Our personal computer is a dear friend, assistant, sometimes breadwinner and even a source of inspiration. The performance of our “metal-plastic friend” is an indicator of the health of its operating system. Therefore, the question of how to remove a service in Windows and do it correctly is far from idle.
Stopping unnecessary services will help speed up your computer's performance.
Reasons for deleting services
Once upon a time you installed the service that was necessary at that time on your PC. Maybe it didn't even work right away. Then you decide to add something else. It seems that everything fell into place and, one might say, the dancing with the tambourine ended in victory. But over time, you got tired of it or began to interfere with your new idea.
Another situation is possible. One day you discover that someone or something has installed a new “Service Windows” on your PC. This may well happen from “communication” with one of your relatives, especially children, with your friend. And the performance of the PC after this strangely drops completely.
How to remove a Windows 7 service from the command line
If anyone doesn’t know, the command line absolutely always saves you. Does the system not work or does not boot? No problem - three commands, and everything works again. The same applies to some components installed on the system, which can, to put it mildly, simply interfere or take up too many resources (for example, program updaters or the same flash player, installers of Windows modules and updates, etc.).
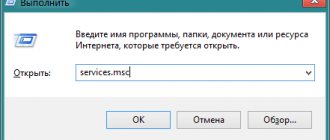
In principle, it is possible to fight all these manifestations. We run the services.msc command from the standard “Run” menu and stop the required component.
After that, go directly to the command line where we enter sc delete “service name” (without quotes) and press Enter. By the way, in order not to do unnecessary things, you can simply copy the name of the process from the editor mentioned above.
How are services managed?
The creation, deletion, start and stop of services in the operating system is managed by the Service Control Manager (SCM).
Starting when the operating system boots, the Service Control Manager, for its part, starts all of them, for which the startup mode is set to “automatic”. Along with the launch of those that have an “automatic” type, all services that depend on them are also launched, even if the “manual” mode is specified for them. After the system has finished loading, the network administrator has the opportunity to manually start (disable) any of the services using the management console.
For services in Windows OS, the following launch modes (types) are provided:
- Prohibited;
- Manually;
- Automatic when system boots;
- Deferred (for some operating systems);
- Mandatory (starts automatically and cannot be stopped by the user).
Windows has several possible operating modes for system services.
How to completely remove a service in Windows 10
Beginner users sometimes ask what Windows services are and how they differ from other programs. Windows services are the same programs, only they start automatically with Windows and are not able to interact with the system's graphical environment or even the command line, although exceptions are possible for some services. Most of the services found in Windows are system services, and if they become damaged or stopped, the system may not work correctly or even be unable to boot.
But among the services there are also those that are installed by third-party applications. They can remain, start and work autonomously in the system, consuming resources that could be used to solve much more important tasks.
These are the services that can be safely removed. Today we will show how you can completely remove unnecessary services in Windows, but we warn you again - be extremely careful when deleting this or that service, you must be fully aware and understand what you are doing . If you are going to get rid of a system service, be sure to test the result on a virtual machine, and at the same time take care to create a backup copy of your system.
So let's get started. First, you need to know exactly the name of the service you want to remove. Through the Win + X menu, open the Computer Management snap-in.
And expand the “Services and Applications” branch in the left column.
Find the service to be deleted in the list and double-click on it.
In the “General” , at the very top the service name will be indicated, this is what we will use. Copy it to the clipboard, run the command line as administrator and run the following command, where Service is the name of the service to be deleted:
sc delete Service
For example, you can delete the biometrics service in Windows 10 using the sc delete WbioSrvc . Before deleting, it is advisable to stop the service, although this is not a prerequisite; simply after updating the contents of the snap-in, the deleted service will still be displayed until the system is rebooted.
Note: Some services do not appear in Computer Management . If you need to get a complete list of all services available on the system, open the registry editor and expand the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services . The name of each subkey in the Services folder will be the name of the service.
Warnings
Before deleting, you need to understand that:
- This process is irreversible;
- Removal will render dependent programs inoperative;
- The operating system will crash when deleting a service associated with one of its components;
- In some cases, reinstallation will be necessary, and this is not always easy to do. More often than not, this is very difficult.
What can be disabled
It is clear that a user, for example, does not need Print Manager if he does not have a printer. But does it make sense to remove such a service? After all, tomorrow he may have a printing device. And you can simply turn off the service!
Similar, often not always necessary services also include:
- Windows Search (Windows Sich). Performs content indexing;
- Offline files. Offline file cache control, tracks user login and logout.
- Secondary login. Starts processes on behalf of other users.
- Server. Supports access to files, devices, channels to the computer through network connections.
- Windows Time Service. Manages date and time mapping on clients and servers on a network.
This list can be continued for a very, very long time.
Some services you don't need in your daily work
Windows XP services - which Windows XP services can be disabled
By default, the Windows XP operating system includes many system services that perform certain tasks. As you know, performing certain tasks requires a certain amount of time and resources. Thus, by disabling unused services, we can significantly speed up our OS, saving valuable resources.
The most important role in improving OS performance can be affected by disabling some services, of which many are enabled by default. Most of them, I’m sure, you won’t need at all (depending on the purpose of your PC). Running services consume valuable resources. Thus, by disabling some of them, we can significantly speed up our computer.
In this article we will look at which Windows XP services can be disabled. In order to go to the services manager, run the command services.msc in the Start menu > Run. You can also get to the service manager through the control panel - go to Control Panel > Administration > Services.
Before disabling services, I strongly recommend a Windows restore point or saving the HKEY_LOCAL_ MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServices registry key (right-click on the specified key and select “Export”). This should also be done because re-enabling some services requires a certain pattern.
Here is a list of services that you can safely disable.
QoS RSVP - Provides network alerting and local traffic control for QoS programs and control programs.
This service provides traffic control on the network using IPSEC, programs, and adapters that support QoS technology. The QoS packet scheduler is automatically installed for each TCP/IP connection. It is recommended to disable this service, because... in 99% of cases it is not necessary.
You can start this service if your applications use QoS notifications. This service does not affect the overall performance of the computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
Telnet —Allows a remote user to log on to a system and run programs, and supports a variety of TCP/IP Telnet clients, including computers running UNIX and Windows operating systems. If this service is stopped, the remote user will not be able to run programs. If this service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it cannot start.
When this service is disabled, users will not have remote access to programs. This service, if enabled and running, may slightly slow down your computer. If this service is enabled and running, the level of system security is significantly reduced.
"Automatic Update" - Enables downloading and installation of Windows updates. If the service is disabled, this computer will not be able to use Automatic Updates or the Windows Update website.
If you don't have a permanent Internet connection or if you want to control everything your computer does, you can update the software included with Windows XP manually. However, it is recommended that you leave the service startup type at Automatic so that the operating system downloads updates automatically. So decide for yourself whether to disable this service or not.
“Print Spooler” - loads files into memory for later printing. The print spooler is a key component of the Windows printing system. It manages print queues in the system, and also interacts with printer drivers and input/output components, such as USB ports and TCP/IP family protocols. If you do not use printing and do not have a single printer installed on your system, it is recommended to disable this service.
If this service is disabled, printing on the local machine will be unavailable. This service, if enabled and running, may slightly slow down your computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
Remote Desktop Help Session Manager —Manages Remote Assistance capabilities. Once this service is disabled, Remote Assistance will no longer be available. Before disabling this service, in the Properties window, on the Dependencies tab, check the service dependencies.
It is recommended to disable this service, because... in idle mode it takes up 3 to 4 MB of RAM. This service, if enabled and running, may slightly slow down your computer. If this service is enabled and running, it may reduce the level of system security.
Performance Logs and Alerts —Manages the collection of performance data from local or remote computers based on a specified schedule and ensures that the data is logged or triggers an alert. If this service is stopped, no performance data is collected. If this service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it cannot start.
Depending on the value of the named log collection setting, the service starts or stops each named performance data collection. The service starts only if at least one performance data collection is scheduled.
This service starts according to a schedule and, if there is no work, is automatically disabled. The service, if enabled and running, may slow down your computer slightly. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
“Uninterruptible Power Supply” - Controls the operation of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) connected to the computer.
Some uninterruptible power supplies connected via a serial port may require running this service. If this service is disabled, some manufacturers' uninterruptible power supplies will not work. This service, if enabled and running, may slightly slow down your computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
NetBIOS over TCP/IP Support Module —Provides NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) support and NetBIOS name resolution for clients on the network, allowing users to share files, printers, and connect to the network. If this service is stopped, these features may not be available.
For small networks, this service may be necessary if you need to share files and folders. For large networks with central file servers, keep this service disabled.
If this service is disabled, all services that explicitly depend on it will fail to start. This service does not affect the overall performance of the computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
"Smart cards" - controls access to smart card readers. If this service is stopped, this computer will not be able to read smart cards. If this service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it cannot start.
This service, if enabled and running, can greatly slow down the computer, for example, the speed of access to the hard drive can seriously slow down. This service, if enabled and running, increases the level of system security.
I think hardly anyone uses smart cards now, so it’s better to disable this service.
“Computer Browser” - maintains a list of computers on the network and provides it to programs upon request. If the service is stopped, the list will not be created or updated. If this service is not allowed, any explicitly dependent services will fail to start.
Computers that act as browsers maintain browsing lists that contain all the shared resources on the network. Viewing features are required by earlier Windows operating systems such as Network Neighborhood, the net view command, and Windows Explorer. This service does not need to be run at home. All actions that you did before will be available to you. In a large network, one computer is called the main computer, and the rest are called backup computers. The reserves report every 12 minutes that they are available to take over the lead role if necessary. Disabling this service on all computers on the network except one will not create any problems.
If you disable this service, your computer will be unable to locate other Windows computers on the network. Sharing files with other Windows computers will be blocked. This service does not affect the overall performance of the computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
“Task Scheduler” - allows you to configure a schedule for automatic execution of tasks on this computer. If this service is stopped, these tasks cannot run at the scheduled time. If this service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it cannot start.
This service is your memory assistant and is used in conjunction with programs such as virus scanners, backup programs, defrag utilities, etc. If you remember every task that needs to be done without help, you can disable this service.
If you disable this service, you will not be able to perform scheduled tasks. This service does not affect the overall performance of the computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
“Portable Media Device Serial Number” - Retrieves the serial numbers of all portable media devices connected to the system.
Network Logon —Supports end-to-end identification of account logon events for computers in a domain.
If this service is stopped, the computer may be unable to authenticate users and services, and the domain controller may not be able to register DNS records. If this service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it cannot start.
This service is not required on a computer that is not connected to a network, or on a computer used on a “home” network.
Once this service is disabled, the server will be unable to properly participate in the domain and will reject NT Local Area Manager (NTLM) requests. This service does not affect the overall performance of the computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
“COM Service for CD Burning IMAPI “ - management of CD burning using IMAPI (Image Mastering Applications Programming Interface). If this service is stopped, this computer will not be able to burn CDs using built-in Windows tools. If this service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it cannot start.
If you use third-party applications to burn discs, I advise you to disable this service to avoid problems.
Windows Time Service " - manages date and time synchronization across all clients and servers on the network. If this service is stopped, date and time synchronization will not be available. If this service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it cannot start.
Uses Network Time Protocol (NTP) to keep computers in a synchronized domain. This service is required if you use software that works with the Kerberos protocol.
After disabling this service, time synchronization will not be possible, and if you use the Kerberos protocol for authentication, you will be denied authorization on the Kerberos server.
This service does not affect the overall performance of the computer. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
“ SSDP Discovery Service ” - Enables discovery of UPnP devices on your home network.
If you have increased network activity on your system, although no activity is taking place on the network, then this service may be the source of this problem. The service uses port 1900 for transmission over the UDP protocol.
If you disable this service, your computer will not be able to detect uPnP devices on the network.
This service, if enabled and running, may slightly slow down your computer. If this service is enabled and running, the level of system security is significantly reduced.
“Message service” – using this service, messages sent by administrators or the notification service are sent and received.
Terminal Services —Enables multiple users to connect interactively to a computer and displays the desktop and applications on remote computers. Provides the basis for Remote Desktop (including remote administration), Fast User Switching, Remote Assistance, and Terminal Services.
May make your computer vulnerable and unreliable from a security point of view. If you do not use Remote Desktop, it is recommended to disable this service.
“Removable storage” - this service manages removable media, ZIP disks, magneto-optical drives, libraries, tape drives, etc. If you have such media, then set the startup type of this service to “Automatic”, otherwise it is recommended to disable this service.
“Remote Registry” - using this service, remote users can “dig” into the registry on our computer, but do we need it? So we disable this service.
“Error Logging Service” - this service manages the system for collecting messages about unexpected system failures. The service consumes quite a large amount of system resources, so if your system is stable, you can disable it. However, if your system is unstable and many programs do not work as expected, you can leave this service enabled in order to be able to receive information about the reasons for such behavior of the system or installed programs.
When this service is disabled, reports will only be generated for kernel errors and some user mode errors.
This service, if enabled and running, can greatly slow down the computer, for example, the speed of access to the hard drive can seriously slow down. The operation of this service does not in any way affect the security level of the system.
Here is such a list. I would also like to note that all experiments with system services are undertaken at your own peril and risk. I’ll repeat myself by saying that you should definitely create a Windows restore point. I will tell you how to do this in another article.
Correct name and disablement
Before deleting (disabling) one of the services, you need to know its original name.
To do this, you can follow the path - <Start> / <Control Panel> / set the “small icons” mode / <Administration>. In the window that appears, you need to launch the “Services” shortcut. A window with a list will open in front of you, in which you can familiarize yourself with their description, status (working or not), type (mode) of launch and on whose behalf the login is required.
From the specified location you can both start them and stop them (disable them).
The "Disable" button is available if the service is currently running
The “Name” field contains the name that is copied to the clipboard.
In the tab, copy the service name
Before you remove a service in Windows, you must disable it!
Using Registry Editor
You can also remove a Windows service using the Registry Editor, to launch which use the Win + R key combination and the regedit command.
- In Registry Editor, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SYSTEM/CurrentControlSet/Services
- Find the subkey whose name matches the name of the service you want to remove (use the method described above to find out the name).
- Right-click on the name and select “Delete”
How to remove a service in Windows 7 and Windows 8.1-03
Close Registry Editor. After this, to permanently remove the service (so that it does not appear in the list), you must restart the computer. Ready.
This is how easy it is to remove a service in Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
Site material
Uninstallation and command line
To get rid of the service directly, we follow the path - <Start> / <All Programs> / <Standard>. Right-click on “Command Prompt” and select “Run as administrator.”
Right-click on the "Command Prompt" icon
In the command line, enter sc delete service name and press Enter.
Enter the desired command in the window that appears
If you enter the command and name correctly, a notification indicating successful deletion will appear.
If the name consists of several words with spaces, then quotes are used: sc delete "service name".
In general, services can be managed via the command line (not forgetting to run it as an administrator).
To do this, the following commands are used:
- View status: sc qc "service name".
- Setting the startup mode (type): sc config “service name” start= startup parameter.
- Launch parameters: auto (automatically), demand (manually), disabled (disabled).
Be extremely careful and be aware of your actions!
Uninstalling Windows 10 services via PowerShell
You can also use PowerShell to remove a service in Windows 10. Just like a regular command prompt, the PowerShell console must be run with administrator rights. To do this, open the Start menu, enter the search query “PowerShell” and run it as administrator.
You can start working in PowerShell by running the “Get-Service” command (cmdlet), which will display a list of all services registered in the system with their names. But, if the service name is too long, it will not fit on the screen. In this case, you can find it through “services.msc”, as it is described at the beginning of the article.
After this, it is advisable to stop the service being removed. To do this, execute the command “Stop-Service -Name ServiceName -Force”, where “ServiceName” is the name of the service that you learned in the previous step.
The final stage is to remove the service from Windows 10. To do this, run the command “Remove-Service -Name ServiceName”. As in the previous case, “ServiceName” must be replaced with the name of the service you need.
More information about managing services using PowerShell can be found on the Microsoft website: Get-Service, Stop-Service, and Remove-Service.