The purpose for which users create a bootable DOS flash drive is to restore the functionality of computer equipment running operating systems of the Windows family. Detecting and correcting errors is much easier, at a low DOS level, before loading the system files of the main operating system. To do this, you need to make changes in the BIOS, specify specific hardware in the “boot loader” section.
- 3.1 Advice for owners of popular versions
In what cases do you need to create a bootable DOS flash drive yourself?
The question may seem strange to most users. Why return to ancient methods, transfer DOS to a flash drive at the current level of development of information technology? Its presence will help the owner:
- safely reflash the BIOS;
- fix damaged configuration files;
- update system drivers;
- gain access to all files.
IMPORTANT. For diagnosing, troubleshooting and testing workstation hardware, a DOS bootable flash drive is extremely useful. The proof is the “MemTest86+” RAM testing utility built in, without fail, by Microsoft to identify errors.
In addition, a bootable MS DOS flash drive will help you recover any operating system that has failed for various reasons. In most situations, she remains the only “savior” from suddenly arising troubles. History once again proves that a bootable flash drive and DOS have not lost their relevance.
Booting from a flash drive with DOS operating system
First you need to set the BIOS to boot from a flash drive. How this is done is shown in detail in the manuals:, and. Everything is described there in detail.
Boot from a flash drive. If you did everything correctly, DOS should start:
To start the file manager, enter the command boot\dn\vc.com
:
In the same way, you can run any other application from a flash drive or hard drive. You can also perform various manipulations with files there.
That's all. Thank you for your attention.
You can make all comments and suggestions regarding the article itself through this contact form: Please note that if something doesn’t work out for you, then you should only ask. These types of emails will be ignored.
Sometimes you need to run a program from the command line. This could be flashing the BIOS, or some other task.
For these purposes, it is best to use a bootable USB flash drive with DOS. In this case, having a working operating system is not necessary.
How to create such a flash drive will be discussed in this guide.
Multitasking options
System administrators prefer to create bootable DOS flash drives, which eliminate conflicts on many platforms (Windows and Linux). Utilities, file manager, anti-virus programs, and other applications are copied to the connected external media.
Before making a bootable DOS flash drive, the set of software necessary for installation and a wide range of tasks is determined.
A universal bootable USB flash drive running MS DOS can work wonders when working with FAT32, NTFS, UEFI.
A flash drive running MS DOS is a must for every PC owner
Step-by-step instruction
To create an image of a bootable flash drive in DOS format, it is recommended to download the Easy2Boot (E2B) archive.
- Unzip to any directory on your PC.
- Run the file called _ISO\docs\Make_E2B_USB_Drive.cmd.
- To burn a Live-CD image, specify the path by selecting the disk from the list.
- Answer the question about the options for the proposed media formatting.
When transferring MS DOS to a flash drive, several problems arise:
- FAT32 works well with UEFI and supports files no larger than 4 GB;
- NTFS without UEFI has no restrictions;
- for images up to 4 GB, you can safely create a bootable USB flash drive in FAT32.
In order for NTFS to be able to interact with UEFI under MS DOS, creating a bootable flash drive is similar to the previous description. But in the BIOS you need to select a UEFI image so that Easy2Boot changes the entry of the first boot sector on the MBR disk (this is true provided that the bootia32.efi, bootx64.efi configuration files are available).
Creating a bootable USB flash drive ms dos: explaining from all sides
The purpose for which users create a bootable DOS flash drive is to restore the functionality of computer equipment running operating systems of the Windows family. Detecting and correcting errors is much easier, at a low DOS level, before loading the system files of the main operating system. To do this, you need to make changes in the BIOS, specify specific hardware in the “boot loader” section.
Recommendations on how to make a bootable one for legacy Windows
The described method is suitable when you need to install MS DOS on a flash drive to work with Windows version no older than version 7. Otherwise, the risk of irretrievable data loss is inevitable.
It will not be possible to create a bootable card or USB drive using standard Windows tools unless you additionally download usb_and_dos.zip.
Insert the drive into the connector, then unpack the archive and click hp_usb_tool.exe.
After starting the program, specify FAT. Before creating an MS DOS bootable USB flash drive, use the corresponding checkbox to indicate the path to extract the files.
After installation is complete, restart your computer. Enter the “BOOT” section of the BIOS, change the disk priority by moving the USB-HDD to the top line.
Advice for owners of popular versions
To restore Windows 7, 8, 10, you need modern programs launched by a privileged user as root.
There are several ways to create an MS DOS bootable USB flash drive for popular operating systems. One of them is the reliable software Boot_USB_Sergei_Strelec_2015_v.8.0_x86.
The assembly includes Acronis Disk Director for disk partitioning and Acronis True Image for recording a finished image and backing up the system. All utilities have an intuitive interface. Any user can understand them.
To start a Live CD, you need to change the “boot loader” priorities.
Creating a bootable USB flash drive
First you need to download the archive with the necessary files from these links: /
Run the downloaded file:
We indicate where the archive should be unpacked and click Extract
:
Go to the folder USB-Flash-www.site
and run the file
hp_usb_tool.exe
:
We insert the flash drive, copy all the information from it to the laptop’s hard drive or to another flash drive
During the preparation of the bootable flash drive, all information from it will be deleted
Launch the HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool
:
At the top in the Device
indicate the drive on which your flash drive is located.
Check the box next to Create a DOS startup Disk
, check
using DOS system files located at
and indicate the path to the DOS folder in the folder where you unpacked the archive.
In the File System
, specify
FAT32
.
We start the process by clicking Start
.
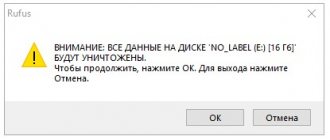
The utility will issue a warning that all information on the flash drive will be deleted. Click Yes
:
We wait until formatting is completed:
At the end of the process, the following window will appear:
We insert them onto your flash drive:
If everything is done correctly, then the bootable flash drive should have the following files:
You can also copy files and programs that you will run from DOS to a flash drive.
Without removing the flash drive, reboot the laptop, press F2 to enter the BIOS. We look in the BIOS where the boot order is indicated (sometimes this section is called Boot options
). Using the F5 and F6 buttons, we ensure that your flash drive is at the very top, that is, loading starts from the flash drive, and not from the hard drive or DVD drive.
Let's reboot. Volkov Commander file manager should launch
.
Now you can run the necessary programs for flashing the BIOS, restoring the MBR and for other tasks.
Edited by: FuzzyL
— March 4, 2011 Reason: Update of materials
The update program, together with the latest firmware, takes 1 156 258
byte.
And the BIOS itself does not have the ability to self-update. On the motherboard developer's website it is written that to update the BIOS you need to boot from a Windows 95
or
Windows 98
... Jokers...
To make everything completely clear, three files from DOS (COMMAND .COM, IO.SYS, MSDOS .SYS) take up space 316 400
bytes on a floppy disk with a capacity of
1,457,664
bytes.
It turns out that all this equipment simply cannot fit on one floppy disk! Of course, it was possible to make a DOS floppy disk with support for a CD drive... But, as it turned out, the BIOS firmware program for this motherboard does not work if the additional (extended memory) and HMA memory driver for the MS-DOS operating system is used, which provides support for additional memory ( extended or expanded). The so-called HIMEM.SYS
.
This driver is required to load CD drive drivers. I just needed more space on the boot device than a 1.44 floppy disk! Having scoured the Internet, I found a wonderful utility from Hewlett-Packard
for creating bootable flash drives - . This was my salvation!
Archive USB_boot_Flash.zip
, and unzip to any location on your disk.
Go to the unzipped USB _boot_Flash
and run the installation file for the utility to create bootable flash drives
hp_usb_tool.exe
.
Click Next >
.
Accept the terms of the license agreement and click Next >
.
In the next window, click Next >
.
Accept another license agreement by clicking Yes
.
At this stage, you can change the destination folder for the installed program by clicking the Browse…
or continue installation to the default folder
c:\DriveKey
by clicking
Next >
.
In the last window, complete the installation of the utility by clicking the Finish
.
On your desktop you will find a shortcut to the installed HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool
.
Warning:
In the process of creating a bootable flash drive, all information from it will be deleted!!!
Run HP Windows Format Utility for USB Drive Key or DiskOnKey
using this shortcut.
At the top in the Device
indicate the device on which your flash drive is located.
Check the box next to Create a DOS startup Disk
, check
using DOS system files located at
and indicate the path to the DOS folder in the folder where you unpacked
the USB _boot_Flash.zip
(in my case this is the folder
C:\USB_boot_Flash\dos
) .
In the File System
we indicate
FAT32
, in the
Volume label
you can specify the label of the future bootable flash drive.
We start the process of creating it by clicking Start
.
In the warning window that appears that all information located on the flash drive will be destroyed, click Yes
.
In the next window you will see the status of the process of creating a bootable USB flash drive.
At the end of the creation process, you will see an information window about the status of your flash drive. Finish the process with OK
.
Returning to the previous window, close it by clicking Close
.
All we have to do is copy the entire contents of the folder C:\USB_boot_Flash\USB
to your flash drive. You can also copy the programs needed to run from DOS there; in my case, I copied the program for updating the BIOS and the new firmware itself (there is now more than enough space!)
All that remains is to go into the BIOS and in the boot method settings, select boot from our newly created USB flash drive as the first item. When you boot from it, you will see a clean DOS with the Volkov Commander
.
Finally, for those who may need a Windows 98
With the ability to access a CD drive, I offer a utility that creates such a floppy disk.
Unpack the contents of the archive to your disk and run the file boot98se.exe
, which will do all the dirty work for you. During the boot process from it, you can select boot items either with or without CD drive support drivers.
There is nothing surprising about the evolution of operating systems. Every day new ways of processing information appear, and new software components are required for support. But something always remains at the primitive level. So, for example, to operate and configure the BIOS, you may need a bootable DOS flash drive.
To create or not
Flash drive is a very useful thing. The disadvantages include: the discomfort of constantly switching boot disks in the BIOS. But the user is given the right to choose life-saving utilities for multiboot media.
Devices with DOS are incredibly useful for system recovery after failures, when you need to quickly access the hard drive partitions of a “dead” machine. The graphical shell of a file manager, for example, Norton Commander, has been helping system specialists for many years.