How to access the processes tab
While the computer is working normally, the average user is of little interest in what processes are running in the system and what they are needed for in general.
But the non-standard behavior of Windows XP/Vista/7 - slowdowns, freezing, frequent reboots - forces us to look for reasons.
Where to start your search? Let's try to launch the "Task Manager".
Launch options.
- Press the key combination “Ctrl” + “Alt” + “Del”.
- Click the “Start” button, select the “Run” command, enter taskmgr.exe and click the “Ok” button.
Now go to the “Processes” tab and study the list.
A large number of svchost.exe processes is immediately alarming. Well, it's time to understand the capabilities of this application.
Return to content ^
The principle of correcting a problem in the system
Before thinking about how to remove svchost.exe, which is completely loading up the computer’s memory and processor, you need to ask yourself about the tools available in the OS that can fix an unexpected problem in a few minutes. The fact is that haste in this matter is not entirely appropriate, since a problem that arose due to the fault of Windows OS may disappear on its own after some time. To do this, the user only needs to reboot the device.
If this does not help, you can try to delete the most resource-intensive process in the Task Manager, having first examined everything that is loaded through svchost.exe. Simultaneous pressing of the Ctrl+Alt+Del keys will help you carry out the procedure. After downloading the system application, you need to go to the “Processes” section. Then click on the “Display tasks of all users” button located at the very bottom of the dialog box. Thus, the PC owner will be able to directly track what is loading memory “thanks to” svchost.exe. You should try to close the largest resource by clicking on the “End process tree” button.
It would not be superfluous to pay attention to the performance of the memory, which can be checked using specialized applications. Your PC needs to be cleaned of accumulated dust at least once every few months. A dirty cooler can make a loud noise, which is a direct signal that the central cooling system is overfilled. It is necessary to remember to replace the thermal paste, which is located in the main processor. Hardware problems cause your computer to slow down and add additional load to svchost.exe.
The system application loads the computer's memory and processor during failures that occur due to automatic updates regularly downloaded from the Internet to the user's computer. It is preferable to install all Windows Updates or disable the service. To no longer receive updated applications, you should go to the “Start” menu, in the “Control Panel” select the “System and Security” section, and in it - “Windows 7 Update”. A window with many options will open on the screen. Among them, you need to find the category responsible for setting the parameters; the user must check the box next to the “Do not check for updates” command.
A system rollback can greatly simplify your PC's work. To do this, you need to remember the date when the owner of the device did not observe significant problems caused by the operation of svchost.exe.
Among other things, one should not rule out the assumption that the svchost.exe system program is loading the processor due to the presence of viruses. You can scan your device with several antivirus applications to make sure the system is clean. Initially, you need to go to the “Task Manager”, in the “Processes” section, view the resources of all users. Those who directly load the svchost.exe process deserve fundamental attention. Do not worry if the “Users” column contains the following inscriptions: system, local service, network service. Otherwise, if a different name is entered as a user, it would be reasonable to assume that third-party virus programs have appeared on the PC. The user must delete them by clicking on the “End process tree” button. It would be a good idea to check your system with a proven antivirus application.
After all the above steps, you should delete the Prefetch directory, which serves as a system accelerator for the functioning of most services. This folder is located on the system drive (usually C:) in the Windows OS folder. After you have managed to delete the directory, it is important not to forget to restart the gadget.
The wuauclt.exe resource can function in the Task Manager; you can clear its contents by deleting all directories contained in the Software Distribution directory, which is also located in the Windows system folder.
The last step to get rid of unnecessary applications that load the computer, in particular the processor, will be to clear the log file located in the OS log. After pressing the Win+R buttons simultaneously, a window will appear on the screen in which you need to specify the eventvwr command and confirm it with the “Ok” key. In the "Windows Logs" section, which is located in the upper left corner, you need to find the categories "Applications", "Security", "Installation" and "System". In each of them you should “Clear log”. After the manipulation, you should restart the computer.
First acquaintance with svchost.exe
Recently, dynamic link libraries with the .dll extension are increasingly being used to compose Windows services instead of the usual executable files with the .exe extension.
This method is considered more effective. However, a library file, unlike an executable one, cannot start on its own.
The svchost.exe application “helps” to start a service from a dll file.
For example, here's how the DNS Client service starts:
C:\WINDOWS\system32\svchost.exe -k NetworkService.
Return to content ^
How the process works
This process is present in almost every version of Windows, but its potential was revealed only with the release of Windows XP. Before that, he was primarily responsible for the network connections through which the computer connects to the Internet. But Microsoft developers decided not to stop there, so now the service is designed to run background local processes related to dynamic libraries that have the “.dll” extension.
Interesting! Dynamic libraries cannot be launched in normal mode.
svchost.exe allows you to save computer resources because you don't need to physically run the executable file when using the service. Therefore, the number of processes loading RAM and virtual memory of the PC is reduced. It is because of this that several services with the same name are simultaneously displayed in the Task Manager.
In addition, the svchost.exe file is automatically launched when Windows starts, regardless of what programs are “hanging” in autorun. Therefore, completely disabling unnecessary services and applications will not affect its loading.
A few words about svchost.exe processes
Each instance of the svhost.exe process is initiated by its parent, the services.exe system process.
A single svshost.exe process can run one service or a group of several logically related Windows services.
The launch option “one svchost process -> several Windows services” allows you to save RAM and processor resources.
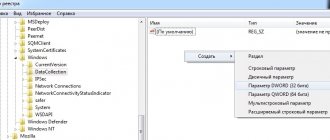
To view svchost groups and their composition, go to the Windows registry:
- Click the “Start” button and find the “Run” command;
- In the command line, enter regedit.exe and click the “Ok” button.
- in the registry go to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Svchost branch;
- we find the REG_MULTI_SZ parameters with lists of services for each group.
For example, the DcomLaunch group includes the following services:
- Power – a service that manages power configuration and sends notifications about installed power configurations;
- PlugPlay is a service through which the computer automatically recognizes devices connected to it and configures them to work without user interaction or minimize this participation.
- DcomLaunch is a service for launching COM and DCOM servers for stable operation of programs using server data.
It is not recommended to disable any of the above services.
When viewing the svchost process data, be sure to pay attention to the Username column.
It can only contain one of the following values: “Local Service”, “System”, “Network Service”.
Where does the file live?
In Windows XP/Vista/7 operating systems, the location of the svchost.exe file is standard:
- 32-bit OS – C:\Windows\System32\;
- 64-bit OS – C:\Windows\SysWOW64\.
Let's remember the exact address of the file. This will be useful to us later.
Return to content ^
Examining processes and files
The main tool that will help us diagnose and solve problems with svchost is the Windows Task Manager. In the “ten” after updates for 2020, host processes are designated in it as “Service Node” or “Node Service”. Each of them runs one or more services. Services are grouped by levels of access to system resources.
Normally, all host processes are created by the same file - svchost.exe, which is located in the \Windows\System32 folder . To make sure that the process that loads the system is launched from there, call its context menu and click “Open file location”. Did the System32 folder open? This means the first test was successful.
All normal host processes have a common parent - the services.exe process, launched by the file of the same name . Unfortunately, the system task manager does not show it. To see this, you can use an improved alternative to the dispatcher - the free and installation-free utility Process Explorer.
In addition, a normal svchost.exe file is supposed to be digitally signed by Microsoft . To check it, open the “Processes” tab in the system task manager, right-click on the suspicious line and click “Details”.
While in the Details tab, right-click the suspicious svchost again and select Properties.
Open the digital signatures tab of the service host. If its contents look something like the screenshot below, then everything is in order.
Detailed information about the file that spawned the host process can be obtained from the contents of the “Details” tab.
And if you install a simple free HasTab utility on your computer, “without leaving the cash register” you can get the checksums of the file of interest.
Then check its MD5 on Virustotal.com (an online service for checking files and other objects with a variety of antiviruses). If the service shows that the file is clean, then the source of the problem is not there.
The svchost.exe process and its connections
The task manager gives us a whole list of running svchost.exe processes, but this information is clearly not enough.
Naturally, we are interested in which services are launched by a specific instance of this process.
So, several ways to find out about svchost's connections.
Tasklist and sc commands.
The tasklist and sc commands can be used in any version of Windows. Therefore, this method can be considered universal.
First of all, launch cmd – the Windows command line interpreter:
- press the “Start” button;
- select the “Run” command;
- enter cmd and press the “Ok” button.
To get a list of services on the interpreter screen, run the tasklist command with the svc key and press the “Enter” key:
- tasklist /svc "Enter".
To save the query results to the text file svc.txt located on drive C: in the temp folder, we redirect the output of the tasklist command:
- tasklist /svc > C:\temp\svc.txt “Enter”
Note that the file will be saved in DOS encoding.
Fragment of listing tasklist.exe.
Service PID Image Name:
+++
- svchost.exe 1216 DcomLaunch
- svchost.exe 1300 RpcSs
- svchost.exe 1384 WudfSvc
- svchost.exe 1528 Dnscache
- svchost.exe 1584 LmHosts, SSDPSRV
+++
Table columns:
- “Image name” – the name of the executable file;
- “PID” – process identifier;
- “Services” – list of services.
To obtain information about a specific service, set its short name as a parameter of the sc service management command.
An example of obtaining information about the TermService service.
– sc qc TermService “Enter”.
Two ways to get to the list of services.
- Click the “Start” button, find the “Run” command, enter services.msc in the command line and click the “Ok” button.
- Click the “Start” button, then select Settings -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services.
Windows Vista/7 Task Manager.
We get a list of services associated with the svchost process using the Windows Vista/7 task manager:
- place the cursor on the process name;
- Call the context menu by right-clicking and select the “Go to services” option;
- We get a list in which the services associated with our process are highlighted.
In the Windows XP operating system, the “Go to Services” option, unfortunately, is missing. This option cannot be considered universal.
Process Explorer utility.
This program is not included in Windows distributions, but is available for download from the Microsoft website or from the Process Explorer download page.
The launch process is very simple and does not require installation:
- download the zip archive;
- unzip to a folder on disk;
- run the file procexp.exe.
The utility provides detailed information about the processes running in the system: pid, cpu load, brief description, information about the manufacturer, etc.
When we hovered the mouse over the name of one of the svchost instances, we received the following information:
- Command Line – line for launching a service or group of services via svchost;
- Path – path to the svchost.exe file;
- Services – list of services.
The right-click context menu provides greater control over the process and the services it runs.
AnVir Task Manager utility.
The AnVir Task Manager program not only provides management of running processes, services, drivers and startup, but also performs antivirus functions.
The startup order is the same as for Process Explorer:
- download the free version of AnVir Task Manager in zip archive format;
- unzip to a folder on disk;
- run the AnVir.exe file.
To switch the language when you first start the program, use the main menu:
"View->Language->Russian".
Select the “Processes” tab to obtain detailed information about our svchosts.
In the process line we see information about the manufacturer, the path to the executable file, the CPU load percentage, etc.
But the most interesting data is presented in the “Startup” column. Here you will find a list of services launched by svchost.
Double-click the left mouse button on the process name and get more detailed information about it (a window with tabs at the bottom of the screen).
Clearing event logs
In some cases, the process consumes a high percentage of memory due to the log files being too large.
Open the Run window (Win + R keys), enter the command eventvwr.msc, press Enter to enter the Event Viewer section.
On the left side, expand WIndows Logs. Right-click on the Applications, Security, Installation, System, Event Redirection subsections and select “Clear Log”.
The system is slow, what should I do?
What symptoms indicate the culprit of svchost and how to fix the problem. Let's figure it out.
The system may slow down for various reasons. But if in the task manager you find the svchost.exe process with a high percentage of CPU load (sometimes even about 100%), it is likely that this is the reason.
Many users believe that in this case svchost is definitely a virus. But that's not true. A process can load the system for other reasons.
Let's look at how to solve the problem with svchost in both cases.
Return to content ^
Process Definition Method
Although the command line is our everything, and using the command:
tasklist /svc /fi “imagename eq svchost.exe
Can:
- Find out the short name of the process.
- Determine its ID and compare it with what shows 100% load in the task manager.
- Determine the executable service by clicking the commands in “Services”.
- Put it into “reload” or stop it, removing the colossal CPU load.
But you can take a shorter route and download the utility, which already contains all the necessary information. The utility is called “Process Explorer”, and you can download it from the Microsoft website.
After downloading and running the software (for x64 operating systems from the archive it is better to run the procexp64 version), you can see a list of all system processes, for example: smssvhost, sihost and the expanded svchost tree and others.
By hovering your mouse over the process that is heavily loading the system, you can extract the necessary information.
By right-clicking on it in the program, you can:
- Kill Process – kill a process (can shut down or restart).
- Kill Process Tree – kill the process tree (helps if it is connected to others and cannot be disabled alone / or work without others).
- Restart – restart (sometimes it works and no longer loads the system).
- Suspend – pause without turning it off (rarely works).
Experiment with turning it off (kill). You won’t be able to catch anything worse than a blue screen, which is eliminated by rebooting the system (the system will not allow it).
Is Svchost a virus or not?
Many Trojans and other computer viruses disguise themselves as well-known Windows system applications. Svchost is no exception.
According to Kaspersky Lab, the viruses Trojan-Clicker.Win32.Delf.cn, Virus.Win32.Hidrag.d, Net-Worm.Win32.Welchia.a, as well as the Kido virus known to most users, “pretend” to be svchost.
So, let's start checking our process.
First of all, pay attention to the location of the svchost.exe file. If it differs from the standard one, you can safely delete the file.
Check the username that started the process. A list of valid names is given in the section “A few words about svchost.exe processes”.
Carefully re-read the process name. Virus writers often use similar names: svhost, svchosts, etc.
An application can never be launched through the "Run" key of the Windows registry.
Therefore, you definitely need to check its presence in startup:
- click the “Start” button, select the “Run” command, enter msconfig and click the “Ok” button;
- go to the “Startup” tab;
- if the svchost.exe file is found, disable the launch.
To delete a suspicious process in the task manager, call up the context menu by right-clicking and select the “End process tree” command.
After completing all the described steps, you must run an anti-virus program and disinfect your computer.
Return to content ^
What to do if svchost.exe loads the processor at 100%
One of the most common problems associated with svchost.exe is that this process loads the system at 100%. The most common reasons for this behavior:
- Some standard procedure is performed (if such a load is not always present) - indexing the contents of disks (especially immediately after installing the OS), performing an update or downloading it, and the like. In this case (if it goes away on its own), you usually don’t need to do anything.
- One of the services is not working correctly for some reason (here we will try to find out what kind of service it is, see below). The reasons for malfunction can be different - damage to system files (checking the integrity of system files can help), problems with drivers (for example, network ones) and others.
- Problems with the computer’s hard drive (it’s worth checking the hard drive for errors).
- Less commonly, it is the result of malware. Moreover, the svchost.exe file itself is not necessarily a virus; there may be cases where a third-party malicious program accesses the Windows Services Host process in such a way that it causes a load on the processor. It is recommended to scan your computer for viruses and use separate malware removal tools. Also, if the problem disappears when you clean boot Windows (starting with a minimum set of system services), then you should pay attention to what programs you have in startup; perhaps they have an impact.
The most common of these options is the incorrect operation of any service in Windows 10, 8 and Windows 7. In order to find out which service is causing such a load on the processor, it is convenient to use the Microsoft Sysinternals Process Explorer program, which can be downloaded for free from the official website https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/processexplorer.aspx (is an archive that needs to be unpacked and run the executable file from it).
After launching the program, you will see a list of running processes, including the problematic svchost.exe, which is loading the processor. If you hover your mouse over the process, a tooltip will display information about which specific services are running by this instance of svchost.exe.
If this is one service, you can try to disable it (see Which services can be disabled in Windows 10 and how to do it). If there are several, you can experiment with disabling, or you can use the type of services (for example, if all of them are network services) to suggest the possible cause of the problem (in this case it could be incorrectly working network drivers, antivirus conflicts, or a virus using your network connection , using system services).
Svchost is not a virus, but it loads the system
If you are convinced that svchost is a real system process, let's look at the services it runs.
The procedure is as follows: one by one we stop the services associated with the process and see what happens.
We have already talked about how to go to the list of services in the section “The svchost.exe process and its connections.” Now let's figure out how to stop them.
Disabling a service in the standard Windows Services program:
- place the cursor on the service name and double-click the left mouse button to open the service window;
- go to the “General” tab, click the “Stop” button, then “Ok”.
Disabling a service in Process Explorer:
- place the cursor on the desired svchost.exe process, call up the context menu by right-clicking and select the “Properties” option;
- in the window that opens, go to the “Services” tab;
- select the desired service in the list and click the “Stop” button.
Disabling a service in AnVir Task Manager:
- place the cursor on the desired svchost.exe process, call the context menu by right-clicking and select “Go->Go to service”;
- select the desired service in the list, call the context menu by right-clicking and select the “Stop” option.
Disabling a service using the sc command:
- press the “Start” button;
- select the “Run” command;
- enter cmd and press the “Ok” button;
- In the interpreter window, enter the command: sc stop “service name” “Enter”.
If the service you stopped is not causing the CPU load, you should start it and repeat the same steps with the next service.
Restarting services:
- Services program - Start button;
- Process Explorer program – “Restart” button;
- AnVir Task Manager program – “Start” button;
- sc command - sc start "service name" "Enter".
Note that stopping the service only lasts until Windows is restarted. Therefore, if you find the “culprit” that is loading the system, you need to disable its launch in the “Services” program:
- Click the “Start” button, select the menu “Settings -> Control Panel -> Administration -> Services”;
- place the cursor on the service name and double-click the left mouse button to open its window;
- go to the “General” tab;
- find the “Startup type” parameter, set the value to “Disabled” and press the “Ok” button.
Before disabling a service, you should be clear about what functions it performs and whether disabling it will not disrupt the system.
Note that when installing Windows, a standard set of services is enabled. Some of them may be completely unnecessary for your work and will only consume computer resources.
Therefore, it is advisable to understand the purpose of each of them and disable unnecessary services.
Return to content ^
Understanding services, drivers and hardware
Often the cause of high CPU load on the service host is services. In the latest version of Windows 10, it has become easier to find the problematic service, since the majority of host processes contain one of them. In Windows 7 and XP, there is usually a group of services per 1 service host, sometimes 8-12 of them.
To see a list of services that are potential culprits for problems in Windows 10, do the following:
- Open the context of the suspicious svchost process in the task manager on the “Details” tab and click “Go to services”.
- Everything that is running in this process is highlighted in blue on the Services tab. If one line is highlighted, chances are you've found the likely culprit. If, as in my example, this is the wuauserv service, you can breathe easy: your operating system is simply downloading updates. And if the computer is not very productive, svchost.exe at this time can load the processor by 100 percent. After the update the load will return to normal.
- If several services are highlighted in blue, stopping one by one will help you find the problematic one. To do this, in the context menu of one of the services, click on the “Stop” item. If the load does not decrease, start this service and stop the next one.
By the way, in Windows 10 you can stop and start services directly on the “Processes” tab.
Attention! Before diagnosing using the above method, save any unsaved documents, as shutting down a critical system service may cause your computer to freeze, reboot, or get a Blue Screen of Death (BSoD).
If the detected service is related to a device driver, for example, sound (Windows Audio), Bluetooth (Bthserv), printing (Spooler), etc., the cause may not lie in it, but in the driver or a malfunction of the device itself. If the driver was installed shortly before the problem occurred, roll it back to a previous version. If it has not been updated for a long time, update or reinstall it. If you suspect a problem with the equipment, check it by disconnecting it or replacing it with a known good one.
How to recognize a virus?
It is easy to recognize a virus that disguises itself as the svchost.exe file. It runs under the user account or any other processes except Local Service, Network Service or System.
Another characteristic feature is “mistakes” in the name. Processes called svhost, svchosts or others are malware that need to be removed.
"Cleaning" the system
If you find a virus on your computer masquerading as the svchost.exe file, run an in-depth system scan with installed antivirus software.
Important! Surely scanning with installed software will not bring results.
But it’s better to use special utilities from well-known companies: Dr.Web CureIt, Malwarebytes Anti-Malware or Kaspersky Rescue Disc. They will identify and neutralize malware.
Reasons for downloading resources
Often, users notice that a process loads one of the resources (processor or RAM) of the device, regardless of whether programs are running or not. There are various reasons for this.
Viruses
The main reason is malware that has entered the computer and “masquerades” as the svchost.exe file. Sort processes in Task Manager by name and see on whose behalf these services are running. If this is done on behalf of a user account (your account), then this is the “tricks” of the virus. If the “Username” column indicates: Local Service, Network Service or System, such a file is safe.
If you think you have discovered a virus, right-click on the process → Open file location. This way you will determine the location of the malware and check it through the VirusTotal.com portal. But it’s better to immediately scan the system using Dr.Web CureIt or Malwarebytes Anti-Malware. The fact is that deleting one executable file will not help get rid of the virus, since there are probably auxiliary fragments on the computer that will restore it after a reboot or simply prevent it from being deleted.
Downloading updates
Since in most cases the user does not change OS settings, Windows is set to automatically download updates by default. This is also the “responsibility” of svchost.exe. To disable downloading updates:
- enter services.msc in the search bar → the Services window will open;
- RMB on Windows Update → Properties → Startup type: “Disabled”.
Problematic programs
This reason is typical for those users who install a huge number of programs and applications on their computer and do not monitor them. To identify unnecessary software, install Process Explorer on your PC. It will help you determine which programs are taking up device resources, but you are not using them.
Another advantage of Process Explorer is that it works closely with the file checking service for malware - VirusTotal, so it will help distinguish system services from viruses.
To check a file, select it in the program window → Options → VirusTotal.com → Check VirusTotal.com.
Using µTorrent
Often, the µTorrent program loads computer resources when downloading files. To reduce CPU load:
- press Ctrl+P → Advanced section in the program window;
- set the switch on the “net.low_cpu” parameter to the “Yes” position, and on the “net.max_halfopen” parameter the minimum value (number) and then increase it until loading problems arise again - this is the maximum parameter.
How do viruses work through svсhost?
Svchost loads memory, interfering with the normal operation of the computer. The disguised virus redirects Internet traffic, thereby eating up a significant part of the processor and RAM resources. Malicious software is placed on the drive with Windows installed, and the actions it performs are hidden so that they are not visible in the task manager. A virus can masquerade as a system process. This increases his lifespan, which directly affects the number of actions and damage caused.
When opening the task manager, you need to carefully check the user on behalf of whom this task is running. Windows runs the main process as: LOCAL SERVISE, NETWORK SERVICE, system.
All svсhost.exe are system ones and are not run on behalf of the user. Everything that is performed by the current user is used by malware.
WATCH THE VIDEO
Look carefully at the spelling of the name. It may resemble svchost.exe in design, but differs in letter or number (svch0st.exe - a zero is used instead of the letter “o”, svchoоst.exe – two letters “o”, svehost.exe – instead of the letter “c” is written “e” ). These names of executable programs are usually malicious.
Look carefully at the startup section, if you find an automatically launched item with the same name there, you definitely have a virus in front of you. Uncheck the checkbox and scan the system with an antivirus.
The system svchost.exe is located: for 32-bit Windows in the folder C:\WINDOWS\system32, and for 64-bit C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64. The screenshot shows the location C:\WINDOWS, this process is rather malicious. If a virus or malicious utility is detected, run an anti-virus scan (Dr.Web Cure IT).
If there are no software conflicts, you have checked and there are no viruses, and 100% processor load has not gone away, then you can use special software (Process Explorer) to determine which program is affecting the processor so much. As you can see in the Windows screenshot, the system is being updated.
Process Explorer helps you determine what is affecting the svchost process
If the update center is loading the system, then disable it or schedule it so that it checks, downloads and installs updates when you are not using the computer.
Disabling automatic system updates helps reduce the load on your computer's RAM
To prevent the appearance of viruses, install reliable anti-virus protection, which will avoid problems with the system.
Now you know what Svchost is and why Svchost loads the processor.
And having discovered a lot of entries in its list of processes with the same content - svchost - many users fall into premature panic. This usually happens when the performance of the system is in question - everything freezes, windows do not respond, even a reboot does not help. The first process to come under suspicion is usually the svchost exe? Is the Windows Services host process really to blame for the CPU usage? And if this is so, then how to deal with it?
Generic Host Process for Win32 Services, which is what the name of the Windows service in question stands for, is a critical operating system utility. You cannot disable this service, as otherwise it will become impossible to use one of the most important Windows tools—subroutine libraries shared between applications—the so-called dll libraries. And since the entire Windows architecture is based on such libraries, working with disabled svchost.exe is absolutely unrealistic.
The problem is that hackers prefer to disguise their malware as one of the system processes, and the Generic Host Process is an ideal candidate for such manipulation.
The system automatically launches not one but many of these processes, so it’s impossible to figure out which of them is “healthy” and which is a virus.
What to do if the processor is 100% loaded
Let's say that svchost is not a virus, but it still “takes away” all available system resources. Reasons for this behavior:
- If the load arose unexpectedly and disappeared after some time, the basic system procedure was performed (indexing, downloading updates, etc.).
- The load is constant - one of the services is unstable due to corruption of system data, lack of network drivers, etc., or there are problems with the HDD.
The option associated with incorrect operation of services is the most common. To identify the problematic one, you need to use the Process Explorer utility, distributed through the official Microsoft website. Having installed and launched this program, you will be faced with a list of processes, among which will be our svchost.exe. By hovering your cursor over it, you will see which services are running by the problematic host process - they will be listed in the “Services” column.
Viruses masquerading as svchost.exe
Svchost is a frequent victim of malicious software. Various types of viruses choose this particular type of process for obvious reasons: there are quite a lot of svchost running on PCs, so the chance that the user will notice the substitution is small.
Typically, viruses replace some Latin letters in the process name with their Cyrillic counterparts. There are such popular replacements for letters in the name:
- svcchost.exe - the letter c is repeated;
- svhost.exe - here, on the contrary, it is skipped;
- svchostt.exe - this malicious process has the letter t added;
- svshost.exe - s is used instead of c.
The process may be genuine, but this does not mean that its hyperactivity cannot be associated with a malware or spyware utility.
Viruses on a PC can:
- change system parameters;
- launch browser pages that the user did not request;
- load the processor, RAM, hard drive;
- “eat up” network traffic and lead to frequent and sudden Internet outages and slow page loading.
The svchost process (both genuine and viral) loads not only the processor, but also the RAM and hard drive
In this regard, scanning with an antivirus will be mandatory, regardless of whether the process turns out to be false or not.
How to recognize the authenticity of a process
What can a false svchost produce? First of all, its physical location on the hard drive is incorrect. The legal place for svchost on the system drive is various directories in the Windows folder:
- System32;
- SysWOW64;
- prefetch;
- ServicePackFiles/i386;
- WinSxS.
In the last section of WinSxS there may be another folder with a long name, in which the active svchost will be located. The name can be an arbitrary and strange set of characters, for example, amd64_3ware.inf.resources_31bf3856ad353e35_6.3.9600.16564_ru-ru_7f622cb60fd69b1c. This folder will also contain only the genuine process. Another exception is the section of the anti-spyware utility Malwarebytes Anti-Malware.
The svchost file may be located in a folder with a long name in the WinSxS directory
If the process file is in any other folder, such as Windows root folder or user partitions, it means that the process is false.
To find out the exact location of the process, do the following:
- Right-click on an empty area (without icons) on the “Taskbar”. In the black context menu, click on the third section from the bottom “Task Manager”.
In the “Taskbar” menu, click on “Task Manager”
- Switch to the penultimate tab “Details”. In the list, look for the svchost process, which consumes the largest amount of PC hardware resources. Right-click on it and in the small list of options click on “Open file location”.
In the process context menu, click on “Open file location”
- The standard “Explorer” will launch on the screen - the folder in which the file corresponding to the active process is located. This file will also be highlighted in the directory.
Pay attention to the folder that Explorer opened: if the file is in the wrong location, then it is a virus
- You can view the location of the file without launching Explorer. Right-click on the process item in the same “Details” tab and select “Properties” from the menu. An additional smaller window will open. In it, pay attention to the “Location” parameter.
Look at the location of the svchost process in the Properties window
How to cure a system with a virus?
If the process turns out to be a virus, scan the OS with an antivirus installed on your PC. It will accurately determine the authenticity of the process and, if necessary, offer to delete it. At the same time, the antivirus itself and its databases must be up-to-date, that is, updated to the latest versions.
You can also check with an online antivirus service called VirusTotal or use the built-in Windows Defender antivirus to be sure. Let's look at treating the system using the example of the popular Avast antivirus:
- All antivirus programs must run in the background, which means they must have an icon in the Windows tray. We will open the utility through it. Click on the up arrow icon at the right end of the “Taskbar” next to the time. In the small menu, click on the Avast icon. If you have an antivirus shortcut on your Desktop, use it.
In the Windows tray, click on the icon of your antivirus
- Click on the “Protection” section in the left panel. In the menu, select the first tile “Scanning”.
In the Avast window, go to the "Protection" section and click on the "Scans" tile
- We give preference to deep verification. It will take longer, but will be more effective.
Select full scan for more efficient scanning of hard drives for viruses
- We are waiting for the end of the process. A virus should appear in the results. From the menu with available action options, select “Delete.”