Reward accrued
This material was written by a site visitor and was compensated for.
High frequency or a large number of cores is an eternal question that plagues users when assembling a gaming or work PC. In this article, we will comprehensively compare a slow processor with a large number of cores and a high-frequency processor with an average number of cores and find out which is preferable to choose right now.
The purpose of this article is simple - to find out which processor will be objectively better and more relevant in work tasks and games - with a larger number of cores or with a higher frequency. For greater clarity of testing, “standard” processors will differ from each other only in clock speed and number of cores.
announcements and advertising
2080 Super Gigabyte Gaming OC for 60 rubles.
Compeo.ru - the right comp store without any tricks
RTX 2060 becomes cheaper before the arrival of 3xxx
Ryzen 4000
series included in computers already in Citylink
The price of MSI RTX 2070 has collapsed after the announcement of RTX 3xxx
Core i9 10 series is half the price of the same 9 series
The price of memory has been halved in Regard - it’s more expensive everywhere
The processors will be “synthetic”, “created” based on the multi-core Ryzen 7 2700 processor. Due to the fact that this processor refuses to run at a frequency of 2 GHz (but this comparison would have nothing to do with reality), only two were created "standard" processor.
As planned, the “synthetic Ryzen 5” will have 1/3 more cores than its rival, the “synthetic Ryzen 3”. The latter, in turn, will have a 1/3 higher clock frequency. Total: “synthetic Ryzen 5” is a processor with six cores, operating at a fixed frequency of 3 GHz with SMT technology disabled; “synthetic Ryzen 3” will be a CPU with four cores without SMT technology, overclocked to a frequency of 4 GHz. The remaining parameters of these processors will be identical to the Ryzen 7 2700.
Even by simply multiplying cores by frequencies, it is not difficult to guess that a configuration with six cores operating at 3 GHz will be slightly stronger than a configuration with four cores operating at 4 GHz. In a conditional “mathematical benchmark” (this “benchmark” is valid only for “synthetic processors” that differ only in the number and frequency of cores), the total performance of these CPUs will be comparable as “18” and “16” in favor of a processor with a large number of cores, since for greater fairness of this testing, it should have been “locked” to a frequency of 2.66 GHz.
But this action was impossible for the same reason that the testing did not include a “synthetic Ryzen 7 / Xeon” with a frequency of 2 GHz. The ASUS TUF B450M-PRO GAMING motherboard cannot run the Ryzen 7 2700 processor with a frequency below 2.8 GHz: firstly, this is not implied, since the minimum multiplier for this processor is 28; secondly, when trying to “take” the required frequency using a multiplier/divider combination (the formula is as follows: Ratio=2*FID/DID), the system refuses to start with any voltage, even in the “auto” value.
And someone will notice that this comparison of two mathematically unequal processors supposedly loses its meaning, since “it is clear that a processor with six cores will be a little stronger.” But in this case, the processor frequencies are close to real ones, and comparing processors at 2 GHz, 2.66 GHz and 4 GHz would be at least ridiculous, since there are simply no Ryzen processors with such low frequencies. And again, this is in no way a “simulation of known processors”, this is just an attempt to compare high frequencies and a large number of cores, which is more important now.
In general, there is no point in going further into the nuances of this experiment; we suggest moving on to real research.
But first, inspect the test configuration.
Test bench
"Synthetic" processors were tested on the following configuration:
- Motherboard: Asus TUF B450M PRO GAMING;
- RAM: CRUCIAL Ballistix BL2K16G30C15U4B 2×16 GB, 3333 MHz CL14
- CPU cooling system: AMD Wraith Spire;
- Thermal paste: AMD;
- Video adapter: GeForce GTX 1060 Xtreme Gaming 6G;
- Drives: Samsung SSD 850 120GB (for Windows), Western Digital WD Blue 1 TB (for games);
- Power supply: Enermax Revolution DF, 650 Watt;
- Case: Thermaltake View 31 TG;
- Monitor: Sharp Aquos lc-26le320e-bk ;
- Operating system: Windows 10 Pro x64 (1909).
The voltage for a processor with six cores was set to 0.8125 volts, while the voltage for a processor with four overclocked cores was 1.25 volts. The LLC was adjusted so that the voltage remained stable as the load increased.
What is a computer's CPU?
Externally, a modern CPU looks like a small block about 4-5 cm in size with pin contacts on the bottom. Although it is customary to call this unit a processor, the integrated circuit itself is located inside this housing and is a silicon crystal onto which electronic components are applied using lithography.
The top of the CPU housing serves to dissipate the heat generated by the billions of transistors. On the bottom there are contacts that are needed to connect the chip to the motherboard using a socket - a specific connector. The CPU is the most powerful part of a computer.
Testing in synthetic programs: CPU-Z
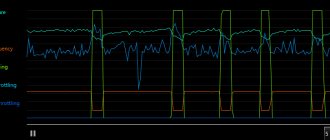
Now that we have figured out the behavior of two instances in the stress test, I propose to compare the performance of processors in CPU-Z.
6 cores
4 cores
To simplify the perception of the test results, all data was displayed in the form of a diagram with a table of values.
The results of the “mathematical benchmark” were confirmed. The four overclocked cores, although they outperformed the six low-power cores in single-thread performance, were seriously inferior in multi-core performance. The slow six cores outperform the four fast ones by 12.5%, this difference was known in advance from the “mathematical benchmark”: the difference between 18 and 16 is 12.5%.
CPU-Z testing
Clock frequency as an important parameter of processor operation, and what it affects
The performance of a processor is usually measured by its clock speed. This is the number of operations or clock cycles that the CPU can perform in a second. Essentially, the time it takes the processor to process information. The catch is that different CPU architectures and designs can perform operations in a different number of clock cycles. That is, one CPU for a certain task may need one clock cycle, and another - 4. Thus, the first one may turn out to be more efficient with a value of 200 MHz, versus the second with a value of 600 MHz.
That is, the clock frequency, in fact, does not fully determine the performance of the processor, which is usually positioned by many as such. But we are used to evaluating it based on more or less established norms. For example, for modern models the actual range in numbers is from 2.5 to 3.7 GHz, and often higher. Naturally, the higher the value, the better. However, this does not mean that there is not a processor on the market with a lower frequency, but which works much more efficiently.
Energy consumption/noise/temperature testing
The processors were tested using the 10-minute OCCT test version 5.5.7 using AVX2 instructions.
To simplify the perception of the test results, all data was displayed in the form of a diagram with a table of values.
OCCT 5.5.7
Thus, in OCCT testing, a processor with six slow cores turned out to be cooler than a processor with overclocked four cores. But the results of this testing cannot be interpreted on the supposed Ryzen 5 3500X and Ryzen 3 3100/3300X. All processors are unique and this test only shows seriously increased heat dissipation rates with slight overclocking, which is typical for all Ryzen processors.
Operating principle of a clock generator
All PC components operate at different speeds. For example, the system bus might be 100 MHz, the CPU might be 2.8 GHz, and the RAM might be 800 MHz. The baseline for the system is set by the clock generator. Most often, modern computers use a programmable generation chip, which determines the value for each component separately. The principle of operation of the simplest clock pulse generator is to generate electrical pulses at a certain time interval. The most obvious example of using a generator is an electronic watch. By counting ticks, seconds are formed, from which minutes and then hours are formed. We will talk about what Gigahertz, Megahertz, etc. are a little later.
Assassin's Creed Odyssey
Graphics settings and benchmark comparisons
Graphics settings are the minimum possible.
Additional weak cores had a positive impact on performance in Assassin's Creed Odyssey.
To simplify the perception of the test results, all data was displayed in the form of a diagram with a table of values.
Even at minimum graphics settings they could not “save” four overclocked cores from losing in Assassin’s Creed Odyssey. Unfortunately, the gigahertz difference did not give the four cores a head start.
How the speed of a computer and laptop depends on the clock frequency
The processor frequency is responsible for the number of clock cycles a computer can execute in one second, which in turn reflects performance. However, do not forget that different architectures use different numbers of clock cycles to solve one problem. That is, “measuring by indicators” is relevant within at least one class of processors.
What is affected by the clock speed of a single-core processor in a computer and laptop?
Single-core CPUs are rarely found in nature anymore. But you can use them as an example. One processor core contains at least an arithmetic-logical unit, a set of registers, a couple of cache levels and a coprocessor.
Lithography layout for placement on the CPU. The frequency with which all these components perform their tasks directly affects the overall performance of the CPU. But, again, with a relatively similar architecture and command execution mechanism.
What is affected by the number of cores in a laptop?
The CPU cores do not add up. That is, if 4 cores operate at 2 GHz, this does not mean that their total value is 8 GHz. Because tasks in multi-core architectures are executed in parallel. That is, a certain set of commands is distributed to the cores in parts, and after each execution a common response is generated.
Each core is a separate CPU. Thus, a certain task can be completed faster. The whole problem is that not all software can work with multiple threads at the same time. That is, until now, most applications, in fact, use only one core. There are, of course, mechanisms at the operating system level that can parallelize tasks across different cores, for example, one application loads one core, another loads a second, etc. But this also requires system resources. But in general, optimized programs and games perform much better on multi-core systems.
Synthetic testing: Cinebench R20, CPU Queen, CPU PhotoWorxx
Before we move on directly to games, I suggest you familiarize yourself with the summary testing of processors in popular synthetics.
To simplify the perception of the test results, all data was displayed in the form of a diagram with a table of values.
As we can see, the processors are very close in their performance in synthetic tests. But a processor with a low frequency and six cores has a natural lead in Cinebench R20 and a slight advantage in PhotoWorxx CPU. Based on the results of “general synthetics”, it is difficult to identify a clear favorite; the processors are very close, but due to purely “mathematical superiority”, 6 cores with a frequency of 3 GHz become more preferable.
Synthetics
How is processor clock speed measured?
The unit of measurement Hertz usually indicates the number of times periodic processes are executed in one second. This became the ideal solution for the units in which the processor clock frequency will be measured. Now the work of all chips began to be measured in Hertz. Well, now it’s GHz. Giga is a prefix indicating that it contains 1000000000 Hertz. Throughout the history of PCs, set-top boxes have changed frequently - KHz, then MHz, and now GHz is the most relevant. In CPU specifications you can also find English abbreviations - MHz or GHz. Such prefixes mean the same as in Cyrillic.
RAM or simply “RAM”
The speed and number of operations performed in a certain amount of time depend on the amount of RAM and its frequency. In this case, at least two indicators must be indicated on each board: volume and frequency. Many users are chasing volume, believing that the most important thing in RAM is a larger number of GB (2, 4, 8). Although the amount of maximum processed information at a time depends on this. The speed of the computer is determined by the specified frequency. Modern DDR4 has a speed of up to 3200 MHz, which makes them the most productive at the moment. Therefore, when choosing RAM, you need to be guided not only by the amount of memory, but also by the clock frequency, which, together with a good processor, will allow you to overclock your PC to really high speeds.
How to find out the processor frequency of your computer
For the Windows operating system, there are several simple methods, both standard and using third-party programs. The simplest and most obvious is to right-click on the “My Computer” icon and go to its properties. Next to the name of the CPU and its characteristics, its frequency will be indicated.
Among third-party solutions, you can use the small but well-known CPU-Z program. You just need to download, install and run it. In the main window it will show the current clock speed. In addition to this data, it displays a lot of other useful information.
Far Cry New Dawn
To simplify the perception of the test results, all data was displayed in the form of a diagram with a table of values.
In this game, six low-frequency cores suffered a devastating defeat in terms of smoothness, losing to four fast cores.
Test results and settings
Ways to increase productivity
In order to increase performance, there are two main ways: increase the multiplier and the system bus frequency. The multiplier is a coefficient showing the ratio of the base frequency of the processor to the base speed of the system bus.
With the help of nitrogen cooling, overclockers overclock their PCs to fantastic performance. It is installed by the manufacturer and can be either locked for changes in the final device or unlocked. If it is possible to change the multiplier, it means that you can increase the frequency of the processor without making changes to the operation of other components. But in practice, this approach does not provide an effective increase, since the rest simply cannot keep up with the CPU. Changing the system bus indicator will lead to an increase in the values of all components: processor, RAM, north and south bridges. This is the easiest and most effective way to overclock a computer.
You can overclock a PC as a whole by increasing the voltage, which will increase the speed of the CPU transistors, and at the same time its frequency. But this method is quite complicated and dangerous for beginners. It is used mainly by people experienced in overclocking and electronics.
"Game synthetics": Ashes of the Singularity: Escalation
Graphics Settings
Testing was carried out with an emphasis on the CPU.
To simplify the perception of the test results, all data was displayed in the form of a diagram with a table of values.
It is worth noting that both processors coped with this game mediocrely, but visually the smoothness of the picture was still due to the processor with six cores.
Test results
Operating principle of the gas turbine unit
The clock generator creates pulses that are subsequently sent throughout the device. They speed up the computer architecture, simultaneously creating synchronization between individual elements. That is, the GTC is a kind of “commander” who connects the working computer links into one sequence. So, the more often the clock frequency generator creates pulses, the better performance the computer/laptop/smartphone will have, and so on.
It is logical to assume that if there is no clock generator, then there will be no synchronization between the elements. Therefore, the device will not be able to operate. Let's assume that somehow we managed to bring such a device to life. So what's next? All parts of the computer will operate at different frequencies at different times. And what is the result? As a result, the speed of the computer decreases by tens, hundreds, or even thousands of times. Does anyone really need such a device? This is the role of the clock generator.
HDD
It would seem that this cannot in any way affect the performance of the computer. This was the case on older cars. The rotation speed of the magnetic plates on the HDD fully satisfied the speed of command execution, and there was no need to speed up the modules for storing and accessing information. However, new PCs are equipped with fairly “fast” CPUs with the same RAM, and the main “brake” that holds back the speed of task execution is the hard drive. Read and write times play a significant role in the operation of a PC, including when loading the OS, as well as during task execution. The speed of a computer depends on the hard drive so much that in recent years an alternative to them has appeared on the market - solid-state SSDs, which provide unlimited speed (at the moment) for accessing physical memory. As a result of testing, it was found that the same machine, to which either an HDD or an SSD was connected in turn, showed different performance. With the latter, the system “flyed” compared to the first.