Open the command line using special. teams
The easiest way to open a command prompt in Windows is to use the Run . To open it, press the combination consisting of the Win + R (where it is located, how to press).
In the window that appears, enter “cmd” (without quotes) and click OK .
Done, the command prompt window is open.
It is worth noting that the command line launched in this way has the same rights in the system as other programs. However, if you intend to change some system parameter by entering the corresponding command into the command line, then in this case it is recommended to run it as an administrator. Otherwise, the entered command will most likely not work properly due to insufficient access rights.
Read on to learn how to open a command prompt with administrator rights.
Basic Commands
- Dir – view the contents of the directory. Command format : dir [drive_name:][directories][file_name] [parameter]
If you run the command without parameters, the contents of the current folder will be displayed. You can use a template with the characters ? as a file name. And *. Symbol ? replaces one letter or number in the name, * – several. Some commonly used options :
Authentication - what is it?
/ A – output files with certain attributes;
/ P – after filling the screen with information, there is a pause;
/ O – sorting information.
As an example , display information about the drive C: dir C:\
Here's how you can see what's stored in temp: dir C:\ temp
- Chdir (short for cd) – changes the current directory. General view : chdir [/D] [drive_name:] [directories]
/D parameter is indicated if you need to change the current drive and directory.
For example , to make the docum folder on drive C current, you need to type: chdir C:\ docum
Here's how to go to the root directory: chdir \
- Mkdir (or md) – creates a new folder. General view : mkdir [disk_name:] folder
Example : mkdir C:\newcat
- Rmdir (or rd) – deleting a folder.
General view: Rmdir [keys] [drive_name:] folders
The /S switch allows you to delete the entire contents of a folder.
- Cls simply clears the screen.
- Edit – launches a text editor, used in Windows XP and older versions. This program allows you to edit text documents using a fairly large set of tools - copy+paste, search, replace.
- Del (analogue - erase ) is used for deletion. Format : del [keys] [drive_name:][directories] file_name
As a name, you can use a pattern with the characters ? And * . For example, you can use / P (confirm the deletion of each file) and / Q (cancel the confirmation request) as keys.
- Rename (or ren ) renames. It is used in general form : rename [drive_name:][directories] file_name_1 file_name_2
Example : rename primer.txt primer2.txt
- Move – moving files and folders. Format for moving files : move [/Y | /-Y] [drive_name:][ directories] file_name_1[,...] new_location
/Y option allows you to replace existing files without confirmation.
/-Y – includes mandatory overwrite confirmation.
The format for moving folders is similar. Example: Move c:\temp\cat1 c:\temp\cat2
- Copy is used for copying. General view : copy [parameter] file_name_1 [+file_name_2 [+...]] resulting_files
All ways to register in ICQ from a computer or phone
Some options: /Y replaces existing files without confirmation;
/-Y – includes mandatory rewrite confirmation;
/ V – checks for correct copying.
You can create small files using copy. Run the command copy con f.txt (copying the console to f.txt), type the text, press Ctrl+Z and Enter.
- Xcopy is a more advanced version of the previous command; it allows you to copy files and folders while maintaining the structure. General view : xcopy source_files [resulting_files] [keys]
Some keys: / S – copy only non-empty folders;
/ E – copying contents, including empty folders;
/ H – copy hidden and system files.
Windows Command Prompt: List of Basic Commands
Review the table that lists the commands used in the Windows Command Prompt. If I missed any important command, write about it in the comment to this article, I am adding the command to the table.
| Team | Action to be performed |
| appwiz.cpl | launching a system tool to change or remove programs |
| arp | display and change ARP tables for converting IP addresses to physical ones used by the Address Resolution Protocol |
| assoc | displaying or changing mappings based on filename extensions |
| at | launch programs at specified times |
| attrib | display and change file attributes |
| azman.msc | authorization manager |
| bcdboot | Boot Configuration Data File Creation and Recovery Tool |
| bcdedit | editing changes to the system's boot database |
| break | changing the processing mode of the key combination “Ctrl” + “C” |
| blastcln | worm cleaning utility |
| bootcfg | setting, retrieving, changing, or removing command line options in the Boot.ini file in Windows XP |
| call | calling one batch file from another |
| cacls | viewing and editing changing access control tables (ACLs) to files |
| calc | launching the Calculator application |
| CD | displaying the name or changing the current folder |
| charmap | symbol table |
| chcp | displaying or changing the active code page |
| chdir | display or change the current folder |
| copy | copying one or more files |
| chkdsk | checking the disk for errors and displaying statistics |
| chkntfs | display or change disk check options during boot |
| ciddaemon | file indexing service |
| cipher | encryption of files and folders in NTFS |
| cleanmgr | Disk Cleanup utility |
| cls | clearing the screen |
| cmd | launching another Windows command line interpreter |
| compmgmt.msc | opening the Computer Management console |
| color | setting default foreground and background colors |
| comexp.msc | component services |
| comp | comparing the contents of two files or two sets of files |
| compact | viewing and changing file compression settings on NTFS partitions |
| compmgmt.msc | Computer management |
| computerdefaults | selecting default apps |
| control | Control Panel |
| control admintools | administration |
| control desktop | screen customization and personalization |
| control folder | folder properties in Explorer options |
| control fonts | fonts |
| control keyboard | opening the keyboard properties window |
| control mouse | mouse properties |
| control printer | devices and printers |
| control scheduled tasks | Task Scheduler |
| control userpasswords2 | user account management |
| convert | converting the volume file system from FAT to NTFS (does not work on the current disk) |
| copy | copying files to another location |
| credwiz | archiving and recovery of usernames and passwords |
| date | display or set the current date |
| debug | program debugging and editing tool |
| defrag | start disk defragmentation |
| del | deleting one or more files |
| desk.cpl | setting screen resolution |
| devicepairingwizard | adding a new device |
| devmgmt.ms | device Manager |
| dfrgui | disk optimization (defragmentation) |
| dir | display a list of files and subfolders from a specified folder |
| diskmgmt.ms | opening the Disk Management snap-in |
| diskpart | displaying and setting disk partition properties |
| diskperf | enable or disable the performance counter |
| dokey | editing the command line, re-invoking Windows commands, creating macros |
| dpiscaling | adjusting display settings |
| dxdiag | DirectX Diagnostic Tool |
| echo | displaying messages and switching the mode of displaying commands on the screen |
| endlocal | completing local environment changes for a batch file |
| erase | deleting one or more files (overwriting) |
| esentutl | Microsoft Windows database maintenance utilities |
| eudcedit | personal sign editor |
| eventcreate | creates a special event entry in the specified event log |
| eventvwr.msc | event viewer |
| expand | unpacking compressed files |
| explorer | Windows Explorer |
| fc | comparing files or sets of files, displaying differences between them |
| find | search for a text string in one or more files |
| findstr | searching for a text string in a file |
| finger | information about users of the specified system running the Finger service |
| firewall.cpl | Windows Defender Firewall |
| for | running the specified command for each file in the set |
| format | disk formatting |
| fsmgmt.msc | shared folders |
| fsquirt | transfer files via Bluetooth |
| fsutil | showing and setting file system properties |
| ftype | output or change file types when matching filenames |
| ftp | file sharing via FTP |
| goto | passing control to the specified line of the batch file |
| getmac | displaying MAC addresses of one or more network adapters |
| gpresult | Group Policy information for a computer or user |
| graftabl | display extended character set in Windows graphical mode |
| gpedit.msc | Local Group Policy Editor |
| gpupdate | updating multiple group policy settings |
| hdwwiz | hardware installation wizard |
| icacls | display, change, archive, restore ACLs for files and directories |
| iexpress | creating a self-extracting archive |
| if | conditional processing in batch programs (files) |
| ipconfig | IP address information |
| joy.cpl | gaming devices |
| label | creating, changing and deleting volume labels for disks |
| lodctr | updating registry settings related to counter performance |
| logman | Manage the Alerts and Performance Logs service |
| logoff | end session |
| lpksetup | installing or removing Windows interface languages |
| lusrmgr.msc | local users and groups |
| magnify | launching the Magnifier application |
| main.cpl | mouse properties |
| makecab | archiving files into CAB archive |
| md | creating a directory (folder) |
| mdsched | RAM error checking tool |
| mkdir | create a directory (folder) |
| mmsys.cpl | properties of sound |
| mode | configuration of system devices |
| mofcomp | 32-bit compiler |
| more | sequential data output in parts the size of one screen |
| mountvol | creating, viewing and deleting connection points |
| move | moving one or more files from one folder to another |
| mrinfo | working with multicast messages |
| mrt | launching the Malicious Software Removal Tool |
| msconfig | system configuration |
| msg | sending messages to the user |
| msinfo32 | system information |
| mspaint | launching the Paint graphic editor |
| msra | Windows Remote Assistance |
| net | network resource management |
| ncpa.cpl | network connections |
| netstat | displaying protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections |
| netplwiz | user account management |
| notepad | launching Notepad |
| odbcconf | ODBC driver setup |
| openfiles | displaying a list of open files and folders open in the system |
| optional features | turn Windows features on or off |
| osk | launch on-screen keyboard |
| path | output or set search path for executable files |
| pause | pause batch file execution, display message |
| perfmon | system monitor |
| resmon | resource monitor |
| popd | restoring the previous value of the current folder saved by the pushd command |
| prompt | changing the Windows command line |
| pushd | saving the current directory and then changing the directory |
| ping | sending packages to the specified address |
| powercfg | managing system power parameters |
| printing a text file | |
| qprocess | displaying information about processes |
| qwinsta | display information about Remote Desktop Services sessions |
| rd | deleting a directory |
| recover | recovery of saved data on a damaged disk |
| recdisc | creating a Windows recovery disc |
| reg | command for working with the registry |
| regedit | Registry Editor |
| rem | placing a comment in a batch file or in the config.sys file |
| ren | renaming files and folders |
| rename | renaming files and folders |
| rmdir | deleting a directory |
| replace | replacing files |
| rstrui | restoring Windows from system restore points |
| runas | to use applications on behalf of another user |
| rwinsta | resetting the values of equipment subsystems and session programs to their initial state |
| secpol.msc | local security policy |
| services.msc | services |
| set | displaying, setting and removing Windows environment variables |
| setlocal | starting local environment changes in a batch file |
| sc | displaying and configuring services (background processes) |
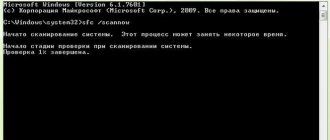
| sfc | checking the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect ones |
| sigverif | file signature verification |
| shift | changing the contents of overridden parameters for a batch file |
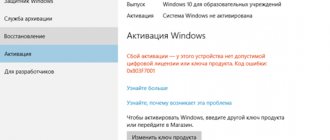
| slui | Windows activation |
| sndvol | volume mixer |
| start | run the specified program or command in a separate window |
| schtasks | launching programs and executing commands on a PC according to a schedule |
| sdbinst | compatibility database installer |
| shutdown | restarting or shutting down the computer |
| sort | sorting program |
| subst | mapping the drive name to the specified path |
| sysdm.cpl | properties of the system |
| systeminfo | operating system configuration information |
| taskkill | force termination of a process or application |
| tasklist | showing all currently running tasks, including services |
| taskmgr | Task Manager |
| tcmsetup | installing a telephony client |
| time | viewing and changing the current time |
| timedate.cpl | setting time and date |
| title | assigning the title of the current command line interpreter window |
| tracert | trace the route to a specified node |
| tree | graphical display of the structure of a given disk or folder |
| tscon | attaching a user session to a remote desktop session |
| tsdiscon | disconnecting a Remote Desktop Services session |
| tskill | termination of the process |
| type | output text file contents |
| typeperf | display performance information on screen or in a log |
| utilman | accessibility center |
| ver | displaying Windows version information |
| verifier | Driver Verifier Manager |
| verify | setting Windows to check whether files are written to disk correctly |
| vol | displaying the volume label and serial number for the disk |
| vssadmin | command line program for administering Volume Shadow Copy Service |
| w32tm | show current settings for time zone display |
| winver | Windows version information on screen |
| wmic | information about WMI in the interactive shell |
| write | WordPad text editor |
| wscui.cpl | security and service center |
| wusa | offline update installer |
| xcopy | copying files and folder trees |
How to open the command line via Run
The CMD launch method using the special “Run” utility is perhaps the most frequently mentioned on the Internet. This method allows you to open the command line on a computer with any version of Windows: from the beloved XP to the flagship of the line - Windows 10.
You can (and should) open the command line via “Run” by performing the following sequence of actions:
- Launch the Run utility by pressing the Windows key combination (the "windows" button in the lower left corner of the keyboard) and R.
- In the empty field of the window that appears, write cmd.
- Click "OK".
The result of these operations will be an open console. In my opinion, this method of initializing CMD is not a priority, since it includes an unnecessary action - launching the “Run” utility.
Popular network command line commands
From the Windows command line, you can interact with network connections, change their settings, view various information, and much more. Let's look at the most popular network commands.
ping command
This is probably the most popular command among Windows OS users (as well as other operating systems). It is designed to check the availability and quality of communication between the computer and the target IP address. The command can also be used to determine the IP address of a site by the site’s domain name and to perform other tasks.
Let's determine if there is a connection with any IP address. Let it be - 173.194.73.139 (Google search engine IP address). Enter the following command:
ping 173.194.73.139
As you can see, packets are exchanged with the specified IP address, which means there is a connection. If it were not there, the picture would be as follows (let’s remove the last digit from Google’s IP):
“100% loss” means that the connection could not be established.
Now let’s determine the site’s IP address by its domain name. Let's take the address softsalad.ru:
ping softsalad. ru
In the image above you can see the site's IP address determined by its domain name.
tracert command
And this command is used to track the network route from the computer to the target IP address (you can also use the domain name of the site):
tracert softsalad. ru
You see, in order to “reach” the site, the computer in this case needed to contact 12 intermediate IP addresses (your provider, site server, etc.).
ipconfig command
Using this command, you can obtain information about the computer’s IP protocol settings (or, roughly speaking, network card settings). Let's use this command with the / all , which will allow us to display more detailed information:
ipconfig /all
getmac command
If you only need to determine the MAC address of the network card, use this command without any attributes:
getmac
How to open the command line via Start
Using the built-in search in the Start menu can be used not only to access the Command Prompt, but also to launch any other utilities and applications installed on the computer.
To launch the console in Windows 7, open the Start menu by clicking on the corresponding icon in the corner of the screen, find the search bar and start typing “command prompt” or “cmd”. After this, the system will search and display the access shortcut on the screen. Click on it to access the command line.
You can also run the console with administrative rights. To open Command Prompt as an administrator, right-click on the shortcut and select the appropriate item in the context menu.
A significant difference between this method of launching the console in the case of Windows 8/8.1 or Windows 10 is the fact that there is no search bar (or rather, its explicit presence) in the Start menu. However, CMD can still be loaded by opening Start and just starting typing!
You can also initiate a search using the button next to “Start”.
How to install a console shortcut on the desktop?
To quickly launch it, it is recommended to create an icon for this tool on the Windows 7 desktop. To do this, you need to do the following:
- Open the “My Computer” window and enter the system volume “C”;
- Then find and open the directory called “Windows”;
- Next, go to the “System32” directory (for example, if 32-bit “Seven” is installed);
- Call the context menu on the “cmd.exe” file;
- Click on the line “Create a shortcut”;
- Then drag it to the desktop, simply by grabbing it with the mouse;
- Ready!
You can also do this by calling the context menu from the desktop and going to the “create” line and then clicking “Shortcut”.
After that, in the menu that appears, type: “C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe” and click “Next”. Give a name to the shortcut you are creating and click “Done.”
Via "Start"
The algorithm of actions consists of the following points:
- Click the “Start” button on the taskbar or simply click the “Win” key;
- Next, type “cmd” in the search box;
- In the list that appears, find “cmd.exe” and double-click to launch it.
You can also go to the Start menu, go to All Programs, and in the Accessories section, click Command Prompt.
How to call the command line in Windows 7?
The time comes and a PC user is faced with a situation when it is vital to execute various commands in the Windows system. To perform such manipulations, the good old command line is used, otherwise it is also called the console. Well, let's take a closer look at what this thing is.
The command line (console) is a utility that provides the user with access to the operating system by entering commands. As a rule, the command line is used by advanced users, but we hope that thanks to this article, a novice user will be able to easily set the desired command and at the same time save time. The console is a black dialog box with a continuously blinking cursor, and these commands are actually written into it.
And now, from talking directly, let’s get down to business and find where the command line in Windows 7 is hidden and how to get to it.
There are many options for calling the command line, let's focus on the main ones.
Using the Run dialog box.
- We go to the well-known “Start”;
- "All programs";
- Go to the “Standard” folder;
- We look for the line “Run” in the list;
- And in the window that opens, enter cmd;
- Press “Enter” and the command line will open to our eyes.
Note: It is much easier to open the Run window using the Windows + R shortcut.
Through the main menu of the "Start" button.
- We start the journey with the “Start” button;
- Next, open “All Programs”;
- Find the “Standard” folder;
- And in it we look for “Command Line”.
Also, after activating the menu through “Start”, you can enter the phrase “command line” in the search bar, which will lead to the appearance of a shortcut, activate it by clicking the mouse and see “Command Prompt”.
Using the folder's context menu.
- On any folder, press “Shift” and the right mouse button at the same time;
- You will be presented with a list where you need to find the line “Open command window”;
- The “Command Prompt” will open, where you will be lucky enough to see the previously selected folder.
The Command Prompt utility is located in the Windows folder.
To find it there you need to go through this simple path: Drive “C”, then go to the “Windows” folder, in it go to “System32”, and in it we find a file called “cmd.exe”. By running it we will open the command line.
Sometimes, to perform certain actions, the system will ask you to open a command prompt with administrator rights, to do this, in the second option described above, use the right functional mouse button, and click on the “Command Prompt” entry, from the list that appears, select “Run as administrator” "