Possible reasons
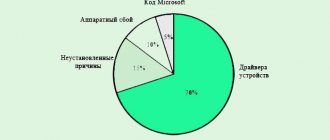
The appearance of a blue screen (BSoD) is often associated with software problems that occur due to:
- lack of compatibility of software (software) important for the operation of the operating system (OS);
- conflict of installed hardware drivers;
- exposure to malware.
- program malfunction.
Note! If the cause is system problems, you can fix the problem without the use of auxiliary equipment by starting in safe mode.
BSoD can occur due to damage or incompatibility of the computer hardware, for example:
- failure of the random access memory (RAM) or hard drive;
- lack of compatibility of installed components;
- equipment failure due to improper overclocking of the graphics chip or processor.
Important! In the event of a hardware malfunction, replacement or repair of system unit elements will be required.
Reasons for the appearance of BSOD - screen of death
The Windows 7 Blue Screen of Death occurs due to problems in individual devices of the computer system or errors in the drivers responsible for supporting these devices. BSOD in some cases occurs due to a failure in the operating system kernel; it is commonly called low-level software.
Windows 7 screen of death errors cannot be caused by problems in individual applications that are not part of the operating system. In such cases, the OS operates normally. System kernel mode and user mode are separated. If Windows finds a STOP error, a Blue Screen appears. This situation stops the operating system.
At the same time, it is the “Screen of Death” that is a protective mechanism for Windows. To understand how this works, we can use the human body as an example. If the pain is too severe, the person loses consciousness from shock to avoid dying. Blue screen works in a similar way.
When an incorrect code is detected, Windows shuts down, providing us with information about the problem in the form of code on the screen. Then the user can only restart the computer or turn it off for a while.
Applications in such circumstances do not have the means or time to save information, so some data may be irretrievably lost. Only those applications that automatically and regularly save changes made are insured against losses.
When a failure of interest to us appears on the screen, Windows automatically creates a special file into which data is entered from the system’s physical memory. Error data is stored there. By looking at this file, you can even find out after a while what caused the failure and protect yourself from its recurrence.
Diagnosis of the problem
To diagnose the problem that has arisen, you need to look at the text of the report. By default, the screen automatically disappears after a certain time; to find out the information, you will need to make changes to the system configuration:
- Expand the “Start” menu, right-click (RMB) on “Computer”, select “Properties”.
- In the sidebar, click on the “Advanced system settings” link.
- On the “Advanced” tab, click Options in the “Boot and Recovery” block.
- Uninstall it and select “Small memory dump (256 KB)” from the drop-down menu below.
- Click OK.
After the specified parameters, when a blue screen appears, there will be time to study the information in detail and, if necessary, rewrite it for further decryption.
Computer settings
If the user did not have time to capture the necessary information from the screen, then a little PC setup will be required.
After this, once you know the code, you can use it to find an effective “medicine” that can cure your iron friend.
You need to do the following:
- Call the context menu from “Computer”;
- Then in the window that appears, go to the “Advanced system settings” tab;
- Next, go to the “Advanced” tab;
- In the “Boot and Recovery” column, click the “Options” virtual key;
- Uncheck the “Perform automatic reboot” box;
- Click “Ok”;
- All. Now, the next time a BSOD appears, the user will have enough time to calmly read it and rewrite the error codes.
It is recommended to study the meaning of the error code on the resource “bsodstop.ru”. For example, “0x0000004e” may appear due to an incorrectly installed driver.
To find out exactly what software caused problems in the system, you should use the BlueScreenView application, which automatically identifies files that cause a critical error. The user only needs to install and open the application.
Based on the detected file, you can find out for which equipment you need to reinstall the drivers. From the above figure we can conclude that there are difficulties with the graphics accelerator, since “ati2dvag.dll” is associated with the video card.
In this case, installing the correct software for the video accelerator will allow you to get rid of the screen of death.
After reinstalling the driver, you need to restart the PC. If the problem could not be corrected, then it means that there are other reasons.
Often the error occurs after updating or installing a new program, and the best way out of the situation is to roll back the OS.
Error interpretation
The text of the error report is unique for each case. The system automatically analyzes possible causes and provides detailed information with accompanying instructions for correction. Below you will find information based on the example of driver failure.
- The first paragraph reports an error in the system.
- The following is the name of the error; from the content you can understand that the cause is an incorrectly installed driver.
- Then, in three paragraphs, solutions to the problem are proposed, which will be discussed in detail below in the text of the article.
- After the word STOP there are fault identifiers for a clearer understanding of the current situation. The information is intended for specialists and does not carry any useful load to the average user.
- Depending on the type of fault, at the end the address of the RAM in the sector of which the error appeared will be reported. The presented code is intended for specialists.
For the user, only the second paragraph is important, which will suggest further solutions to resume the operation of the OS.
Error codes
To “treat your computer” faster and more effectively, you need to have an idea of what error codes mean and how to fix the blue screen of death problem. Therefore, it is extremely important not to ignore the text that displays the BSOD. The most important information on the blue screen of death is the hexadecimal error code and its description.
The number of BSOD errors reaches several hundred. It is simply impossible to know or describe all error codes and how to eliminate them . It is much easier and more optimal to use specialized resources that contain detailed information about errors and describe the sequence of actions to solve the problem in the most effective and safe way.
To do this, you just need to go to the appropriate resource, find the error with the required code, study the information about it and restore the operating system in accordance with the recommendations received.
The most common errors:
- 0x00000001 – internal kernel error;
- 0x0000000A – inaccessible memory address;
- 0x0000001E – incorrect processor command;
- 0x00000020 – driver error;
- 0x0000002B – stack overflow;
- 0x00000051 – registry error.
In some cases, the operation of the Windows operating system may end with the appearance of a blue screen of death, which displays a certain sequence of characters.
The appearance of BSOD indicates a critical error in the operation of the operating system. The method for resolving the failure depends on the system error code, which can be viewed at the bottom of the blue screen.
Ways to fix Blue Screen of Death in Windows 7
There are several ways to fix the Blue Screen of Death in Windows 7, but the effectiveness directly depends on the cause of the problem. In the absence of this information, it is recommended to follow the instructions below one by one.
System Restore
Among the standard programs there is a system recovery tool using pre-created checkpoints. To use this feature, you must run the OS in safe mode:
- To restart a computer.
- During startup, press the F8 key.
- In the additional boot options menu, select “Safe Mode”.
After the desktop appears, you need to run the appropriate utility and perform a recovery:
- Expand the Start menu.
- Enter “System Restore” in the search bar and click on the item of the same name.
- In the initial window, click Next.
- Select the previously created impression from the list and click Next.
- Confirm the action with the Finish button.
If the BSoD screen appears when you try to start in Safe Mode, you must use the recovery environment. For this:
- When the computer starts, press F8.
- Select “Troubleshoot computer problems” from the list.
- In the new window, click on “System Restore”.
The corresponding utility will launch, which will require you to select a control cast of the system and perform a rollback.
Important! This method can be used if there are restore points.
Installing the latest updates
Early versions of Windows 7 are not stable, so it is recommended to install the latest updates, which will help solve many problems.
Note! It is recommended to start the system in safe mode.
Step by step guide:
- From the Start menu, launch Control Panel.
- Go to the "System and Security" section.
- Log in to Windows Update.
- Click on the “Search for updates” link in the sidebar.
- After completing the search, click Install Now.
Note! It is recommended to periodically check for updates and install them.
Removing viruses
Virus software can disrupt the correct operation of the OS. If an error occurs, you should check the system using specialized software. Guide to using the standard Windows 7 tool:
- In the Start menu, search for “Windows Defender” and launch the program of the same name.
- Click on the “Check” drop-down list on the top panel.
- Select the "Full scan" option.
Once the scan is completed, a report will be provided. When prompted to take action on viruses, you must remove them.
As an alternative, you can use third-party antiviruses, for example: AVG Antivirus, AVZ, 360 Total Security, Kaspersky Anti-Virus or Avast.
Recovering damaged system files
Often BSoD occurs due to corruption of system files. You can restore them using the built-in console utility SFC:
- In the search bar of the Start menu, enter “Command Prompt”.
- In the results, right-click on the component of the same name.
- Select the “Run as administrator” option.
- In the console window, enter and run the command sfc /scannow.
After a lengthy scan, the utility will detect and replace damaged system files.
Reset BIOS
Incorrect setup of the input and output utility (BIOS) can cause an error to appear on the screen. To fix it, you should reset the settings to the initial ones:
- While the computer is starting, press the BIOS start key. This could be Delete, F2 or Esc → F10.
- Go to the Exit section using the arrow keys on your keyboard.
- Highlight the Load Setup Defaults line and press Enter.
- Confirm action.
Attention! Depending on the BIOS version, the location of this option may differ.
Restoring functionality
It is better to leave the study of the reasons that led to a failure in the system kernel to specialists. They will be able to read BSOD codes much better than the average user. Let's look at how, following Microsoft's recommendations, you can remove the blue screen of death yourself.
- If any changes were made to the BIOS before the OS crash, return the settings to their original state and disconnect peripheral devices. If possible, we also try to return the hardware configuration to a state that ensured stable operation. For example, if the error appeared after replacing components, replace the old video card or RAM sticks. Thus, we undo all recent physical actions on the PC that could lead to the system error.
- You can fix a blue screen caused by software errors by installing the latest OS updates or the latest driver versions from the manufacturer’s website. In some cases, on the contrary, you have to roll back the system to a stable state using restore points.
- We test the hardware configuration to identify any errors or conflicts.
Fix when loading or installing Windows
A blue screen may appear during download or installation only in three cases:
- damage to computer components (error code: 0x00000116, IGDPMD64.SYS, fltmgr, ntoskrnl).
- The operating system image was damaged while loading or writing.
- The BIOS configuration is incorrect.
If the image or boot drive is damaged, you should replace the flash drive and download Windows 7 from another source.
If there is a problem with the hard drive or RAM, you will need to carry out diagnostics with possible subsequent replacement of the equipment. Without lack of experience, it is recommended to contact a specialist.
What it is
The appearance of a blue screen of death means that the operating system has crashed. The reason for such a failure can be very diverse. A similar problem can happen to anyone, so you need to know what to do if a BSOD appears.
There is no need to worry or fuss too much. It is recommended to reboot the system unit; in this case, all unsaved data will be lost.
Often, when you reboot, the problem disappears, but it is still useful to know the reason why the failure occurs. To do this, you need to analyze some line located on the blue screen of death, which contains the error verification string and error verification code, in order to find information on them on the Internet.
Prevention of occurrence
To prevent the blue screen from appearing again, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- systematically scan the system for viruses;
- clean the components of the system unit or laptop case;
- check for updates and then install them;
- do not allow the system partition to become clogged; the CCleaner program is suitable for cleaning;
- Periodically defragment your hard drive.
Fixing a critical BSoD error involves interacting with system components and utilities to restore damaged files. If the cause of the malfunction is a software component, restoring the functionality of the computer will not be difficult. If a component breaks down, you will need to replace the equipment.
System Setup
In order to be able to diagnose the problem and fix it if a critical failure occurs in the operating system, you should configure the operating system in a special way.
To do this you need:
- check that memory dump saving is enabled in Windows settings;
- Based on the required size of the memory dump file, you need to check whether there is enough free space on the system disk to accommodate it;
- disable rebooting the operating system after a BSOD appears.
Windows XP
To configure the settings of the Windows XP , you must:
- enable recording of debugging information, namely go to:
- "Control Panel";
- "System and safety";
- "System";
- “Advanced system settings”;
- "Additionally";
- "Options".
- specify how much debugging information should be written if a failure occurs.
WindowsVista/7
WindowsVista/7 settings are similar to Windows XP settings.
Windows 8
In Windows, you can configure settings so that the operating system does not automatically reboot. In Windows 8, this requires:
- right-click on the “Computer” icon and then select “Properties” from the menu that appears;
- in the left menu of the active window, select “Advanced system settings”;
- click on the “Advanced” section;
- in the “Boot and Recovery” field, select “Options...”;
- in the “Boot and Recovery” window, uncheck the box next to “Perform automatic reboot”;
- Additionally, you need to change and save the options for saving debugging information. To do this, in the “Write debugging information” window, it is recommended to select the “Small memory dump (256 Kb)” value. It is advisable not to change the directory into which mini dumps will be loaded. The default is C:WINDOWSMinidump.