Overclocking a processor (CPU) is an alternative option for increasing the performance of a personal computer (PC). The popularity of this method of increasing productivity is due to the absence of the need to spend any additional funds on it. Theoretically, any processor from any manufacturer can be made to work at least a little faster.
If we describe the operation of the CPU in a very simplified way, we can say that its functioning occurs as follows: when a clock pulse arrives at it, it performs some action (described by the program) and waits for the next clock pulse.
These pulses are generated using a special device - a clock generator. The CPU frequency is the maximum repetition rate of these pulses in the nominal mode of its operation. It is measured in hertz; One hertz is 1 pulse per second. Accordingly, 4.5 GHz is four and a half billion pulses per second.
Of course, with modern CPUs things are a little more complicated. Firstly, there may be several such generators, as well as the frequencies they generate. Secondly, modern CPUs operate at fairly high frequencies, the creation of generators for which is technically quite difficult, so they use the principle of multiplying a certain base frequency by a certain multiplier.
The components of modern PCs (including the CPU) are synchronized with the so-called. system bus frequency (front side bus or FSB). For example, the CPU takes the FSB frequency value as the base one and multiplies it by some value, and its core operates at an increased frequency.
For example, the fourth generation of modern Haswell CPUs have an FSB value of 100 MHz and multipliers from 20 to 35. That is, CPUs of this type operate at frequencies from 2 GHz (100 x 20 = 2000 MHz or 2 GHz) to 3.5 GHz.
Important! In some CPU models, the FSB bus is replaced by the QPI bus (for CPUs from Intel) or the related Hyper Transport (essentially the same thing, but from AMD). Despite the stated differences, the mechanism of the processor remains the same.
There are several ways to overclock the CPU: increasing the multiplier or increasing the FSB speed. Each of them has its own characteristics and limitations.
This article will look at how you can overclock a processor, and how to avoid the possible negative consequences of this phenomenon.
Simple ways to overclock your processor
Modern overclocking has some limitations, primarily related to the complex structure of the CPU. Modern CPUs contain several blocks on their chip, directly connected to the processor (the device that executes the program), which have no relation.
These are cache memory of the second and third levels, a memory access controller and an auxiliary video controller (in some models). All of them are connected to the system bus, so overclocking, if any, applies to them.
Previous generations of CPUs were much simpler in structure and did not contain these elements; they were located in the northbridge chipset and processor acceleration did not have a significant effect on them. All of the above is the reason that overclocking modern CPUs will be relatively small - no more than 10-30% of the existing nominal frequency.
On the computer
The simplest way to speed up a processor is to increase the system bus speed while maintaining the processor multiplier. It can be done by changing the settings in the BIOS, or using special programs. Conventional bus overclocking is the safest and most correct way to increase system performance.
Let's look at how to overclock an Intel Core processor.
The overclocking process includes two components:
- Setting the FSB bus to a higher value.
- Checking the stability of the system at the new frequency.
The first point is implemented using a special program or directly in the computer BIOS settings. And if everything is more or less clear with the programs, because... Their interfaces are quite simple; when working with the BIOS, certain difficulties may arise.
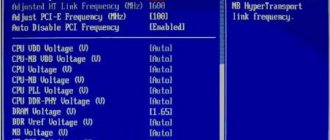
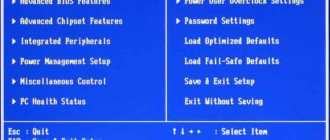
In the BIOS you need to enter the “CPU Settings”, “CPU Frequencies” or “Overclocking” section, where there will definitely be a line with setting the FSB frequency. Usually, it is called FSB Clock. It is recommended to install it slightly higher than the nominal value.
For example, if the FSB is 100 MHz, it is recommended to start testing at 105 MHz. If the stability tests go well, set it to 110 MHz and so on.
After installing the FSB, you should restart your PC and run some kind of PC stability testing program or stress test. As such, you can use the built-in tools of the AIDA program, the S&M program or CPUBurn, etc.
Testing time is about half an hour or more. If no unpleasant events (PC freezing or resetting, blue screen, etc.) occurred during the stress test, then the processor works stably when overclocked. You can leave this operating mode or try increasing the FSB a little more.
On a laptop
Laptops are not a very good field for overclocking experiments, since they are already running almost at the limit of their capabilities. First of all, overclocking laptops is limited by the capabilities of their cooling systems, increasing the efficiency of which is impossible due to size limitations.
In general, working on an overclocked laptop causes a lot of inconvenience, since their cooling systems, operating in this mode at maximum speed, make too much noise. Therefore, in many laptop models, overclocking capabilities are significantly reduced. The exception is products from HP, Lenovo or Asus, and even then, their overclocking functions are significantly limited.
Recently, manufacturers have been using a wide range of processor multipliers in laptops to create the illusion of overclocking. Typically, a laptop runs at the minimum multiplier values, but its performance can be accelerated by forcing it to move to a higher multiplier. How to overclock the processor of a laptop with Windows 10?
To do this, select “High performance” in the power settings. This will immediately set a multiplier that will increase the processor frequency to its maximum value. At the same time, the performance of the laptop will increase, but the noise emitted by its cooling system will also increase.
Is it possible and necessary to overclock the processor on a laptop?
In general, overclocking the processor on a laptop is a risky and unpromising endeavor. It won't be possible to achieve much of a performance boost due to the fixed power supply and limited cooling. This procedure can be carried out on more or less old laptop models, which you don’t mind losing, and you want to squeeze maximum performance out of them. However, in most cases, overclocking results in unstable operation.
Easy CPU overclocking using Windows
Such overclocking, in fact, is not exactly overclocking. This is just a simple optimization of the power system. First, we need to go to “Power and Sleep” in the Control Panel. Depending on the version of Windows, there are different ways to get there. Here you are interested in the “Advanced power settings” item.
You can customize any meal plan you want. It includes power management circuits. By default, there is a balanced option, which, if necessary, increases performance and reduces power consumption when idle. To see all possible schemes, you need to click on the “Show additional schemes” arrow. You need to select high performance from the list. This mode, due to higher power consumption, will use the processor and the system as a whole for maximum performance.
Overclocking the processor via BIOS
There are no particular differences from overclocking via the BIOS of a desktop computer. The technology and methodology are the same. Just keep in mind that the power supply circuits and cooling of the laptop are not designed for increased performance. Therefore, if you increase the bus frequency, you need to do this in very small steps, each time checking the system for stability and paying attention to the temperature. In general, if you decide to do this, you can additionally install a cooling pad with a good cooling coefficient. This will at least to some extent help protect the laptop from overheating.
How to increase processor power through multipliers
Typically, processors have a fairly wide range of frequency multipliers. In this case, the maximum value of the multiplier is not 2-3 units higher than the nominal value for the processor.
For example, a processor with FSB = 100 MHz has multipliers from 20 to 35, while the standard multiplier value is 33, that is, its frequency in normal operation is 100 x 33 = 3300 MHz.
By setting the multiplier value to 34 or 35 in the BIOS or program, you can get an overclocked processor with frequencies of 3400 and 3500 MHz, respectively.
Effective programs for overclocking Intel processors
Overclocking a processor can be accomplished by more than just low-level settings in the preinstallation program.
These programs allow you to change the FSB and multiplier values within the limits allowed for a given processor when working in the operating system, without going into the BIOS settings. Let's consider such programs.
SetFSB
ABO product. Allows you to program clock generators of various motherboards (MB) and set FSB values and memory speeds within the limits allowed by the manufacturer. Allows you to fine-tune the control registers of generators.
Has simple and advanced configuration methods.
CPUFSB
Developed by Podien. It is a lightweight version of the CPUCool program. The program database has a large selection of MP. Allows you to change not only the FSB and memory speed, but also the CPU multiplier. It has a simple and intuitive interface.
SoftFSB
I'm satisfied with the old program with minimal functionality. Practically unsuitable for fine-tuning modern PCs and laptops. It only performs normal FSB control, and not on all MP models.
Programs for overclocking AMD processors
Overclocking an AMD processor is practically no different from this process for Intel chips. In this case, the same programs are used that were discussed earlier. Peculiarities of acceleration of work may concern only the values of frequencies and multipliers.
However, the idea of overclocking remains the same - minor increases in performance while checking the stability of the entire system as a whole in order to find out the maximum frequency value at which stable operation is ensured without significant overheating.
In addition to the listed programs, the overclocking process can be implemented through msi afterburner. This is a universal tool for computer monitoring and fine-tuning, which can not only change many system parameters, but also record the operating modes of individual PC parameters over time. This is one of the best programs for overclocking AMD processors.
In addition, this program is able to control the performance of other computer nodes; in particular, it can also be used to overclock a video card on a computer.
How to increase the core voltage
Often, even when the processor frequency increases by 10% of the rated power, the voltages supplying it are not enough to ensure the stability of its operation. In this case, it is necessary to increase the supply voltage to the CPU.
Attention! The process of fine-tuning the CPU supply voltage is quite complex and can lead to irreversible consequences. It is strictly prohibited to exceed the standard tolerances for increasing the supply voltage by more than 20% of the nominal!
The CPU has several supply voltages. The one that “affects” overclocking is called “core voltage”. In the BIOS and most programs it may be called VCore or CPU Voltage.
In modern PCs, this voltage is relatively small (from 1.2 to 2.2 V) and can vary with fairly high accuracy - up to several hundredths of a volt. This allows fine tuning of the voltages powering the CPU. This can be done in the same programs that were discussed earlier, as well as when changing BIOS settings.
What is the danger of overclocking a CPU with increasing supply voltage and how can we understand that we have reached a critical operating mode?
According to standards for electronic devices, a long-term excess of the supply voltage is allowed by no more than 10% of the nominal one. That is, if the CPU has a supply voltage of 1.4 V, it is allowed to supply 1.4 + 0.14 = 1.54 V to it. Despite the fact that the heat dissipation will increase slightly, this operating mode will not be critical and the CPU will work in it for a very long time without any problems. there were no problems.
But its further increase can already be dangerous, since the dependence of heat release on current (or voltage) is quadratic. This means that an increase, for example, in voltage by 15% will lead to an increase in heat release by 30%; an increase in voltage by 20% leads to an increase in heat generation by 45%, etc.
That is, not only will the semiconductor components of the CPU themselves be exposed to high voltages, but its temperature will also increase significantly, which can lead to its failure.
Important! In overclocked systems with increased CPU voltage, it is very important to monitor the temperature of the device to prevent overheating of the processor.
Typically, the maximum temperature of modern CPUs should not exceed +85°C. If this happens, the chip fails. Therefore, if as a result of the stress test the temperature approaches +80°C, then the test should be completed and overclocking should be removed. Or, you should replace the CPU cooling system with a more advanced one, and repeat the stress test with it.
Determining computer settings
In order to understand how to increase the performance of your PC and which parts need overclocking, you need to test it. This will make it possible to determine how to overclock your computer in a safe way. Overclocking enthusiasts subject the processor and the system as a whole to extreme overclocking. But this requires significant funds, and maximum overclocking is not safe, because there is a high probability of computer components failing.
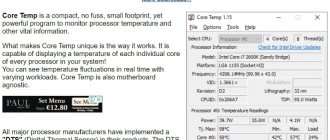
An overall assessment of system performance can be seen even in a special section of the Windows 7 operating system. To obtain more accurate information, special utilities are used. This can be done using SiSoft Sandra, AIDA 64, CPU-Z and others. After testing, you can see detailed information about the installed components and their performance.
From the information received, you can conclude whether it is worth overclocking or whether it is better to purchase new equipment. You can also see in the test results which component does not meet the system requirements of the game. Or get an idea of which device is the bottleneck of the system, the least productive of all.
This weak component should be accelerated first. But all computer components are interconnected, and overclocking will inevitably affect them all. Before overclocking your computer, you should clearly understand that overclocking by 10-30% is safe.
Even if you manage to overclock the processor to 50%, the performance gain will be offset by reduced memory speed or slower devices. The fact is that when overclocking modern processors, you have to raise the system bus frequency, and it, in turn, raises the memory frequency, at which it cannot operate stably. Therefore, we have to lower the memory timings, which are responsible for its performance.
How to disable CPU overclocking
To disable processor overclocking, you simply need to return the system settings to their original, “factory” state. This can be done in the following ways:
- Set the FSB frequency, multiplier, and supply voltage values in the BIOS to automatic detection mode (Options “Auto” or “Default”).
- In advanced BIOS versions, disable overclocking mode. It can be called by different names, for example, "Turbo Mode" or "Overclocking". You can disable it by selecting the “OFF” or “Default” option in its parameters.
- Hardware reset the BIOS or CMOS settings by pressing a special button on the motherboard or short-circuiting a jumper specially designed for this purpose. As a rule, next to it on the substrate there is the inscription “Clear CMOS”.
- Set the nominal frequencies and voltages to the initial position using overclocking programs (CPUFSB, MSI Afterburner, etc.).
- Also, overclocking settings are reset automatically when changing the processor, and in some cases, any system component (for example, memory modules).
You can also read articles on the topics: CPU temperature - programs and CPU load 100 percent windows 10
Computer overclocking control
Of great importance for how to properly overclock a computer is constant monitoring of the parameters of all components related to overclocking. This is achieved through monitoring in the BIOS, as well as using special applications. The most advanced of them provide comprehensive information about the temperature, supply voltage, and fan speed of all system components.
It is not enough to know how to overclock a computer; you also need to determine the stability of its operation under load. Such functions are also available in many programs. To do this, either complex mathematical functions or playing excerpts from computer games are used. The most popular include the following:
- CPU-Z;
- 3DMark;
- AIDA 64;
- PCMark
Many motherboard manufacturers complete their products with appropriate programs for monitoring physical parameters.