Good day everyone! Fedor Lykov is in touch. Today I want to discuss with you a very interesting and pressing question: how to choose a processor for the motherboard.
This question is quite relevant, given that now in the Internet era, more and more people are becoming technically literate in the computer field due to the growing number of tech bloggers on YouTube. Now the system unit no longer seems like some kind of incomprehensible device, but on the contrary, it is already familiar and understandable to a large number of people.
If earlier people preferred to contact computer technicians with questions about assembling or upgrading a computer, now the level of knowledge of ordinary users has increased. Add to this also free access to the Internet, where you can find a lot of information on a wide variety of computer topics.
That is why today we will try to figure out how to correctly select such an important computer component. Enjoy reading!
What types of processors are there?
To choose a fully compatible motherboard for the processor, let's figure out what types of processors there are and how they differ.
Two popular processor manufacturers: Intel and AMD
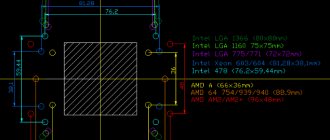
First of all, all popular processors for home computers are produced by two large companies - Intel and AMD. Which manufacturer is better to choose for your computer is the topic of a whole separate article. Let's just say that Intel and AMD processors are physically very different. AMD processors have so-called “legs”. They are inserted into the motherboard. For Intel processors, these same “legs” are located on the motherboard, which makes transporting the processors more convenient. There is only one conclusion - the motherboards for these processors are fundamentally different. Moreover, processors from the same manufacturer can also differ greatly.
Processors have different sockets
Socket
How do you know which processor can be installed in your motherboard? For this purpose, the concept of a socket was introduced. A socket is a connector or space for a processor on the motherboard. When choosing a motherboard, first of all, you need to pay attention to it. After all, a processor that has a different socket from the motherboard cannot be installed correctly in it. A simple example will help you understand this better. There is no way to insert a Euro plug into a regular Soviet socket. Same with processors. Therefore, the socket of the processor and motherboard must match.
The processor socket and motherboard must match
Fortunately, it is very easy to find out the processor or MP socket. This is basic, very important information that is necessarily written in the technical specifications of the computer component you are purchasing. You can find technical specifications in the place where you are going to buy the processor or motherboard, or on the websites of their manufacturer.
Power
First of all, processors differ in power. They may have a different number of cores, which will operate at different frequencies, have different cache sizes, and many other different parameters. Fortunately, power does not affect compatibility in any way. For example, the INTEL Core i3 7100 processor has an LGA 1151 socket. The INTEL Core i7 7700 processor has exactly the same socket, which is several times more powerful than i3 and costs much more. You can easily install this processor on a computer with a Core i3, and you don’t even have to change the motherboard, since the processor socket is identical.
Processors have different power
Important! There are processors with video footage built into them. This function allows you not to use a discrete video card in your computer. This way you will save quite a lot of money. This solution is often used in inexpensive office computers. For modern games, computers without a discrete video card are practically unsuitable. If you decide to choose a processor with video, then make sure that the selected motherboard will have the necessary outputs for the monitor. As a rule, if the processor and motherboard socket are the same, then such outputs will be present.
Case types and sizes
Computer cases are divided into horizontal (Desktop) and vertical (Tower). But both of them can have different sizes.
6.1. Horizontal enclosures
Horizontal cases were previously used mainly in offices to save space and monitors were installed directly on them.
Now such cases can be found in some supermarkets, but they are mainly used for assembling multimedia centers that can be located in a TV stand.
Horizontal enclosures have the following types:
- Slim-Desktop - thin body
- Full-Desktop - standard case
6.2. Vertical enclosures
To assemble modern computers, mostly vertical cases are used. Usually they are installed on a special stand or simply on the floor.
Vertical enclosures have the following types:
- Micro-Tower - miniature case
- Mini-Tower - low case of an outdated format
- Midi-Tower - the most common format
- Full-Tower - a large case for gaming computers
- Super-Tower - a very large case for powerful computers and servers
For office and home computers, it is better to use the most versatile Midi-Tower cases. For powerful gaming computers that install large video cards and coolers, it is advisable to use more spacious Midi-Tower or Full-Tower cases. The placement of components and ventilation are better organized in them.
Motherboards and their differences
Motherboards with different processor sockets
Motherboards also have a socket that must match the processor socket. Otherwise, you will not be able to insert the processor into the motherboard.
Important! Never try to insert a processor into a motherboard socket that is not intended for this purpose. In any case, this will end badly and may lead to damage to computer components.
On some motherboards, you will not be able to install a processor and work with it normally, even if the sockets are fully compatible. The point here is the power supply of the processor. Inexpensive motherboards are sometimes unable to provide adequate power to a powerful and power-hungry processor. Owners of AMD FX-9370 encountered this problem.
A motherboard has such a thing as a chipset. This is a chip unit that is responsible for the operation of all other components. You need to make sure that the chipset supports your processor model. Usually, this will not be a problem, but there may be exceptions.
The chip unit, which is responsible for the operation of all other components, must support the processor model
power unit
A power supply is already supplied with some case models, however, if you need this particular case, but with a higher power supply, then the power supply can be purchased separately. In general, ideally it is better to take a case without a power supply and buy a power supply separately. In this way, you can manually calculate how much power the power supply is needed to operate all components of the system. In order to calculate which power supply is needed, you need to add up the power consumption that each component of the system requires, and add about 15-25%, so to speak, for reserve. Thus, you can get the approximate power of the power supply that will be needed for “ food”
» the entire system.
How to find out if the processor is compatible with the motherboard
Considering all the nuances, you need to know for sure whether a specific processor will work with a specific motherboard. This is possible and quite simple to do. To do this you need:
- Find out the make and model of your motherboard. It can be printed on the board itself; you can also recognize it on the box, receipt or instructions.
The motherboard model is printed on the board itself, you can also find it on the box
- Go to the manufacturer's official website and find the motherboard you need there. Find the CPU support section on the manufacturer's website. In this section you can find a list of processors that work exactly with this motherboard. Select from this list a processor that suits your price and characteristics. That's it, now you can be sure that the processor will work correctly with the motherboard.
On the manufacturer’s website we find a list of processors that work exactly with this motherboard.
Housing materials
For the frame, a stamped profile (angle) made of galvanized or stainless steel with a thickness of 0.8–1.2 millimeters is used. The edges of the frame must be rolled, sometimes connected by additional partitions (stiffeners). Thick metal better dampens noise and vibrations of operating mechanisms. For maintenance, a removable panel for the motherboard is convenient, but more often (to reduce vibrations) the motherboard is mounted on separate stands with strong screws with a hexagonal head (up to 10–12 screws).
The best materials for walls are copper and aluminum, which have good thermal conductivity. But copper is too expensive, and thin aluminum sheet is easily deformed. Therefore, in most office and household computer cases, the side walls, top and bottom are made of steel sheet with a thickness of 0.6–0.8 mm. One or two removable side walls are attached to the frame in various ways.
Another way to find out the compatibility of the processor and RAM
If all of the above is too complicated for you, then you can use another, much simpler method. The Internet is teeming with ready-made computer builds. You can find one of the assemblies that suit your price and repeat it. As a rule, such assemblies will work stably for more than one year. On the Internet you can find configurators where you can find ready-made, working computers with fully compatible components.
Assembling a computer with compatible components
Front Panel
The front panel is most often made of plastic; it can be supplemented with a metal mesh for air intake. As a standard, the front panel of an ATX office computer contains power, shutdown, and reset buttons, audio jacks for a microphone and headphones, several USB outputs, and other connectors.
The tower case of XL-ATX, EATX standards on the front panel can be supplemented with several outputs (for USB 2.0, 3.0), displays, fan speed controls, and backlit buttons. The compartment with numerous connectors and a display is usually closed with a hinged door so that an accidental touch does not disrupt the settings.
This configuration is redundant for novice users; it is used for professional setup of computer equipment. But the backlit buttons are convenient for use in the darkness common to gaming modes. To illuminate and decorate the front panel, LED strips are also used, which case manufacturers offer as an additional option.
Separate connectors for external card readers are rarely placed on the front panel, since they can be connected via the USB 2.0 input. One of the 3.5-inch slots is used to install an internal card reader.
Input connectors and buttons can be located on the top or bottom of the front panel. This factor must be taken into account when choosing a location for installing the system unit in an apartment or office. For floor placement, the top location of the buttons is convenient. For desktop installations, the connectors should be located at the bottom of the case so that you don't have to stand up to connect external devices.
Compatibility of RAM and motherboard
In addition to the compatibility of the processor and motherboard, it is worth paying close attention to the RAM. The motherboard and RAM must also be compatible. Be sure to know the type of RAM you are going to purchase. It can be DDR2, DDR3 or DDR4. The mother's memory must support this type of memory. Otherwise, the RAM will not physically fit into the slot on the motherboard. You will have to purchase a new die that already matches this board.
Additionally, RAM has a frequency at which it operates. For the memory to work properly, the motherboard must support this frequency.
You can find out the type and frequency of RAM on the manufacturer’s website or store.
We find out the type and frequency of RAM on the manufacturer’s website
Case manufacturers
The price difference between the market leaders in popularity and new case manufacturers is constantly decreasing. Expensive computer equipment stores prefer to enter into supply contracts and offer for sale cases from the Cooler Master, Chieftec, NZXT, and Thermaltake brands. But they are successfully competed by the brands Zalman, Corsair, BitFenix, which are not inferior to the sales leaders in the quality and quantity of case models.
It’s not worth buying a case from a little-known manufacturer, despite the favorable price. Sometimes identical cases of the same brand are sold with a large difference in price. If you find a “Made in China” sign on the Cooler Master case, you shouldn’t be afraid. Using cheap labor, many American and European computer manufacturers have built factories in China that use the designers' blueprints and proprietary stamping and assembly technologies. The quality of such cases is not inferior to those assembled in Europe.
List of well-known case manufacturers:
- 3Cott
- 3Q
- ACCORD
- AeroCool
- Antec
- ASUS
- be quiet!
- Chenbro
- Chieftec
- Codegen SuperPower
- Cooler Master
- Corsair
- COUGAR
- CROWN MICRO
- Deepcool
- Delux
- Enermax
- EVGA
- ExeGate
- Formula
- FOX
- Foxconn
- Foxline
- Fractal Design
- GAMDIAS
- GameMax
- Genesis
- GIGABYTE
- Ginzzu
- GMC
- HAFF
- IN WIN
- Intel
- Invenom
- J.N.C.
- Lian Li
- LinkWorld
- Morex
- MSI
- Navan
- NZXT
- Phanteks
- PowerCool
- Powerman
- Riotoro
- SilverStone
- SunPro
- Supermicro
- Thermaltake
- Velton
- Winard
- Zalman
Online prices for enclosures are generally lower. When purchasing, you can compare prices from several sellers. With this approach, the difference in the cost of a large case for a gaming computer may turn out to be, albeit small, pleasant. The sale of cases is accompanied by a manufacturer’s warranty, usually from 18 to 24 months. Warranties cannot be considered an indicator of quality or an important selection factor. In comfortable conditions, without humidity and sudden temperature changes, all enclosures can be successfully used for up to 10 years. And the development of computer technology forces us to change system units more frequently.
Not all novice computer scientists can assemble a system unit on their own. For beginners, it is more convenient to buy a case at a computer store. If you tell the manager your requirements: computer performance, motherboard form factor, power supply power, number of coolers, video card model, then he will offer you several options for cases that will fit the ordered equipment.
Compatibility of motherboard and video card
Users who want to update their system are interested in the issue of compatibility between the motherboard and video card. After all, a video card is the most important element of a computer, especially a gaming one. If you want to install a new, more powerful video card on your computer, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Find out if your motherboard has a PCIe x16 slot. This can be done simply by opening the cover of the system unit or on the manufacturer’s website. If this connector is missing, then you will not be able to install a new powerful video card. If everything is in order and it is present, then proceed to the next step.
PCIe x16 connector on motherboard
- Next you need to find out the PCIe x16 version. The fact is that this connector has several versions. If your motherboard has PCIe x16 3.0, then feel free to install any, even powerful, video card there. It should also have PCIe x16 Gen 3. A motherboard that does not have PCIe x16 3.0 does not support high-power cards. If you install a PCIe x16 3.0 video card in such a slot, you will lose half of its power. This update doesn't make sense.
We can find out information about the PCIe x16 connector on the motherboard on the manufacturer’s website
Read detailed information in the new article - “How to find out the components of your computer.”
Housing design
Structurally, the body consists of:
- racks on which most components are mounted;
- frame with suspended platforms;
- removable side walls (provide access to the inside of the PC for maintenance and repair);
- rear wall (exhaust fan deflectors, ports for connecting to a monitor and keyboard are located on it);
- front panel with power and reset buttons, regulators, slots and connectors for external storage media, a device for using disks.
Additional space inside the case may be required to install a processor with a radiator and its own fan, additional hard drives, and video cards.
The general classification of types of enclosures (including closed, open, bench) is not important for practical choice. Open and bench system units are used in PC development and testing. For office, household, and gaming computers, all manufacturers primarily use closed system units.