Previously, the site’s pages described the process of installing Linux next to Windows using the Ubuntu distribution as an example. In this article, we will look at the reverse process, which sooner or later those users who are not to their liking for Linux will have to resort to. How to remove Linux installed on the same Windows computer? How to get the Windows bootloader back?
To completely get rid of Linux, you need to restore the Windows boot loader, delete Linux files and resolve the issue of the future fate of the disk space that was allocated for installing this operating system (swap partition and partition with Linux files itself). Below we will look at 3 ways to remove Linux and return the Windows bootloader. Two of them are methods for computers based on a regular BIOS; they will differ in the tools used. The third method is to remove the Linux boot loader from the boot list of computers with UEFI BIOS. All operations described below are carried out inside Windows.
Bootice Utility and Windows Disk Management
For the first method of uninstalling Linux and restoring the Windows bootloader, you will need two utilities - the third-party free Bootice and the standard diskmgmt.msc (disk management).
1.1. Recovering the Windows bootloader using Bootice
First of all, download the Bootice utility from its official website. For computers based on a regular BIOS, the 32- or 64-bit edition of the utility does not matter. After unpacking Bootice, launch it. On the first tab, select the desired hard drive from the drop-down list if there are several of them connected. And click the “Process MBR” button.
In the window that appears, for Windows 7, 8.1 and 10, select the “Windows NT 6.x MBR” option. In the case of Windows XP, you need to select the option above - “Windows NT 5.x MBR”. Next, click the “Install / Config” button.
We confirm.
Windows boot loader has been restored.
1.2. Removing Linux partitions in Windows Disk Management
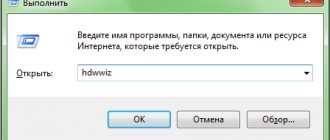
After restoring the Windows bootloader, we go to the standard disk management utility. Press the Win+R keys and enter its name:
diskmgmt.msc
In the utility window, we delete two Linux partitions - specially prepared before installing it manually or automatically created by this system. In the latter case, as a rule, the Linux partitions on the hard drive are located immediately behind the Windows system partition. Without understanding the Linux file system, the Windows operating system does not assign letters to its partitions, and, accordingly, they cannot be displayed in Explorer. But in any case, it is better to focus on both these signs and the sizes of Linux partitions. To delete Linux partitions on each of them, you need to call the context menu and select “Delete Volume”.
The freed disk space can then be organized here, in the disk management utility, into a partition or several partitions acceptable for Windows (in the NTFS file system format). You can read more about creating simple partitions using standard Windows tools in this site article.
Linux Mint
How to uninstall Linux Mint? You can turn off segments using the Fdisk program. Remove the Linux native, swap, and boot partition segments. Boot the device from a floppy disk. Type fdisk at the command line. Press the Enter button. To get information about segments, enter “p” at the command line and press Enter. At the top there is information about the main partition of the hard drive. Type “d” at the command line. Press the Enter button. A window will appear in which you need to specify the number of the partition to be removed.
AOMEI Partition Assistant
An alternative way to get rid of Linux and return the Windows boot loader for users of computers based on a regular BIOS can be offered by the functional program for working with disk space AOMEI Partition Assistant. All the tools necessary for these purposes are available in the free Standard Edition of the program. In the AOMEI Partition Assistant window on the side toolbar, in the “Disk Operations” block, select “MBR Recovery”.
In the window that appears, from the drop-down list, select the type of bootloader for the corresponding versions of Windows.
The program will warn you that after the planned operation, Linux will stop loading. Click “Yes”.
Then we apply the operation with the green button at the top of the “Apply” window.
We go through a couple of stages to confirm our intentions.
That's it, the operation is applied.
Next, in the AOMEI Partition Assistant window, we define the Linux partitions and, using the context menu called up on these partitions, delete them.
We confirm the deletion of each section.
And we arrange the freed space into a partition (or partitions) with a file system understandable for Windows. In the context menu on the unallocated space, select “Create partition”.
If only part of the space is allocated for a partition, indicate the required size. Click "Ok".
We apply planned operations.
How to remove Linux if your computer has only one operating system
Some users are wondering how to remove Linux and install Windows 10 if only one operating system is installed on the PC. You can completely remove the only operating system on a desktop computer or laptop as follows:
- Connect to the PC an external drive with a recorded image of the operating system that the user wants to install. Force shutdown the computer by booting from an external drive.
- In the next step, the user will need to delete the Linux OS partition. As soon as the process of installing the new operating system begins, a window with the corresponding sections will appear on the screen. From the available ones, you need to select the partition with Ubuntu/Linux and delete it.
- Continue installing the OS. After deleting the partition in the previous step, Ubuntu will completely disappear from your laptop or desktop computer. Now you can start installing the new OS.
Installing the full version of the Windows 10 operating system after uninstalling Linux OS
Note! If you do not install a new operating system on your computer, you will not be able to use the device.
Removing Linux bootloader from BIOS UEFI boot queue
To remove the Linux boot loader on computers with UEFI BIOS, we will use the Bootice utility mentioned in paragraph 1 of the article. But in this case, you need to download its 64-bit edition. This includes a special “UEFI” tab. Go to this tab, click the “Edit boot entries” button.
On the left, select the Linux bootloader, in this case Ubuntu. And press the “Del” button at the bottom.
The bootloader has been removed from the UEFI boot queue.
Operations for deleting Linux partitions and creating new partitions with a file system understandable for Windows can be carried out using any of the methods described above - in paragraphs. 1.2 and 2 articles.
Reuse the free space you have
Now you have a lot more free space. But to use it again, you will need to partition the hard drive and format it.
If you are not familiar with these processes, simply launch Disk Management as described above. Select free space, right-click and select New Volume ...the one that suits your needs.
Another way is to right-click on the volume next to the free space, select Expand Volume to increase the size of the partition. This video may help:
So, the free space is now returned to Windows and can be assigned a new letter. Moreover, no matter what you are going to store there: personal data, games, videos or anything else. Everything is back to normal!
Still need to boot Linux from time to time? Why not install Linux inside Windows using the Windows Subsystem for Linux Programs in the Microsoft Store? Or take a look at how to disable the UEFI Secure Boot Protocol for a dual boot system.
Bootloader recovery
After this, the computer must be restarted, but Windows will not start. The bootloader was removed along with Linux. This is not an error, but just a consequence of installing Linux in a Windows environment. During installation, it is clear that there is a second system, so uninstalling Linux also removes the bootloader. And now you need to install it using the Windows installation disk. We connect the disk on which the distribution is stored. Go to the “System Restore” section, where you need to select “Command Prompt”. To restore the bootloader, you need to enter two commands:
- To create a boot entry bootrec /fixmbr
- To write the boot sector to the system partition bootrec /fixboot
After each command you must press the Enter key. The bootloader will now be restored and the system will start. If you install a new version of Linux, you will need to follow the same steps.
There are several ways to remove the system. The simplest is to install a new one on top of the old system. If you need to remove Linux in a Windows environment, then you need to delete the partitions that belong to Linux in disk management and redistribute the free space on Windows.
Uninstalling Linux and reinstalling Windows
It's not just Windows, even if most users think so. Linux distributions are also becoming increasingly popular, including a build called Ubuntu.
The secret of success lies in the free distribution of Linux programs and builds. Therefore, if you buy a computer with the OS preinstalled on a non-commercial basis, you will pay much less than for a Windows equivalent.
But not all users are eager to switch to Linux, and there are both opponents of such an upgrade and its supporters.
Briefly about Ubuntu. How to uninstall Ubuntu
The functionality of this assembly is sufficient to browse online sites, read mail, edit documents and perform other standard tasks. All this has long been common practice for users.
Despite seemingly the same capabilities as Windows, many do not want to rebuild and leave the familiar interface from Microsoft. Everyone is used to working in their native environment, but everyone has their own.
Therefore, when you want to work with DOS systems or install another build of Linux (not Ubuntu), sometimes you have to figure out how to remove Ubuntu from your computer.
I think that it would be natural for you and me to learn about this.
Uninstall Ubuntu. What is necessary:
- You need to boot into a working system.
- Then archive all the most important data. It is advisable to make a backup copy to a separate media or partition that will not be affected during the Ubuntu removal process .
- In a Linux environment, load the terminal and enter the following command: sudo gedit /boot/grub/grub.cfg. This will open the boot loader configuration file.
- Edit the file so that the Ubuntu-related entries are removed.
- Open the Windows Recovery Console. To remove the Ubuntu program ,
you should return Windows boot (if you are going to work in this environment) to default. - Entering the commands to start with fixmbr, then fixboot will help you with this. These tools will restore the master boot record and boot loader to default.
- As a result, after restarting the PC, Windows will be loaded as the operating system to start.
- can be started using the installation CD of the original copy of this operating system.
- And then the question of how to remove Ubuntu is theoretically resolved. In fact, the working copy of this distribution has not disappeared anywhere. She remained where she was before. We simply changed the bootloader and rewrote the MBR ,
the main boot code on the hard drive.
To uninstall a Linux distribution - Ubuntu —
It is enough to format the partition on which this system is installed. Formatting can be done in fat32, or better and more reliably in ntfs.
As a result, the Linux data section will be empty, and you can copy your personal information to it. You will also be able to install one of the versions of Windows, but only if the main logical partition was formatted. Unlike Linux systems, which can be installed on any type of partition.
Re-partitioning the hard drive
The same CD with the Windows distribution will help you do it. Start it as your primary boot device.
Before uninstalling Ubuntu, the installation wizard will load the necessary files into memory. You will then be prompted to install Windows on the system partition, create one if you don’t have one, or format an existing one. To re-partition, use the last option.
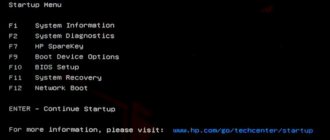
Setting the boot order of devices in the BIOS
Enter the Bios setup utility using a preset key or key combination (contained in the instructions for the motherboard). Find the boot device or order boot list or boot priority item.
Using the +/- or F5/F6 keys, set the first device in the list that contains the abbreviation CD-DVD. Insert the CD into the appropriate drive.
Save your settings. This is usually done via F10 or by selecting save personal setting or something similar. Restart your PC.
Let's try to figure out how to uninstall Ubuntu. Beginner users, faced with a new operating system interface, are lost, since it is much less widespread than Microsoft developments.
↑ Setting up laptop BIOS to boot from USB
If you simply insert a flash drive into a USB port, then most likely, when you reboot, your laptop or computer will simply ignore it. In order to boot from the flash drive we made, you need to make the appropriate settings in the BIOS of your PC.
To get into the BIOS on my new ASER laptop, immediately after turning it on, before booting, you need to periodically press the F2 key. On other gadgets, this may be another F-key or Del.
In the BIOS, go to the BOOT section. All movements are carried out using the function keys, which are indicated on the same page.
- The first thing you need to do there is to disable the UEFI mode in the first line of Boot Mode, i.e. replace it with LEGACI.
- The next step is to set the priority in boot devices. In other words, you need to make sure that your USB drive is number one.
After you have done all this, you need to press F10 and agree with the saves and exit the BIOS. Everything is ready to install Windows 10.
How to install Linux instead of Windows?
If you decide to completely remove Windows and install a free operating system on your computer instead, you need to know how to install Linux instead of Windows.
Ubuntu is considered one of the most famous versions of Linux. It does not place high demands on computer performance and can be installed from any suitable media - DVD, USB drive, etc., provided that loading from this drive is supported by the computer BIOS.
The simplest option is to install Linux from a disk. To do this, just download the required distribution and burn it to disk. If you have Windows 8 installed, you should use a 64-bit distribution. For earlier versions, you can limit yourself to 32-bit. Next, you need to burn the ISO file to disk using a third-party program or using Windows tools. The BIOS is set to boot from disk. In some models of computers and laptops, manipulations with the BIOS are not necessary; before loading the operating system, just press the F8 key on the keyboard and go to the boot menu.
Further installation proceeds as follows:
- Boot from disk. The Linux Ubuntu installer may offer to try the system without installing it on your computer. You can boot from the disk and test Linux without installing it. After this, you need to open the installation file located on your desktop.
- Check free disk space. Installation will require about 5 gigabytes.
- If necessary, check the option to automatically download updates and install third-party programs. Third-party programs include, for example, a flash player for watching videos on YouTube.
- If necessary, configure the wireless connection. If there is none, you can skip the point.
- The next step is choosing an installation option. You can keep the old operating system or remove it. When saving, you will have to choose where to go each time you load. This saves all Windows files and settings. If you refuse to save, all your old files, settings and programs will be deleted.
- Selecting a logical drive for installation. If you decide to install Linux Mint on Windows, you just need to use the slider to mark out the free space for the new system. It should be taken into account that the system itself will take up about 5 gigabytes, and some space will also be needed for additional files and programs. After setting the necessary parameters, you need to click on the “Installnow” button.
- The next stage is choosing a location. If you have an Internet connection, the search will be carried out automatically. Here you need to select your time zone.
- Selecting a keyboard layout. It is selected manually from the list or determined automatically by the system.
- Enter personal information: login, password, computer name if it is connected to the local network. Here you can select the Linux startup type. It can run automatically, or require you to enter a password each time.
- After this, the process of copying files and settings begins. During this process, screensavers with tips on using Linux will be displayed. After installation, you can reboot your computer and use the new operating system.
In a similar way, you can install Linux instead of Windows 7 and other similar systems.
Video on how to install Linux instead of Windows 7
How to install Linux next to Windows?
If you already have Windows 7 or an earlier version installed on your computer, you can use the built-in Windows Setup Wizard when installing Linux.
The eighth version does not support this installation method; in this case, you can install the system from disk.
This method will allow you to install Linux next to Windows and use both systems without restrictions.
- Download the installation file from the official Ubuntu website and run it.
- Select the parameters of the future system: user login and password, volume that will be available to Linux, language. Here you can choose your desktop environment according to your habits and preferences. For example, the KDE interface visually resembles standard Windows, while the Gnome interface is similar to MacOS.
- Start installation. The program will download the required files to the computer. The entire process occurs automatically. The installation time depends primarily on the Internet speed. While the installation program downloads the files, you can use the computer for your own purposes.
- Reboot your computer. You can do this immediately after installation or after some time. When you reboot, you will see a menu asking you to choose which operating system to start.
To install Linux using this method, you must have a high-speed and uninterrupted Internet connection. Otherwise, you risk wasting several hours.
How to install Windows instead of Linux?
Some users are interested in how to remove Linux and install Windows. One reason is that some laptops and computers come with Linux pre-installed.
First of all, you need to prepare two installation disks - Linux and Windows. You will need both during the installation process.
Reinstallation occurs in several stages:
- Set the BIOS to install from a suitable medium and insert a disk or flash drive with a Linux distribution. Preferably the same modification that is installed on the computer.
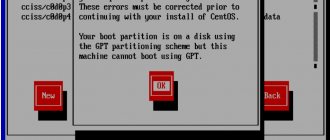
- Boot from disk. When the installer prompts you to select a disk to install, delete the existing EXT4 partition and format it to NTFS. This will remove the operating system, all settings and files.
- Reboot, replace the installation disk and start installing Windows. The installation process depends on which version of Windows you are going to use. You will be required to indicate your user login and password, the name of the machine with which it will be displayed on the local network, and your preferred language. The whole process can take up to half an hour. After automatic installation, you can reboot and start Windows.
Video on how to install Windows instead of Linux
Before installing Windows on Linux on a laptop, you need to connect the machine to the network.
Installing an operating system is a fairly energy-intensive process, and the battery can run out in a few minutes without additional charging.
Useful tips for installing Linux and Windows
It is not necessary to use original versions of Linux. You can install one of the unofficial versions, for example, Linux Mint or Fluxbuntu. These are modified versions with non-standard design and functionality.
Before reinstalling, you should make copies of all important documents. This will avoid unexpected data loss.
Many programs in Linux come pre-installed. However, you will have to install some yourself, for example, players for Flash videos and music files. Most additional applications can be found in the software store, located in applications.
Some experts recommend keeping two systems on your computer. Linux does not support all peripheral devices; modern graphics editors and games may not load here. Windows is considered less resistant to network threats, viruses, etc. The problem of running applications on Linux is solved by using a special Wine emulator. The problem with viruses on Windows can be partly solved by installing a modern antivirus with constant updates.
Have you already tried to install Windows on Linux or vice versa? What difficulties have you encountered? Tell us about it in the comments.