector, we can connect it either to the router or insert the Internet cable from the provider directly.
Another example is the PowerLine adapter, which can simultaneously work to receive an Internet signal via cable and distribute it to other devices.
Theoretical page
So, LAN stands for Local Area Network. This actually translates to local area network.
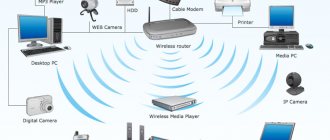
To put it simply, a LAN is several interconnected computers, routers and other devices that can connect to the network.
And they are connected to each other either using cables or using Wi-Fi. In Figure 1 you can see a fairly clear example of a local network.
Rice. 1. LAN example
As you can see, the main element of the network here is a router that is connected to the Internet (WAN). Remember this abbreviation, we will talk about it later.
For now, let’s look at the diagram shown above. On it, numbers indicate network segments, specifically:
1. A switch through which other devices are connected.
As you know, a switch is a device that receives a signal via a cable and, in the same way, transmits it via cable to other devices connected to it.
In fact, the switch can be compared to a Soviet tee, which was plugged into an outlet, and three more devices could be plugged into it, for example, an iron, a TV and a telephone.
Here the principle is the same, only it is not electricity that is transmitted, but information. This, again, if we speak in worker-peasant language.
Rice. 2. Soviet tee
2. A laptop that connects to the router via Wi-Fi.
3. DVD player connected to the router using a cable. For this purpose, the router has special LAN connectors, which are usually marked in yellow. In most cases there are 4 such connectors.
4. A tablet also connected via a Wi-Fi signal.
5. A personal computer that is connected in the same way as a DVD player, using a cable.
6. Another laptop, which is also connected using a wire.
7. Smartphone – uses Wi-Fi signal.
As we said above, a LAN connector is used to connect to the router via cable. We can see this in Figure 3.
Rice. 3. Router - rear view
As you can see, everything is standard in this model - 4 LAN connectors, but there is one more and it is already different in blue.
Actually, this is the WAN (remember, we said that this concept needs to be remembered?). To more accurately understand what a LAN is, you can compare it with this very WAN.
By the way: Both LAN and WAN are connected via the most common cable with an RJ45 tip, shown in Figure 4. Above we said that, for example, segment No. 3 in Figure 1, that is, a DVD player, is connected to the router with using a cable. This cable is a regular twisted pair cable with RJ45 lugs on both sides. It's that simple!
Rice. 4. RJ45 tip
WAN IP
Accordingly, the definition of WAN IP follows from all of the above. This is an external address that does not belong to each individual device individually, but to the entire local network, hidden behind the wifi router’s gateway.
Roughly speaking, this is the address of the router - yours, if a channel in a dedicated white IP is installed in your apartment. Or a provider, which in turn already assigns other internal gray addresses to its subscribers. Sometimes you need to know it to remotely access the router via the Internet.