Default number of running cores in Windows 10
Each individual core may have a different load, which is associated with changes in PC load. BIOS settings allow you to set a separate operating frequency for the cores. When the load on the PC is evenly distributed, the user will receive high performance.
If we talk about a dual-core processor, then only in one case will only one core be used - when loading the computer. On the other hand, there is always the option to activate all resources to speed up the boot process (on the other hand, booting Windows is not the most CPU-intensive process, and you will benefit a lot more if you just put your Windows 10 on an SSD).
What does the number of processor cores affect?
Many people confuse the concept of number of cores and processor frequency. If we compare this with a person, then the brain is a processor, neurons are nuclei. Cores do not work in all games and applications. If, for example, a game runs 2 processes, one draws a forest and the other a city, and the game is multi-core, then you only need 2 cores to load this picture. And if the game has more processes, then all cores are used.
And it may be the other way around: a game or application can be written in such a way that only one core can perform one action, and in this situation the processor with the higher frequency and the most well-built architecture will win (this is why Intel processors usually win slightly over Amd).
Therefore, roughly speaking, the number of processor cores affects performance and speed.
Ways to enable processor cores on Windows 10
To activate all cores of a quad-core (example) processor when turning on the PC, you can use:
- Reconfiguring the system.
- BIOS settings.
The instructions below are suitable for both 32- and 64-bit OS editions of Windows 10:
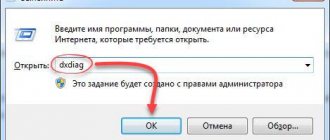
- Open the Run menu by pressing the Windows key + R. Type msconfig and press Enter to open the System Configuration window.
- Go to the “Boot” tab, select the desired OS and click on the “Advanced boot options” function.
- Select the “Number of processors” line and select the maximum available number of cores from the expanded list.
- In addition, you should increase the “Maximum Memory” and disable the “PCI Blocking” option. In this case, the OS will distribute the load evenly across all cores. Confirm the settings by clicking on OK.
_
Note : In the “Maximum Memory” settings, you need to select any numerical value not lower than 1024 MB. Otherwise, the computer's boot speed may even decrease.
To avoid having to perform these steps every time, in the previous “System Configuration” window, check the “Make these boot options permanent” checkbox. Confirm the actions with “Apply” and OK.
Windows won't boot after changing msconfig
You decided to speed up your computer and changed the settings in “msconfig” (system configuration). After which, your computer stopped booting. If this is the case, then this note will help you solve the problem.
A lot has been written on the Internet that you can speed up your computer by specifying the amount of RAM and the number of processors in the “msconfig” system configuration, but, unfortunately, not everything is so simple.
Very often, such changes lead to computer malfunctions. More precisely, the computer simply stops loading the operating system.
From my experience, I can say that even if the operating system boots, it is unlikely that your computer will run faster. Usually the operating system itself perfectly determines the number of cores and RAM, so I do not recommend changing these values.
But you most likely have already changed something, which is why you came to this page. Read on, below I have given a solution to this problem.
People often write to me about this problem, so I decided to make a video about how you can solve the startup problem that occurs after such settings.
The bottom line is that if the operating system has stopped loading, then the processor and RAM parameters must be returned to their original state (default). The question arises: how to do this?
The command line will help us solve this problem, in which we need to enter the following commands:
1) “bcdedit /deletevalue numproc” (without quotes), press “Enter”
2) “bcdedit /deletevalue truncatememory” (without quotes), press “Enter”
You may ask: how to get to the command line with a non-working operating system?
I answer. Using the boot menu, which is called up by pressing and holding the “F8” key when you turn on the computer, or using an installation disk with the operating system.
Look in more detail at the video, I told and showed everything there.
The method works, I checked it.
A new video on this topic has been added to the channel. If the first method doesn't work, try this one:
Processor settings in BIOS
You only need to change BIOS settings if the PC simply won’t boot. There is no need to use this method if you do not have any basic knowledge of working in the BIOS. It is better to use the previous instructions.
To activate all cores of a multi-core processor through the BIOS, follow these steps:
- Enter the BIOS menu (restart the computer and on the initial screen with information about the motherboard, press F3, Del or Esc - depends on the manufacturer). Typically this screen will have information indicating the keys you need to press.
- In the BIOS, find the Advanced Clock Calibration section and select the All Cores options.
- Save all settings by pressing F10 and Y (or use the BIOS prompts).
Activation of cores
There are several built-in ways to change the number of cores that are activated during Windows startup. No matter which one you use, the result will be the same, so choose the one that suits you best.
By changing the system configuration
Windows has a built-in program that allows you to configure system operation and recovery settings:
- Press the Win + R combination on your keyboard to open the Run window.
Write the word msconfig in the window that opens and run the request. Execute the msconfig request
Gone are the days when a multi-core processor was considered something out of the ordinary, and the owners of such computers could be counted on one hand. Today, even the most shabby, budget laptop has at least a couple of cores in the processor. What does this mean in practice? The fact that the work performed almost continuously by a computing device can now be transferred to the shoulders of two or more workers.
Even the most insignificant user actions give rise to a huge sequence of processor instructions. If some of them can be performed on one core, and some on another, then the overall performance of the computer will increase dramatically. Windows potentially supports all available cores, but in practice this option usually needs to be activated first. Read below to learn how to enable all processor capabilities on a computer running Windows 7.
Like any other modern OS, Windows positions itself as a multitasking system. Before the era of multi-core processors, multitasking was something of a convention. From the user's point of view, it looked like several processes were actually running on the computer screen at once. In fact, the system simply distributed time between windows, alternately making one task or another active. Even two cores in the system turn multitasking from fiction into reality.
Standard Windows 10 tools
- Hover your mouse over the Start button in the lower left corner of the screen, right-click and select Settings.
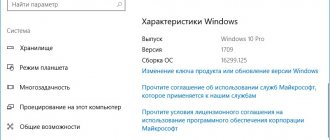
- Go to the "System" category.
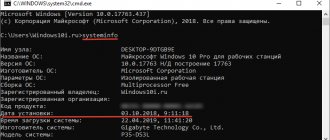
- Open the subcategory “About the system”. A page with information will appear, which will also indicate the names and frequencies of each of the cores.
To find more detailed information about all devices, you need to open the “Device Manager” (DEVMGMT.MSC).
Expand the “Processors” branch and examine the graphs (for a quad-core processor there should be four, etc.). Hover over any line, right-click and select the “Properties” option. Here you will find all the necessary information about the processor.
How to run all processor cores?
So, there will be several ways. That's why I'm showing the first one .
Go to start - run or win + r keys
Next, in the window that opens, go to downloads - additional options.
Select your maximum number of processors.
By the way, you can find out the number of processor cores. But these are virtual cores, not physical ones. There may be fewer physical ones.
Click OK and reboot.
Next is method 2.
- Go to the task manager - ctrl+shift+esc.
- Or ctrl+alt+del and task manager.
- Or right-click on the control panel and select task manager.
Go to the processes tab. Find the game and right-click on the process. By the way, the game must be running. You can collapse it either Win+D or alt+tab.
Select set match.
Select all and click ok.
To see whether all cores are working or not, go to the performance tab in the task manager.
There will be a diagram in all tabs.
If not, then click again to set the correspondence, leave only CPU 0, click ok. Close the task manager, open it again, repeat everything, the same thing, select all processors and click ok.
More!
In laptops, power saving is sometimes configured in such a way that the settings do not allow all cores to be used.
- Win7 - Go to the control panel, go to power options - Change plan settings - change additional power settings - processor power management - minimum processor state.
- Win8, 10 - Or: Settings - System - Power and Sleep - Advanced Power Settings - Configure Power Plan - Change Advanced Power Settings - Processor Power Management - Minimum Processor Status
For full use, it should be 100%.