Desktop solutions from the 8th generation Intel Core processor family include only six models. Two CPUs each among Core i3, i5 and i7. We have already examined in detail the two older CPUs from the i5 and i7 lines: Intel Core i5-8600K and Intel Core i7-8700K. Now let's take on the junior Intel Core i5 processor from the new line - Intel Core i5-8400 .
This article will only talk about the performance of the new processor. We have already reviewed the Coffee Lake architecture, so we will not repeat it in this review. Well, if anyone is interested in what new Intel has brought to its architecture (besides increasing the number of cores), then we suggest that you read its review at this link.
By what parameters to compare?
One of the most important parameters that we need to evaluate is performance. Which processor is more productive? Ryzen or Intel? Typically, the number of cores and their clock speed are used as a measure of performance. And this is true, but this is not enough to evaluate the full picture of processor performance. We will consider the following parameters:
- Clock speed - how many processor cycles can be completed per second;
- Number of cores - how many physical cores the processor has. The higher this indicator, the better;
- Number of instructions per second - how many millions of instructions the processor can execute per second;
- Cache - a large cache size allows the processor to store the necessary information without accessing external resources;
- Data Bus Speed - The data bus allows the processor to communicate with other computer components.
Other important indicators include the generation of the processor. According to many estimates, sometimes the difference between processor generations reaches 20 percent in favor of the new generation. In this article we will try to compare processors of the same generations, although the Intel and AMD generations are not very synchronized.
Intel or AMD. A little background
Well, I'll start with myself. Somehow it happened that my first machines were Intel ones. I remember now 133 Mhz, it seems, the first Intel Pentium and the first Doom on it 
Now I don’t dare to judge why it was Intel that fell into my hands, either AMD had not yet entered the market at that time, or the market was too small, or their advertising was rather weak.. Or it was just a coincidence. Basically, I have no idea.
And then somehow it went like this, from upgrade to upgrade, I increased the frequency, and the sequence of models was clear to me: after the first Pentium comes the second, after the second the third, and so on.
At that time, I still had little understanding of the characteristics (I knew, perhaps, only about the frequency), and therefore I relied precisely on the names from marketers, and, perhaps, I had not even heard about AMD, i.e. for me there was only one manufacturer.
Benefits of Ryzen processors
The second generation of Ryzen processors received many improvements that significantly improved the processor architecture. We can say that the second generation Ryzen is better than its 8th generation Intel counterpart, but not in everything. The new generation has greatly improved energy efficiency.
Performance per watt has also increased significantly with new socket AM4 features such as Precision Boost 2 and Extended Frequency Range 2 (XFR2).
The motherboard recognizes when the processor can run faster and increases the frequency until the system reaches a power or temperature threshold. When Precision Boost reaches its limit, it attempts to maintain the highest possible frequency, with fluctuations around 25 MHz.
- Precision Boost - this technology can operate in two modes: acceleration of two cores and acceleration of all cores. Moreover, the acceleration mode of two cores provides better performance improvements. This technology is used in the Ryzen 5 1600;
- Precision Boost 2 - this technology works the same way, only there is no frequency limit if more than two cores are used. All cores receive the maximum frequency if temperature and power allow;
- Precision Boost Overdrive is an add-on to Precision Boost 2, which was introduced in the Zen+ architecture. It gives a more aggressive performance boost by increasing the voltage and temperature thresholds;
- Extended Frequency Range 2 - works together with Precision Boost 2. Allows the motherboard to understand how much more processor performance can be increased while maintaining an acceptable temperature. The better the cooling system, the higher performance you can get.
AMD Ryzen 5 - Quick Review
AMD Ryzen 5, if we talk only about the top models, is a six-core chip with multi-threading support. That is, they are capable of processing up to 12 computing threads simultaneously. The base clock frequency in both generations is 3.6 GHz, and the maximum clock speed is 4.2 GHz for the more recent one.
In addition, they are equipped with 16 MB L3 cache and have a TPD of 95 W. The chips are designed to work with DDR4 RAM. In general, these are the usual high-class configurations, but not top-end.
Some models are also equipped with an integrated Radeon Vega series video card, which, in principle, is quite powerful - but only if high-frequency RAM is used. The integrated graphics of both models can be compared to the discrete NVIDIA GeForce GT 1030, providing sufficient framerate for many games.
Which is better Intel or Ryzen
Now let's compare several processors from these manufacturers with each other.
1. AMD Ryzen 3 1300X or Intel Core i3-8350K
In the budget processor segment, AMD dealt a serious blow to Intel. But the processors have a few small differences. Although the Ryzen 1300X is 0.5 GHz slower than its competitor, it runs at higher memory frequencies and has 2 MB of L2 cache.
Another important difference is TDP. Thermal Design Power is the maximum amount of energy that a cooling system must dissipate to maintain normal temperatures. The 64W Ryzen 1300X is much easier to cool than the 91W Intel i3 8350K.
The last note concerns overclocking. Both processors have an unlocked multiplier. According to UserBenchmark, the Intel i3-8350K received a score of 26, while the Ryzen 3 1300X received a score of 79.
Of course, it is difficult to compare these processors, since Intel has excellent characteristics, but the Ryzen 3 1300 is the best in its price category.
2. AMD Ryzen 5 1600X vs AMD Ryzen 5 2600X vs Intel Core i5-8600K
Now let's move on to mid-range processors. We have AMD Ryzen 5 1600X, Ryzen 5 2600X and Intel Core i5-8600K. Again, there are significant differences between processors. All of these processors have approximately the same clock speed, and operate at almost the same memory frequency.
But both Ryzen processors have six physical cores and 12 threads, while their Intel competitor only has six threads. The Ryzen 2600X can clock up to 4.2GHz in Turbo Boost, but that's still less than the 4.3GHz of the i5-8600K.
In addition, the AMD Ryzen 5 1600X and 2600X have 3 MB of L2 cache and a huge 16 MB of L3 cache. But the TDP here is already higher for processors from AMD. Ryzen has a TDP of 95 W, while the Intel i5-8600K has only 65 W.
Again, it’s difficult to single out the best processor here. Intel i5 8600K is the best at the moment. But Ryzen's decent base performance coupled with Precision Boost and XFR2 guarantees you a cheap and stable system. UsersBenchmark users also rated the i5-8600K better than both AMD processors in terms of single-core performance. Intel is better for gaming and other single-core tasks, while AMD is better for multi-threaded tasks.
3. AMD Ryzen 7 1800X vs AMD Ryzen 7 2700X vs Intel i7-8700K
Let's take productivity to another level. Here we have the AMD Ryzen 7 1800X and Intel Core i7-8700K - these are the flagship processors for high-end systems. With the advent of AMD Ryzen 7 2700X, the situation has changed a little and now there is something to think about when choosing one of these processors.
Both Ryzen processors have two more cores than Intel. And these two additional cores provide four additional threads. Both processors have better multi-threaded performance, and the newer 2700x runs at higher memory clocks.
But Intel still beats the competition in single-core performance.
AMD Ryzen Threadripper 1950X vs Intel i9-7960X
Finally, let's compare the incredibly powerful Ryzen Threadripper 1950X and the equally powerful Intel i9-7960X. Both processors have 16 cores and 32 threads. But despite the higher frequency of one core of the AMD chip at 0.6 GHz, the Intel i9-7960X outperforms it in many tests.
For example, even in the Corona Renderer test, in which AMD processors usually perform well, ThreadRipper loses. UserBenchmark users also rate the i9-7960X's performance better than Threadripper.
In this regard, Ryzen versus Intel, AMD retains only one advantage. Threadripper is not far behind in performance, but is much cheaper than Intel. In addition, to use Intel you will need a special motherboard on the X299 chipset, which will add even more costs.
Intel Core i5
Intel Core I5 is a six-core processor with new features, powered by the z370 . The box with the processor comes with a standard cooler and user manual. When creating a new product, a silicon-based crystal was used. The base frequency of the Core i5 8600K is 3.6 GHz . There is support for new technologies Turbo Boost and Thermal Velocity Boost , thanks to which the maximum frequency reaches 4.3 GHz. Compared to the previous generation, it was possible to add two new cores and, due to them, increase performance.
In the new model, the developers abandoned the Hyper-Threading . It is responsible for multi-threading: the processor has six cores that process data in six threads, not twelve. On the other hand, there are now few programs optimized for multithreading. Core I5 supports Quick Sync , which provides decoding of video streams. Thanks to this function, video compression is accelerated several times. People who work a lot with video should take this into account.
Differences between Intel and AMD chipsets
Ryzen and Intel processors require special motherboards. Chipsets from different manufacturers vary, and the set of chips you use in your build is also important.
AMD AM4 chipsets
The AM4 socket can accommodate all processors based on the Zen and Zen+ architecture. AMD also previously promised that this socket would be supported by all of the company's products until 2020. Here are a few chipsets and their characteristics:
The main advantages of the X470 chipset are support for faster memory. Another feature of AM4 chipsets is the ability to overclock. You can overclock your CPU and RAM on X470, X370, B450, B350 chipsets. Overclocking is not possible only on basic A-series chipsets. While Intel processors can only be overclocked on the Z370 and Z390 chipsets. Read more about Ryzen chipsets in this article.
Chipsets from Intel
The eighth generation of Intel processors came out with the 300 series of chipsets. Here are their main characteristics:
The Z370 chipset implements a new sleep mode technology, using which the system can connect to the Internet and update information about incoming messages. This chipset also includes the ability to wake up from sleep mode using a voice command.
The new chipset also has disadvantages, first of all, it cannot install older processors of the Sky Lake and Kabby Lake generation. Another drawback of the Z370 is the lack of USB 3.1 ports.
Conclusions from tests
It is worth noting that when purchasing a gaming computer, all parts must be balanced with each other . It is necessary to have a powerful video card with a processor and a large amount of RAM. Also, each processor requires its own specific type of motherboard. This also needs to be taken into account when replacing old components.
From gaming tests it follows that the clear winner is the Core i5 8600K . The number of frames per second is almost always higher, even with a slight difference. This processor is a good solution for a gaming build. Despite the lack of the proprietary Hyper-Threading feature, it can still surprise. Intel engineers added several cores, improved the processor frequency, and these indicators are already enough to overtake the processor from AMD.
However, the choice is not so simple. The Core i5 performs better, and if you have enough money, it's worth choosing. Ryzen 5, despite the fact that it showed worse results than the I5 processor, produces decent values. The average FPS remains high, sufficient for a comfortable game. In addition, the processor is good to use in work, as shown by comparison in benchmark tests. At the same time, its price is significantly lower than Core i5. If you have a small budget, you should choose a processor from AMD.
Don't forget that, unlike Core I5, Ryzen 5 supports multi-threading technology. Accordingly, in the future, games should be better optimized for it.
Electronics and technologyComment
conclusions
We've completed our Ryzen vs Intel comparison. Now you have a complete understanding of the differences between AMD Ryzen vs Intel. You also know what advantages each of the chipsets from these manufacturers has. Choosing and purchasing a new system is always associated with certain difficulties. AMD, with its Ryzen architecture, has forced Intel to accelerate the pace of development of new technologies.
The price/performance ratio of AMD processors makes them very attractive. And even more, it seems that AMD has big plans for the future and a lot more can be squeezed out of the AM4 platform.
However, does this mean that Intel is done? Of course not, no one can stop Intel from making its processors even better in the next generation. Which processor would you choose? AMD Ryzen or Intel? Write in the comments!
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Related posts:
No related photos.
Rate this article:
( 13 ratings, average: 4.08 out of 5)
Tweet Pin It
about the author
Posted by
Gavin Phillips
Original:
https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/amd-vs-intel-cpu/
Translator:
admin
Administrator of te4h.ru, interested in new technologies, cryptocurrency, artificial intelligence, free software and Linux.
4 comments
- Evgeniy 07/07/2019 Reply
Hello. Don't think that I'm a supporter of Intel or Amd. I had computers from both companies and more than one! I propose that the computer industry should not be divided into Intel and Amd, but viewed differently. For example, in terms of productivity costs. At the moment I have an old I7 3770k and I started looking for an upgrade. Of course, I began to look towards 8700k and 9900k. Of course these are leaders. But when I started looking at real tests, I realized that a lot of AMD, starting with Ryazan 5, are much faster and more powerful than my processor. So why should I buy a very hot processor from the dead-end line 9900k for crazy money? Having bought it, I will never be able to buy anything with this mother - this is a dead end. Secondly, due to the furious heating of the latter, you will have to buy not the cheapest cooler!! Namely, not cheaper than 7 thousand. Like Noctua. Or dropsy in general for 10 and above. Since cheap ones won't do any good. And then I realized that between 3770k and 9900k, there is a huge niche occupied by processors from AMD. And their AM4 is not a dead end, processors are still being made for it!! And you don’t have to buy expensive coolers (AMD supplies quite good ones). So should I think that Ferraris are better than Ladas, if between these other cars there is a niche with Toyotas, Kia, Renault, BMW and Merc, etc.? Maybe you don’t have to save up for a Ferrari if you can safely and comfortably drive a Toyota or Mitsubishi? and a hundred times cheaper. Are they so much worse that they should not be considered as cars? It's the same with processors. Do I need to buy for 35 rubles per cent + 7 rubles refrigeration = 41+ not cheap mother. Or for 41 I can buy myself an AMD motherboard cooling memory and have some money left over, as well as the opportunity to buy a more expensive motherboard in the future for the same motherboard. (which won’t happen in the case of Intel)? And with all this, the system blows much faster than mine and is much more powerful and overall cheap but cheerful! Therefore, I suggest everyone not to consider globally which is better, Intel or AMD. It's better what's faster than yours and what you can afford. What difference does it make to me that 9900k is faster than 2700x, if the latter costs 17 rubles and the first 35? and the difference in performance varies by 10 or a little more percent? And the mother on 2700x is much cheaper. You just need to think with your head, and not with your feelings, who is cooler than AMD or Intel. Mike Tyson or Kostya Ju. If any little guy from the neighboring yard can hit you. Therefore, everything needs to be considered based on logic and financial capabilities. For example, it is important for me that my new computer is faster and more powerful than the previous one, and for real money and not mystical ones. And whose company it will be, Intel or AMD, it doesn’t matter to me... - Pavel 05/07/2020 Reply
Great comment, totally agree. All my life I have been an ardent supporter of Intel, I don’t know why, probably since the PIII Tualatin, when AMD analogues burned like matches, if God forbid the radiator was slightly warped. But last year Ryzen let Intel screw it up. And so far the price/performance ratio has shifted heavily towards AMD. Now I’m looking for a laptop for 40-50k, now I’m only looking at Ryzen.
- Ivan 05/29/2020 Reply
If you find it, please send me a link or model. I'm also looking for a laptop in this price range.
- Anatoly 06/21/2020 Reply
The author undertook to compare numerical characteristics, numbers and letters, but did not show an understanding of what is better and what is worse.
AMD Ryzen vs Intel Core: which processor is needed for the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti
Almost a month has passed since we were able to get acquainted with the performance of the next flagship gaming accelerator from NVIDIA, GeForce RTX 2080 Ti. Many were eagerly awaiting the announcement of this new product, but it is still impossible to say that all the hopes placed on it were fully justified. The public reacted very ambiguously to the appearance of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti. The main complaint is that with a 30% increase in performance in regular games, which currently do not support ray tracing and anti-aliasing technologies based on deep learning, the price of the new product has increased by almost one and a half times compared to the same indicator of the previous flagship. Moreover, a 30% increase in gaming performance is a rather optimistic estimate, which is valid only if a number of conditions are met: using ultra-high 4K resolution and testing on systems with the fastest processors.
The remark about processors was made here for a reason. It is enough to pay attention to the fact that the vast majority of independent tests of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, in which that same 30% increase in frame rates in games was obtained, was done in systems built on the Intel platform, not AMD. The fact is that the Intel Core microarchitecture is generally better suited for gaming workloads than Zen. It has a higher IPC (instructions executed per clock), allows higher clock speeds, does not create unnecessary delays during inter-core communication, and provides applications with a memory controller with better parameters. Representatives of the Ryzen family are not so progressive in this regard, and confirmation of this is easy to find in any of our tests where their performance in games is measured.
But there is an important nuance: as long as the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti remained the most productive gaming graphics card, a noticeable difference in the gaming performance of the older Ryzen 7 and Core i7 appeared only in cases where testing took place in low resolutions - primarily in Full HD. The transition to 4K screen resolution led to almost complete alignment of the results of AMD and Intel processors. And this is not surprising: the higher resolution in which 3D images are rendered increases the load on the graphics accelerator. Therefore, in 4K we invariably came to the conclusion that even a video card like the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti was not enough to provide high FPS performance - performance was limited by the power of the GPU, and this masked the differences in gaming performance of processors from different manufacturers.
This fact was actively used by AMD, which in all its marketing materials emphasized the approximately equal speed of Ryzen 7 and Core i7 in games when choosing high resolutions, creating the false appearance that processors with Zen microarchitecture could be the optimal choice, including for high-end gaming systems. level.
Advertising illustration from amd.com
However, such marketing tricks could have been pulled off in an era when the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti did not yet exist. Now, whether we like it or not, the world of gaming graphics has irreversibly changed. New NVIDIA graphics cards have higher potential and may well no longer be a bottleneck at high resolutions, exposing the lack of processor performance in poorly balanced configurations. This means that the appearance of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti is quite capable of dealing a blow to AMD’s positions and turning the situation around so that systems based on Ryzen 7 will be inferior to assemblies with Intel Core i7 processors not only in Full HD and 1440p, but even when choosing the saving for AMD in the past 4K resolutions.
Actually, it is for this reason that most reviewers did not dare to test the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti in systems based on Ryzen 7: no one wanted to be in a position where the performance of the video card was constrained by the incorrectly chosen configuration of the base platform. But as a result, an information vacuum has arisen: there is no factual data yet on how seriously the older processors of the Ryzen 7 family limit the performance of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti and whether the new flagship NVIDIA video cards really should be chosen exclusively from the Intel platform.
We have repeatedly warned in our reviews that with the release of a new generation of graphics accelerators, Ryzen 7 processors may not be good enough for top-level gaming configurations. But this time it was decided not to limit ourselves to hypothetical reasoning alone, but to conduct an experiment, the main result of which will be the answer to the question: can a configuration formed from older Ryzen processors and the latest GeForce RTX 2080 Ti video card be considered balanced.
To do this, we measured the gaming performance of systems built on the Core i7-8700K, Core i5-8600K, Ryzen 7 2700X and Ryzen 5 2600X and equipped with flagship NVIDIA video cards of the past and the latest generation in various resolutions. A comparison of the results obtained should give clear indications whether it is advisable to use the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti in Socket AM4 systems in general; what do the positions of AMD and Intel look like in the eternal confrontation after the next jump in GPU performance and can the older Ryzens continue to be a worthy alternative to the older Cores in terms of gaming performance when it comes to using high resolutions.
Along the way, we will be able to evaluate how suitable the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti and current Intel processors are. It’s no secret that in a week (ideally), the shelves will be bursting with eight-core Coffee Lake Refresh processors with once again increased clock speeds. And maybe, if you are planning to build a gaming system with the most powerful video card, it makes sense not to rely on existing proposals, but to gather your willpower and still wait for more powerful CPUs to appear?
Description of test systems and testing methods
In a nutshell, the testing carried out is very simple to describe: four processors - older models in the Core i7, Core i5, Ryzen 7 and Ryzen 5 families; two video cards – older models in the past and current generations of GeForce GTX/RTX; eleven games and three resolutions.
In more detail, the list of components involved in testing was as follows:
- Processors: AMD Ryzen 7 2700X (Pinnacle Ridge, 8 cores + SMT, 3.7-4.3 GHz, 16 MB L3);
- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X (Pinnacle Ridge, 6 cores + SMT, 3.6-4.2 GHz, 16 MB L3);
- Intel Core i7-8700K (Coffee Lake, 6 cores + HT, 3.7-4.7 GHz, 12 MB L3);
- Intel Core i5-8600K (Coffee Lake, 6 cores, 3.6-4.3 GHz, 9 MB L3).
CPU cooler: Noctua NH-U14S.
- ASUS ROG Crosshair VII Hero (Socket AM4, AMD X470);
- NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080 Ti (GP102, 1480/11010 MHz, 11 GB GDDR5X 352-bit);
Testing was performed on the Microsoft Windows 10 Enterprise (v1803) Build 17137.1 operating system using the following set of drivers:
- AMD Chipset Driver 18.10;
- Intel Chipset Driver 10.1.1.45;
- Intel Management Engine Interface Driver 11.7.0.1017;
- NVIDIA GeForce 411.70 Driver.
All processors were tested twice - in nominal mode and at the maximum stable overclocking, which is achievable with the cooling we use:
- Core i7-8700K at 4.9 GHz at 1.3 V;
- Core i5-8600K at 4.8 GHz at 1.3 V;
- Ryzen 7 2700X at 4.1 GHz at 1.425 V;
- Ryzen 5 2600X at 4.1 GHz at 1.425 V.
The following games and settings were used to test the gaming performance of the platforms:
- Ashes of Singularity. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX 12, Quality Profile = Extreme. Resolution 2560 × 1440: DirectX 12, Quality Profile = Extreme. Resolution 3840 × 2160: DirectX 12, Quality Profile = Extreme.
- Assassin's Creed: Origins. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Graphics Quality = Ultra High. Resolution 2560 × 1440: Graphics Quality = Ultra High. Resolution 3840 × 2160: Graphics Quality = Ultra High.
- Battlefield 1. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX 11, Graphics Quality = Ultra. Resolution 2560 × 1440: DirectX 11, Graphics Quality = Ultra. Resolution 3840 × 2160: DirectX 11, Graphics Quality = Ultra.
- Far Cry 5. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Graphics Quality = Ultra, Anti-Aliasing = TAA, Motion Blur = On. Resolution 2560 × 1440: Graphics Quality = Ultra, Anti-Aliasing = TAA, Motion Blur = On. Resolution 3840 × 2160: Graphics Quality = Ultra, Anti-Aliasing = TAA, Motion Blur = On.
- Grand Theft Auto V. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX Version = DirectX 11, FXAA = Off, MSAA = x4, NVIDIA TXAA = Off, Population Density = Maximum, Population Variety = Maximum, Distance Scaling = Maximum, Texture Quality = Very High, Shader Quality = Very High, Shadow Quality = Very High, Reflection Quality = Ultra, Reflection MSAA = x4, Water Quality = Very High, Particles Quality = Very High, Grass Quality = Ultra, Soft Shadow = Softest, Post FX = Ultra, In -Game Depth Of Field Effects = On, Anisotropic Filtering = x16, Ambient Occlusion = High, Tessellation = Very High, Long Shadows = On, High Resolution Shadows = On, High Detail Streaming While Flying = On, Extended Distance Scaling = Maximum, Extended Shadows Distance = Maximum. Resolution 2560 × 1440: DirectX Version = DirectX 11, FXAA = Off, MSAA = x4, NVIDIA TXAA = Off, Population Density = Maximum, Population Variety = Maximum, Distance Scaling = Maximum, Texture Quality = Very High, Shader Quality = Very High , Shadow Quality = Very High, Reflection Quality = Ultra, Reflection MSAA = x4, Water Quality = Very High, Particles Quality = Very High, Grass Quality = Ultra, Soft Shadow = Softest, Post FX = Ultra, In-Game Depth Of Field Effects = On, Anisotropic Filtering = x16, Ambient Occlusion = High, Tessellation = Very High, Long Shadows = On, High Resolution Shadows = On, High Detail Streaming While Flying = On, Extended Distance Scaling = Maximum, Extended Shadows Distance = Maximum. Resolution 3840 × 2160: DirectX Version = DirectX 11, FXAA = Off, MSAA = Off, NVIDIA TXAA = Off, Population Density = Maximum, Population Variety = Maximum, Distance Scaling = Maximum, Texture Quality = Very High, Shader Quality = Very High , Shadow Quality = Very High, Reflection Quality = Ultra, Reflection MSAA = x4, Water Quality = Very High, Particles Quality = Very High, Grass Quality = Ultra, Soft Shadow = Softest, Post FX = Ultra, In-Game Depth Of Field Effects = On, Anisotropic Filtering = x16, Ambient Occlusion = High, Tessellation = Very High, Long Shadows = On, High Resolution Shadows = On, High Detail Streaming While Flying = On, Extended Distance Scaling = Maximum, Extended Shadows Distance = Maximum.
- Hitman. Resolution 1920×1080: DirectX 12, Super Sampling = 1.0, Level of Detail = Ultra, Anti-Aliasing = FXAA, Texture Quality = High, Texture Filter = Anisotropic 16x, SSAO = On, Shadow Maps = Ultra, Shadow Resolution = High. Resolution 2560 × 1440: DirectX 12, Super Sampling = 1.0, Level of Detail = Ultra, Anti-Aliasing = FXAA, Texture Quality = High, Texture Filter = Anisotropic 16x, SSAO = On, Shadow Maps = Ultra, Shadow Resolution = High. Resolution 3840 × 2160: DirectX 12, Super Sampling = 1.0, Level of Detail = Ultra, Anti-Aliasing = Off, Texture Quality = High, Texture Filter = Anisotropic 16x, SSAO = On, Shadow Maps = Ultra, Shadow Resolution = High.
- Kingdom Come: Deliverance. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Overall Image Quality = Ultra High. Resolution 2560 × 1440: Overall Image Quality = Ultra High. Resolution 3840 × 2160: Overall Image Quality = Ultra High.
- Shadow of the Tomb Raider. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX12, Preset = Highest, Anti-Aliasing = SMAAT2x. Resolution 2560 × 1440: DirectX12, Preset = Highest, Anti-Aliasing = SMAAT2x. Resolution 3840 × 2160: DirectX12, Preset = Highest, Anti-Aliasing = TAA.
- The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt. Resolution 1920×1080: Graphics Preset = Ultra, Postprocessing Preset = High. Resolution 2560 × 1440: Graphics Preset = Ultra, Postprocessing Preset = High. Resolution 3840 × 2160: Graphics Preset = Ultra, Postprocessing Preset = High.
- Total War: Warhammer II. Resolution 1920 × 1080: DirectX 12, Quality = Ultra. Resolution 2560 × 1440: DirectX 12, Quality = Ultra. Resolution 3840 × 2160: DirectX 12, Quality = Ultra.
- Watch Dogs 2. Resolution 1920 × 1080: Field of View = 70°, Pixel Density = 1.00, Graphics Quality = Ultra, Extra Details = 100%. Resolution 2560 × 1440: Field of View = 70°, Pixel Density = 1.00, Graphics Quality = Ultra, Extra Details = 100%. Resolution 3840 × 2160: Field of View = 70°, Pixel Density = 1.00, Graphics Quality = Ultra, Extra Details = 100%.
All gaming tests report the average number of frames per second as well as the 0.01-quantile (first percentile) for FPS values. The use of 0.01 quantile instead of minimum FPS indicators is due to the desire to clear the results from random performance spikes that were provoked by reasons not directly related to the operation of the main platform components.
Full HD performance
Let's start right away with a diagram that displays the average frame rate results for the 11 games that were included in testing.
The main conclusion that can be drawn from these results is that processor dependency in Full HD resolution continues to increase. And for the new flagship video card GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, the choice of processor is noticeably more important than in the case of using an older graphics accelerator from the previous generation. For example, if previously the difference in average FPS obtained in systems with Core i7-8700K and Ryzen 7 2700X processors was 14%, then when switching to a new graphics accelerator it increases to 25%. And this is a very significant advantage, which may cast doubt on the advisability of using the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti in the AMD platform.
There is an even more convincing illustration that the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti is too cool a video card even for older Ryzens: in a system with a Ryzen 7 2700X processor, replacing a previous generation video card with a new one does not lead to any noticeable change in the frame rate in games. The difference in average FPS in a system based on Ryzen 7 2700X, obtained with GeForce RTX 2080 Ti and GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, does not exceed 3%. And this means that due to insufficient processor power, there is no point in using the expensive GeForce RTX 2080 Ti together with Ryzen at this resolution: a much cheaper card from the Pascal generation will give almost the same results. Of course, you need to understand that this conclusion applies exclusively to the “light” resolution for the GPU of 1920 × 1080, however, on a system with a Core i7-8700K processor with the same settings, the transition from GeForce GTX 1080 Ti to GeForce RTX 2080 Ti increases the average refresh rate personnel by approximately 13%.
And even if the core of the gaming system is the Core i5-8600K processor, the performance increase when replacing the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti with the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti is 10%, which clearly indicates the weakness of the Zen/Zen+ microarchitecture in gaming-related tasks. In fact, even the Core i5-8600K, which is more likely to belong not to the top, but to the middle level, together with the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, performs significantly better than the older processor for the Socket AM4 platform.
Moreover, this situation cannot be corrected through overclocking. Ryzen processors operate at the maximum clock frequency achievable for them, and there is no noticeable improvement in the situation, even if you try to increase the frequency of the Ryzen 7 2700X to the limit available to them. The best you can get in this case is an increase in FPS by one and a half to two frames per second. At the same time, it is absolutely impossible to call overclocking the Core i7-8700K and Core i5-8600K processors the same useless exercise: here the increase from moderate overclocking reaches 5 frames per second.
You can find out more about what the performance of processors with flagship video cards looks like in specific games from our test set below.
Intel processors provide the maximum advantage in Far Cry 5, The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt and Hitman. In these games, using the LGA1151 platform instead of Socket AM4 can give a gain of 30%. The most noticeable performance scalability when changing the older gaming Pascal to the older Turing is observed in other projects: Watch Dogs 2, Total War: Warhammer 2 and Shadow of the Tomb Raider.
Performance at 1440p
Previously, when testing the gaming performance of processors, we skipped the 2560 × 1440 resolution, but now we decided to pay attention to it, since 1440p monitors are becoming more and more popular among gamers.
At first glance, using the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti in systems based on Ryzen 7 2700X and Ryzen 5 2600X processors connected to 1440p monitors makes some sense. But it's worth considering this. Reviews of the new flagship video card of the Turing generation say that in regular games, the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti is potentially about 30% more powerful than the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti. However, if graphics upgrades are carried out on the Socket AM4 platform, then the real increase in average frame rate will be only about 15%. The rest will be eaten up by insufficient CPU performance.
With the Core i7-8700K and Core i5-8600K processors the situation is better in this regard. If we talk about Intel gaming systems oriented at a resolution of 2560 × 1440, then they will receive a frame rate increase of 22–24% by moving to the most powerful gaming accelerator at the moment.
And in general, at 1440p resolution, Coffee Lake processors demonstrate significantly higher gaming performance compared to Ryzen. If we talk about configurations with a GeForce RTX 2080 Ti video card, then the advantage of the Core i7-8700K or Core i5-8600K over the Ryzen 7 2700X or Ryzen 5 2600X in terms of average FPS is 13%, and in terms of minimum it reaches 15%. At the same time, when the fastest gaming accelerator was the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, the average gap between the Core i7-8700K and the Ryzen 7 2700X was only 6%. This is a perfect illustration of the fact that as faster graphics cards appear on the market, the gaming advantage of assemblies built on older Intel processors is gradually increasing.
Based on the presented results, the same can be said about the representatives of the “medium” Core i5 family: such processors also look very confident and are even ahead of the Ryzen 7 2700X. In such a situation, AMD can only rely on optimizing games for multi-cores in the future, but so far there is nothing indicating that this will actually happen and that it will really help.
More detailed test results at 2560 × 1440 resolution are collected in the diagrams below.
4K Performance
The 3840 × 2160 mode is the most difficult for a graphics card, and we are accustomed to the fact that in it, performance is limited precisely by the capabilities of the GPU, not allowing processors (if we are talking about sufficiently powerful chips) to somehow show their individuality. However, the appearance of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti has made adjustments to this situation. Now processor dependence can be observed when playing in ultra-high resolution. The graph below, for which we calculated the average FPS for 11 games, illustrates this well.
Of course, we are not talking about the same scale of processor dependence as we saw in lower resolutions. However, if when using the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti video card, the advantage of the Core i7-8700K over the Ryzen 7 2700X was only 2%, now, with the advent of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, it has doubled - to 4%. Of course, here it can be argued that in both cases the difference in performance is a few percent, which can hardly be seen with the naked eye. But in fact, if you look not at the average, but at the minimum FPS, then it is no longer possible to talk about the similarity of gaming performance of older mainstream processors from AMD and Intel: according to this indicator, the superiority of the Core i7-8700K over the Ryzen 7 2700X reaches 9%.
In addition, we must not forget that we are talking about an average, which is calculated over 11 games. If we look at the results in individual games (a set of corresponding diagrams is given below), it turns out that the difference in the minimum FPS obtained in a system with a GeForce RTX 2080 Ti on Intel and AMD platforms can reach up to 15%. As striking examples, it is worth highlighting such projects as The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt, Kingdom Come: Deliverance and Ashes of Singularity – Escalation - in them, a noticeable processor dependence appears even when choosing a 4K resolution.
A similar picture is observed with mid-level processors. The Core i5-8600K in a system with a Turing generation video card provides a 4 percent advantage over the Ryzen 5 2600X in average FPS and a 7 percent advantage in the minimum (first percentile). Moreover, this turns out to be more than enough for the Core i5-8600K to outperform not only the Ryzen 5, but also the older Ryzen 7. That is, even when assembling a gaming system aimed at working with a 4K monitor, choosing a Ryzen processor is by no means the optimal solution .
In the introduction to this testing, we said that comparing the gaming performance of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti and GeForce GTX 1080 Ti on a system based on the Ryzen 7 2700X can lead to unexpected conclusions due to the fact that the bottleneck in this configuration will be the CPU. But, apparently, this still applies to 4K resolution to a low degree. So, if upgrading a video card with the transition to a new graphics flagship in a computer with a Core i7-8700K processor improves the frame rate by an average of 33%, then a similar upgrade of the platform based on the Ryzen 7 2700X increases performance by 30%. From all this it naturally follows that in systems focused on gaming in 4K resolution, Ryzen processors, although not optimal, are still applicable. However, if you look into the future and think about subsequent graphics upgrades, there are serious doubts that AMD processors will be able to endure another step in GPU performance relatively painlessly.
In addition, testing results in individual games allow us to see that not all situations fit into the average picture.
If previously the processor dependence in 4K resolution when using top-level chips was negligible, now there are situations where CPU power really noticeably affects the comfort of the gameplay. This means that the selection of configurations with the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti video card must be approached with special care. In future issues of our “Computer of the Month” column, we will voice more specific recommendations on this matter.
conclusions
The release of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti became a landmark event not only for the gaming graphics market. The new video card indirectly affected the balance of power in the processor market. We knew before that the Core i7-8700K is the best processor for gaming systems, but now it has become even more clear. In systems with a GeForce RTX 2080 Ti graphics card, no AMD chips can compete with the older Coffee Lake, and the only thing that can dislodge the Core i7-8700K from the pedestal is the imminent appearance on sale of ninth-generation Core processors, which, on the one hand , will have a large number of computing cores, and on the other hand, will receive increased operating frequencies.
| NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti | ||
| Advantage of Core i7-8700K over Ryzen 7 2700X (average/min. FPS) | Advantage of Core i5-8600K over Ryzen 5 2600X (average/min. FPS) | |
| 1920 × 1080 | 25,2 % / 26,2 % | 22,0 % / 19,1 % |
| 2560 × 1440 | 13,3 % / 15,1 % | 13,4 % / 14,5 % |
| 3840 × 2160 | 4,3 % / 9,3 % | 3,8 % / 7,2 % |
Meanwhile, speaking about the superiority of the Core i7-8700K over representatives of the Ryzen family, we cannot ignore the following fact: the difference greatly depends on what graphics modes and what quality settings we are talking about. The advantage of Intel processors is especially pronounced in Full HD, while an increase in resolution leads to an increase in the role of the GPU and a decrease in the gap in frame rates that platforms from different manufacturers can provide. However, if in the case of the GeForce GTX 1080 Ti video card we came to the conclusion that in 4K resolution the Core i7-8700K and Ryzen 7 2700X processors were approximately equal in performance, with the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti such parity is no longer observed. Even when selecting the highest resolution, the Core i7-8700K-based system definitely performs better, which is clearly visible in the higher minimum frame rate.
We are well aware that everything said above looks like an advertisement for Coffee Lake, but you can’t argue with the facts: if we talk about games, the modern Intel Core microarchitecture is really better suited for them than Zen.
Of course, a more affordable price plays in Ryzen’s favor, especially now when, due to a shortage, the Core i7-8700K has become more expensive and costs significantly more than the recommended values. However, if you have one hundred thousand rubles to buy a graphics accelerator of the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti level, then there is no reason to save several thousand rubles on a processor and choose Ryzen 7 instead of Core i7. Moreover, if you really cannot do without saving, then instead of the Core i7-8700K it is better to choose the Core i5-8600K: even this Intel processor is ahead of the Ryzen 7 2700X in games.
In conclusion, I would like to note the following: in a global sense, today’s entire story suggests that the configuration of an assembly aimed at gaming use must be balanced and the flagship GPU must be matched with a good and fast processor. Saving on a processor can easily result in the graphics card not being able to deliver the performance it is capable of.
However, there is no simple answer to the question of which processor should be considered the optimal choice for the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti. Firstly, the formula for selecting a CPU and GPU must also include a monitor that will set the required resolution (and, as the results show, a lot depends on it). Secondly, in some cases, even the performance that the Core i7-8700K can guarantee is not enough. In particular, in Full HD and even at 1440p, overclocking this processor leads to a noticeable increase in frame rate, and this is a clear sign that at the present stage, higher CPU performance can be demanded by gaming systems without any problems. Therefore, it’s clearly worth waiting for the release of the Core i9-9900K: the best option for top-level gaming builds may not be the Core i7-8700K, but it.
Test results
Assassin's Creed: Origins
This relatively new game takes a lot of CPU load. In combination with an AMD video card, the Intel processor shows the largest gap in FullHD resolution, which gradually decreases and practically disappears when moving to 4K.
The NVidia video card allows you to show higher FPS values, but at low resolutions the difference between the processors is small, and with ultra settings in WQHD the Core i5 unexpectedly “failed” compared to its opponent. True, in 4K he made up for it with interest.
Battlefield 1
In this game, in all exercises and combinations, the results differ little between processors. Moreover, the connection with the NVidia GPU reduces the difference between AMD and Intel almost to the measurement error values.
The situation is similar between video cards. In FullHD, the NVidia graphics processor turns out to be a little faster, but when the load increases, it lets its competitor ahead.
In general, we can say that in Battlefield 1, when choosing an NVidia GeForce GTX 1070 Ti, there is no difference between the CPUs. With an AMD video card, the Intel stone is a little faster.
Destiny 2
A situation similar to what we saw in the last game. In all variants, the difference between the CPUs is within 1-3 FPS in favor of Intel, with a tendency to decrease as the screen resolution and graphics settings increase.
NVidia shows better results, but also with increasing load the gains compared to AMD come to naught.
We can draw the same conclusion, NVidia GeForce GTX 1070 Ti with any processor is preferable.
Far Cry 5
In this game, in all test options, the Intel “stone” turned out to be at least no slower than its opponent. The biggest difference of 10 FPS was recorded at FullHD resolution. Further, the gap decreases, and at 4K the results are generally identical.
Moreover, all this is fully true for video cards. Only in FullHD does NVidia noticeably take the lead. At 4K resolution, the graphics chips demonstrate exactly the same performance.
In this case, we can conclude that for FullHD the Core i5 + NVidia combination is preferable. By the way, the Intel processor, in principle, does not care which video card it works with, because the results in both cases are very close. At WQHD resolution, the difference between the results is at most a couple of FPS.
Forza Motorsport 7
Here we see the superiority, albeit small, of the AMD Radeon RX Vega 56 video card when working with an Intel processor. However, AMD keeps close, and at 4K resolution it generally takes the lead, which is especially noticeable with the NVidia graphics chip.
Choosing an AMD processor with a video card of the same brand seems to be a more balanced option.
Ghost Recon: Wildlands
The game is picky about hardware and happily loads the graphics subsystem at full capacity. This can be seen in the results where, starting from WQHD resolution with ultra settings, the results between video cards are almost identical and hardly change when moving to 4K.
Although the difference between the processors is in favor of Intel, it does not exceed 4 FPS.
At high resolutions NVidia is slightly preferable. Processor - any. At lower resolutions, the Intel/NVidia combination also shows better results. However, AMD is not far away, but this applies to the CPU. The graphics processor from this manufacturer looks a little weaker, but not so much that it cannot be considered if it has a “nice” price.
GTA V
It’s hard to say why the game doesn’t like the AMD processor so much, but the difference between the Ryzen 5 2600X and the Core i5 8600K is impossible not to notice. AMD's smallest loss is at WQHD resolution with ultra settings - only 5 FPS. In other variants, Intel “brings” almost up to 30 additional FPS to its competitor, depending on the game mode.
The worst thing is the combination of AMD CPU and GPU. Replacing the video card with NVidia allows you to gain quite a lot of FPS, especially at high resolutions, but the Core i5 is still confidently ahead.
GTA V requires Intel, and preferably in combination with NVidia. If the choice is still for AMD, then the GPU should be NVidia.
Prey
If the video card is from AMD, then there is no fundamental difference what the CPU will be. Intel is slightly ahead, especially in FullHD, but as the load increases, the difference disappears.
As for the NVidia video card, there is an interesting point. With ultra settings in FullHD, the Ryzen 5 2600X processor does not care which video card it works with, but if the resolution is already higher, the NVidia graphics chip shows noticeably better results. Intel is faster here too, especially in FullHD.
For a screen resolution of 1920x1080, the Intel/NVidia combination is preferable; when moving to higher resolutions, you can prefer any CPU, but leave the same video card.
PlayerUnknown's Battlegrounds
The Core i5 8600K processor is always faster. With an AMD video card, it beats its competitor by 3-7 FPS, depending on graphics settings and resolution. NVidia adds agility to both, but Intel has a stronger lead over its competitor.
Thus, we have that the combination of Core i5 and GTX 1070 Ti is the best option.
The Division
It is difficult to choose a winner, because in all cases, with the exception of the “1440p – medium” mode with an AMD video card, the processors show almost identical results.
Total War: Warhammer
An Intel processor coupled with an AMD video card is ahead only in FullHD mode. As the load increases, Ryzen 5 is at least no worse.
With the NVidia CPU video card, Intel feels much better, ahead of its competitor. For an AMD processor, replacing the video card does not bring significant speedup.
Again, the combination of Core i5 and NVidia allows you to get more pleasant FPS values. Although there is also no need to talk about AMD’s “failure”.
Wolfenstein II: The New Colossus
With AMD Radeon RX Vega 56, it makes absolutely no difference what processor you have, that is, absolutely.
NVidia favors Intel a little more, but not in all modes and not by much. That being said, it's hard to say that the GTX 1070 Ti is superior to the Radeon.
For this game you can use any CPU, and the choice of video card (from those under consideration) does not play a big role.
Test conditions
In addition to processors, two video cards with similar capabilities will also participate in the test: AMD Radeon RX Vega 56 and NVidia GeForce GTX 1070 Ti. Their choice is also determined by the fact that for a CPU of a given level this is the most optimal combination. For something like the GeForce GTX 1080Ti, it is still advisable to have an i7 class processor, no lower, otherwise there may well be situations where the CPU will become a bottleneck in the system.
Test benches:
| Platform | AMD | Intel |
| CPU | Ryzen 5 2600X | Core i5 8600K |
| Motherboard | ASUS Crosshair VII Hero | ASRock Z370 Extreme4 |
| Memory | G.Skill Trident Z 16GB DDR4-3000 @ CL15-15-15-36 | |
| SSD | Samsung 850 Evo 1 TB | |
| power unit | Seasonic Prime Titanium 650W | |
| CPU cooler | NZXT Kraken X62 | |
| External video card | AMD Radeon RX Vega 56 (18.5.1) & Nvidia GeForce GTX 1070 Ti (397.93) | |
All tests will be carried out on 4 different screen resolution and graphics quality settings:
- Full HD (1920×1080) with ultra settings.
- WQHD (2560x1440) at medium settings.
- WQHD (2560×1440) with ultra settings.
- Ultra HD/4K (3840x2160) at medium settings.
Details, specification
Core processor from Intel is a chip assembled on the Coffee Lake architecture.
It offers the user six full-fledged computing (physical) cores, but is distinguished by the lack of Hyper-Threading support.
It is present only in i7 series models. The hero of this review has only three main differences:
- Lack of overclocking support. Yes, dear fans of overclocking and increasing operating frequencies. There is no , at the end of the device name, so it will not be possible to increase the clock frequency of the computing cores limited by the manufacturer - the multiplier is fixed.
Some semblance of increased performance is still possible: the user can manipulate the frequency regulation of the basic BCLK clock generator, which is equipped with modern motherboards. But even here you won’t be able to accelerate much: the protection system is triggered when the nominal frequency increases by 2% from 100 to 102 MHz.
Conclusion: when buying a Core i5-8400, you will not be able to increase its performance in any way; you will get exactly what is stated by the developer.
- The processor is characterized by lower clock speeds, which, compared to the Core i5-8600K and i7-8700K, makes the new product a frivolous purchase. Older six-core processors with numbers of 3.6 and 3.7 GHz with a function to increase it versus 2.8 GHz without the ability to increase the frequency. But you shouldn’t immediately abandon this CPU in favor of analogues. Thanks to support for the second generation Turbo Boost, which is already distinguished by a very aggressive configuration, the actual clock speed during serious workloads automatically rises up to 3.8 GHz.
- The last feature of the device under consideration is its efficiency - the thermal package is limited to only 65 W. However, such environmental friendliness is not always good - due to low power consumption, it will not be possible to achieve maximum turbo frequencies. Those remain largely unfathomable for the Core i5-8400. Well, in nominal mode for sure.
Table 1 – Specification
| Model | Intel Core i5-8400 |
| Socket | Socket LGA1151 |
| Base/clock frequency, GHz | 2,8 / 4,0 |
| Factor | 28 |
| System bus frequency, MHz | 100 |
| Number of cores/threads | 6 / 6 |
| Volume L1, KB | 6 x 32 (data and instruction memory) |
| L2 volume, KB | 6 x 256 |
| L3 volume, MB | 9 |
| Microarchitecture | Intel Coffee Lake |
| Maximum power (TDP), W | 65 |
| Technical process, nm | 14 |
| Critical temperature, °C | 100 |
| Built-in memory controller | |
| Memory type | DDR4 |
| Supported frequency, MHz | 2666 |
| Number of channels | 2 |
| Memory limit, GB | 64 |
| Built-in Intel UHD Graphics 630 | |
| Number of execution units | 24 |
| Base / dynamic frequency, MHz | 350 / 1050 |
| Limit amount of video memory (allocated from RAM), GB | 64 |
| Maximum screen resolution at 60 Hz | 4096 x 2304 |
| Supported technologies and APIs | DirectX 12, OpenGL 4.5, Quick Sync Video, InTru 3D, Clear Video HD and Clear Video |
The official price of the device is more attractive than for similar devices from AMD, but do not forget to take into account one important point:
Coffee Lake is only compatible with motherboards running on the Z370 chipset from Intel, characterized by the presence of an electrically upgraded LGA1151 processor socket.
No other motherboards are suitable for installing new CPUs.
And this means only one thing: having bought, at first glance, an attractive central processor, which, alas, is almost impossible to overclock, at a good price, you will have to fork out for a motherboard with the appropriate connector and technologies.
And this is where the price of upgrading a computer increases.
Instead of the official $182, we’ll pay about 250 for the CPU alone, plus the purchase of a motherboard at a price of no less than $130.
The situation can only change in the winter, when Intel plans to implement the production and supply of simplified and updated LGA1151 chipsets.
Purchasing power is also affected by the availability of new products on the domestic market.
Technical indicators and overclocking potential
The Core i5-8400 is based on a six-core die produced using a 16nm process technology, which is currently the limit that Intel has achieved.
The new technological process, called 14++ nm, by and large, differs only in increased optimization, which affected the heat dissipation of devices and slightly affected their cost.
When running in single-threaded mode and the same load, the performance of Coffee Lake and Kaby Lake is similar.
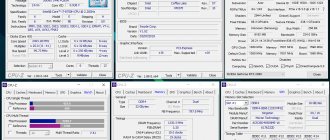
Rice. 4 – Indicators in CPU-Z
The hero of the review has a 65-watt TDP and operates at a base frequency of 2.8 GHz, but when using Intel Turbo Boost version 2, it can theoretically increase up to 4 GHz.
In practice, this figure rarely approaches 3.8 GHz, which is due to low power consumption.
During our acquaintance with the i5-8400, we paid a lot of attention to shaping the operating frequency in Turbo Boost mode.
When it is automatically increased, the central processor must both respond to the number of occupied cores and their level of workload, and ensure that heat dissipation remains within limited limits.
As a result, the declared frequencies for CPU cores (in theory, up to 3.8 GHz) are not something of a target, but only reflect the maximum possible achievable value.
They are selected based on current power consumption, and it can sometimes jump up to 75 W.
In order for the CPU to function while consuming 65 W of electrical energy, its frequencies can be increased to a maximum of 3.5-3.6 GHz, and only briefly jump to the stated 3.8 GHz.
In this mode, with proper cooling (we used the Noctua NH-U14S cooler, because we settled on a sample without it), the temperature does not exceed 57 degrees Celsius.
When a resource-intensive application begins to access AVX, AVX2 or FMA3 instructions, in order to ensure that heat dissipation does not exceed the specified limits, frequencies must drop down to 3.2 GHz (test result in Prime95).
The temperature remains below 60 degrees, which indicates the possibility of installing the CPU in a compact case and using a standard cooling system, which is quite capable of removing thermal energy from the crystal, subject to timely cleaning of the fan blades from dust and replacing thermal paste.
The MultiCore Enhancements function, which is supported by the vast majority of motherboards, allows you to remove restrictions on the maximum permissible electrical energy consumption.
This makes it possible for the processor to operate at full capacity without reducing the frequency under high loads.
Activating it in UEFI made it possible to increase the speed to 4 GHz with a multi-threaded load, which made it possible to pass tests in Prime95 with 128- and 256-bit instructions deactivated.
Temperatures rose to just 61 degrees Celsius, and consumption rose to 95 W, despite the fact that the frequency did not drop below 3.8 GHz, even when the power-intensive instructions listed above were activated.
Rice. 5 – Prime95
Thanks to MultiCore Enhancements, users will still be able to squeeze a little more out of the i5-8400 than specified by the specification, but only if they use a good heat dissipation system and only under high load.
The operating time of the crystal in this mode will naturally decrease. This is needed when encoding video and working with archives.
A tiny number of applications can load the processor to such a limit; games are usually not included in their number.
When solving simple everyday tasks, turning on MultiCore Enhancements does not affect performance at all, including in most entertainment applications.
There are no other options to overclock the Core i5-8400.
By manipulating BCLK, increasing the frequency from the standard 100 MHz to 103 MHz resulted in the system refusing to start, although its increase to 102.5 MHz was successful.
We also were unable to do anything with overclocking the L3 cache: the northbridge operates at a maximum of 3.7 GHz, and it is impossible to influence this value in any way even after changing the multipliers in UEFI.
BIOS and AMD
Historically, AMD released processors and then added to them. This has happened with every Ryzen series and the 3000 series was no exception. There were a lot of problems at the start, but I personally cannot confirm these problems on my board. As I already wrote above, the most important problem is the processor voltage of 1.4V when idle. Many people had this problem with the old BIOS. On the Internet there were a ton of questions about this for AMD, some even called for sabotage: stop putting up with this! Trade in AMD and buy Intel!
It got to the point that an AMD representative on reddit wrote a response on this matter in the form of an article: The final word on idle voltages for 3rd Gen ryzen
My idle voltage is 0.5 - 1.1V, this data is shown by both AIDA 64 and AMD Ryzen Master: